![[M01] Cells - new (1)](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/025656218_1-3f34eeabbe2791293a80d67f6e13d004-768x994.png)
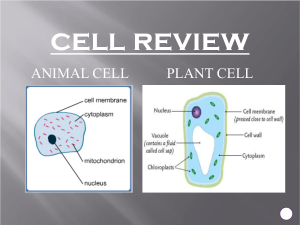
Lower Secondary Science Resource Topic: Cells Let’s look at the differences and similarities between plant cells and animal cells. Only plant cells have these: 3 Questions 1. Why do you only find chloroplasts in plant cells and not in animal cells? Plants carry out photosynthesis. 2. Complete the table below: Animal Cell Plant cell Nucleus Cell Wall Chloroplast X X Ribosomes Mitochondria Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Permanent Vacuole X 4 What are the functions of different parts of a cell? Nucleus: Controls the activities of the cell Cell Membrane: Controls what goes in and out of the cell Cytoplasm: Where most of the chemical reactions happen Cell Wall: Vacuole: Strengthens the cell and gives support Contains cell sap - gives support to the cell Chloroplast: Contains chlorophyll which absorbs sunlight for photosynthesis On the next slide let’s see if you remember how to label animal and plant cells. You are not expected to know the words in the yellow boxes. The Mitochondrion (where respiration takes place) and Ribosomes (where proteins are made) are very small structures not usually visible with a light microscope. 7 Let’s look at some cells under the microscope. Human blood cells White blood cell – with lobed nucleus Red blood cells with no nuclei Human cheek cells Nucleus Human sperm cells Leaf cells Top of leaf Palisade cells Bottom of leaf Think about the root hair cell in plants. It is ‘suited’ to its job of taking in water and nutrients in two ways: 1. It has a large surface area. 2. It has a thin cell membrane. A sperm cell is an example of a specialised animal cell. Strong tail for swimming It has a strong tail for swimming and a vacuole containing enzymes. Vacuole containing enzymes More specialised animal cells ID: Red Blood Cell Function: Carries oxygen around the body. Features: No nucleus, large surface area, packed with haemoglobin to carry as much oxygen as possible. White blood cell Egg cell (ovum) Ciliated epithelial cell The white blood cell makes antibodies and moves to ‘engulf’ harmful bacteria. An ovum contains half of the genes needed to make up a new animal and contains lots of essential nutrients. Nerve cell (neurone) Ciliated cells have hair-like cilia which move mucus containing trapped dust and bacteria. Nerve cells are long and thin and are insulated to keep the electrical impulses in the cell. Cells, tissues, organs and systems ALL living things are made up of cells. A group of cells makes up a tissue. A group of tissues makes up an organ. A group of organs makes up a system. A group of systems makes up an organism. CELLS make TISSUES make ORGANS make ORGAN SYSTEMS make ORGANISMS Let’s look at some systems in the human body. Can you name them? Digestive system Skeletal system Respiratory system Circulatory system Muscular system