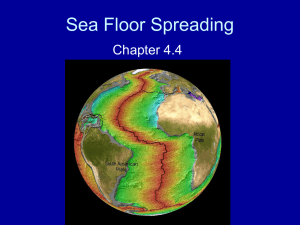
10 Science Quarter 1 – Module 5: Evidences of Plate Movements Science – Grade 10 Alternative Delivery Mode Quarter 1 – Module 5: Evidences of Plate Movements First Edition, 2020 Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for profit. Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalties. Borrowed materials (i.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks, etc.) included in this module are owned by their respective copyright holders. Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them. Published by the Department of Education Secretary: Leonor Magtolis Briones Undersecretary: Diosdado M. San Antonio Development Team of the Module Writers: Name Editors: Name Reviewers: Name Illustrator: Name Layout Artist: Name Management Team: Name of Regional Director Name of CLMD Chief Name of Regional EPS In Charge of LRMS Name of Regional ADM Coordinator Name of CID Chief Name of Division EPS In Charge of LRMS Name of Division ADM Coordinator Printed in the Philippines by ________________________ Department of Education – Region (Ex. Department of Education-Region III) Office Address: Telefax: E-mail Address: ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ 10 Science Quarter 1 – Module 5: Evidences of Plate Movements Introductory Message For the facilitator: Welcome to Science 10 Alternative Delivery Mode (ADM) Module 5 on Evidences of Plate Movements! This This module was collaboratively designed, developed and reviewed by educators both from public and private institutions to assist you, the teacher or facilitator in helping the learners meet the standards set by the K to 12 Curriculum while overcoming their personal, social, and economic constraints in schooling. This learning resource hopes to engage the learners into guided and independent learning activities at their own pace and time. Furthermore, this also aims to help learners acquire the needed 21st century skills while taking into consideration their needs and circumstances. In addition to the material in the main text, you will also see this box in the body of the module: Notes to the Teacher This contains helpful tips or strategies that will help you in guiding the learners. As a facilitator you are expected to orient the learners on how to use this module. You also need to keep track of the learners' progress while allowing them to manage their own learning. Furthermore, you are expected to encourage and assist the learners as they do the tasks included in the module. 2 For the learner: Welcome to the Science 10 Alternative Delivery Mode (ADM) Module 5 on Evidence of Plate Movements! The hand is one of the most symbolized part of the human body. It is often used to depict skill, action and purpose. Through our hands we may learn, create and accomplish. Hence, the hand in this learning resource signifies that you as a learner is capable and empowered to successfully achieve the relevant competencies and skills at your own pace and time. Your academic success lies in your own hands! This module was designed to provide you with fun and meaningful opportunities for guided and independent learning at your own pace and time. You will be enabled to process the contents of the learning resource while being an active learner. This module has the following parts and corresponding icons: What I Need to Know This will give you an idea of the skills or competencies you are expected to learn in the module. What I Know This part includes an activity that aims to check what you already know about the lesson to take. If you get all the answers correct (100%), you may decide to skip this module. What’s In This is a brief drill or review to help you link the current lesson with the previous one. What’s New In this portion, the new lesson will be introduced to you in various ways such as a story, a song, a poem, a problem opener, an activity or a situation. What is It This section provides a brief discussion of the lesson. This aims to help you discover and understand new concepts and skills. What’s More This comprises activities for independent practice to solidify your understanding and skills of the topic. You may check the answers to the exercises using the Answer Key at the end of the module. What I Have Learned This includes questions or blank sentence/paragraph to be filled in to process what you learned from the lesson. 3 What I Can Do This section provides an activity which will help you transfer your new knowledge or skill into real life situations or concerns. Assessment This is a task which aims to evaluate your level of mastery in achieving the learning competency. Additional Activities In this portion, another activity will be given to you to enrich your knowledge or skill of the lesson learned. This also tends retention of learned concepts. Answer Key This contains answers to all activities in the module. At the end of this module you will also find: References This is a list of all sources used in developing this module. The following are some reminders in using this module: 1. Use the module with care. Do not put unnecessary mark/s on any part of the module. Use a separate sheet of paper in answering the exercises. 2. Don’t forget to answer What I Know before moving on to the other activities included in the module. 3. Read the instruction carefully before doing each task. 4. Observe honesty and integrity in doing the tasks and checking your answers. 5. Finish the task at hand before proceeding to the next. 6. Return this module to your teacher/facilitator once you are through with it. If you encounter any difficulty in answering the tasks in this module, do not hesitate to consult your teacher or facilitator. Always bear in mind that you are not alone. We hope that through this material, you will experience meaningful learning and gain deep understanding of the relevant competencies. You can do it! 4 What I Need to Know This module was designed and written with you in mind. It is here to help you master the nature of Biology. The scope of this module permits it to be used in many different learning situations. The language used recognizes the diverse vocabulary level of students. The lessons are arranged to follow the standard sequence of the course. But the order in which you read them can be changed to correspond with the textbook you are now using. After going through this module, you are expected to: 1. investigate the pieces of evidence of the Continental Drift Theory; S9ES –Iaj-36.6 2. illustrate the occurrences of seafloor spreading through demonstration activity; S9ES –Iaj-36.6 3. appreciate the importance of continental drift theory and seafloor spreading theory to the formation of land masses. S9ES –Iaj-36.6 5 What I Know DIRECTION: Choose the letter of the best answer. Write the chosen letter on a separate sheet of paper. _____1. Who is the German Scientist who hypothesized in 1912 that continents were once a giant landmass called Pangaea? A. Alfred Lothar Wegener C. Harry Hammond Hess B. Charles Darwin D. Robert Dietz ____2. What do you call the supercontinent formed million years ago? A. Asia C. Pangaea B. Eurasia D. Panthalassa ____3. According to the Plate Tectonics theory, what was the most visible product after the first break of Pangaea into two large land masses 40-50 million years ago? A. Himalayas C. Underwater Mountain ranges B. Rift valleys D. Volcanic Island arc ____4. What do you call the underwater mountain formed from continents that pushes against each other? A. Island arc C. Mountain ranges B. Mid- Ocean ridge D. Rift valley ____5. What do you call the process that forms a new oceanic crust? A. Convection C. Seafloor spreading B. Magnetic reversal D. Trenching ____6. Which should the Earth's magnetic field have to make the compass point north? A. Magnetic reversal C. Normal polarity B. Mid- Ocean ridge D. Reversed polarity ____7. Which can you infer from the continuous movement of the lithospheric plates over the asthenosphere? A. All the continents will cease to exist. B. All the volcanoes in the Philippines will become inactive. C. The continents will not be located in the same place as they are now. D. The islands of the Philippines will become scattered all over the world. ____8. What discovery provided strong support for Continental Drift Theory? A. Electromagnetism C. Geology B. Fossil evidence D. Paleomagnetism 6 ____9. During the 1960s, scientists were already equipped with gadgets needed to explore the depth of the ocean. What discovery about the ocean floor is associated with the seafloor spreading? a. Mountains are denser than the mantle. b. The rotational poles of the Earth have migrated. c. The crust of the continents is denser than the crust of the ocean. d. The crust of the ocean is very young relative to the age of the crust of the ocean ____10. If you are a cartographer, what would give you an idea that the continents were once joined? A. ocean depth C. shape of the continents B. position of the South Pole D. size of the Atlantic Ocean ____ 11. What happens to old oceanic crust as new molten material rises from the mantle? The oceanic crust A. melts C. volcanic arc B. subducts D. pushes the continental crust ____12. What do you call the deepest part of the ocean floor? a. Mid-ocean ridge C. Trench b. Rift D. Valley ____13. What evidences do scientists use to support the Continental Drift Theory? A. rocks, fossils, air C. rocks, fossils, climate B. rocks, water, ice D. rocks, fossils, human beings ____14. Where can you find the youngest ocean floor? A. at the middle of the ridge C. away from the mid-ocean ridge B. at the subduction zone D. near the mid ocean ridge ____15. Which diagram best illustrates the convection occurring in the mantle? A. C. B. D. 7 Lesson 1 Evidence of Plate Movements: Continental Drift Theory What’s In Have you ever wondered how the continents were formed? Well, if you say YES, then this module will help you find the answer to your question. It will also help you to understand how plate moves and also the different theories. What’s New Continental Drift Theory Look at the figure below. As years passed by, do you agree that continents drift as what was shown in the picture? If YES, then you might agree or believe to Alfred Wegener. Alfred Wegener, a German meteorologist, proposed that the continents were once one large landmass called PANGAEA” which means “All Earth”. Pangaea broke into two smaller supercontinent called Laurasia and Gondwanaland. Continents further broke and are slowly drifting around the Earth. He proposed the Continental Drift Theory. What are the evidences that supported the continental drift theory? https://ar.pinterest.com/pin/501729214734503760/ 8 What is It EVIDENCES: Continental Jigsaw Puzzle The edge of one continent matches the edge of one another. Africa and South America fit together; Europe and North America, India, Antarctica and Australia match one another. https://www.thinglink.com/scene/716674018916171777 Fossils Fossils are preserved remains or traces of organisms from the past. Similar fossils found in places he thought were once connected like GLOSSOPTERIS (extinct plant) were located in the continents of South Africa, Australia, India, Antarctica. LYSTROSAURUS found at Africa, Antarctica & India. CYNOGNATHUS – found at South Africa & Africa. MESOSAURUS (Freshwater dinosaur) South America & Africa. http://publish.illinois.edu/alfredwegener/evidence/ Rocks Fossils found in rocks support the Continental Drift Theory. The rocks themselves also provide evidence that continents drifted apart from each other. http://publish.illinois.edu/alfredwegener/evidence/ Similar layers of rock were formed in Antarctica, Australia, South America, Africa, and India before Pangaea broke apart. Glossopteris fossils were found in the rocks on each continent. Mountain ranges appear to be continuous on neighboring continents 9 Glaciers Glaciers carve rocks and leave marks as they move. In this evidence, scientists can determine the direction of movement of each continent. Coal deposits in Antarctica means that it must have been positioned in a part of the Earth where it once support life. This leads to the idea that Antarctica was once located near the region of the Earth with tropical climate. https://people.highline.edu/iglozman/classes/pscinotes/glacialfit.jpg What’s More To further understand the idea of Alfred Wegener, perform the activity below to learn about the other evidence of Continental Drift Theory. Activity: WORD GAMES I. Identify the numbered continent using the world map (See figure below). Write your answer on the crossword puzzle. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 6. 7 . 4. 5. 2. 1. 3. 10 https://www.123rf.com/photo_58785150_stock-vector-seven-continents-world-map-asia-africa-north-and-south-americaantarctica-europe-and-australia-detai.html II. JUMBLED LETTERS. Arrange the jumbled letters. The clues are in the picture. Write your answer on the space provided. 1. A I C A L O N G I T _______________________________________________ https://www.geolsoc.org.uk/Plate-Tectonics/Chap1-Pioneers-of-Plate-Tectonics/AlfredWegener/Glacial-Deposits-from-Permo-Carboniferous-Glaciation 2. N A N O S https://educatorpages.com/site/Riversideschoolscience /pages/plate-tectonics E J T W N I C L G N I A ____________________________________________ 3. N U G O N T E M R A N A I S _______________________________________________ https://sites.google.com/site/platetectonicsamyg/theoryof-continental-drift/mountain-ranges 4. S https://phys.org/news/2016-04-fast-die-young-life-histoAry.html 11 O F S L I _______________________________ S III. WORD HUNT: Find and encircle the name of the pictures (See figure below). Words are written vertically, horizontally diagonally and backwards. A C K N G L O S S O P T E R I S S L A I N G F F K N J A H T O R G L F M E S S T O G A M L R S Y H O M R D F I S W M E O S U I L E M C S E O F W V E N W H S L G B E Y N G D E A I X C T K U Y Y X S A I N A W G Y L A T L T S E G O N C U S K E N N M J R H T O R S K G E L U W G A U H Q H R U U A R F N I S O K E N U D S O F I U L L Y T N R I Y N L R I S L L R O A H Y D E A H L E N A A C H U S Y C R E W H G B S R E U G F S S N Y U E R Y E M B L Y R M K B N E U R O K D E R U J H U N B Q A Y G H E I T F D N L G S C https://www.sciencephoto.com/medi a/1002814/view/alfred-lotharwegener-german-geophysicist-andmeteorologist http://publish.illinois.edu/alfredwegener/evidence/ 12 What I Have Learned You are a geology student. 1. Write an argument and enumerate the evidences to support Wegener’s Continental Drift theory and theory of plate tectonics. Explain why scientific community rejected him. Rubric for evaluating essay Categories Content 1 Essay generally needs little explanation. Unorganized content. Significant errors in grammar and spelling 2 Essay is lacking in a majority of areas. Frequent errors in grammar and spelling 13 3 Essay is above adequate in most areas. Write clearly but there are few errors in grammar and spelling 4 Essay is exceptional in every way. Write clearly and well organized content with minimal errors in grammar and spelling Lesson 2 Evidence of Plate Movements: Seafloor Spreading Theory What’s In Despite the evidences presented by Alfred Wegener, his idea that the continents were once joined together was not accepted by scientific society because he was not able to explain how this drifting took place. In this lesson, you will learn about the Seafloor Spreading Theory that will strongly support the idea that continents are drifting and find out the site of origin of plate movements. What’s New https://theconversation.com/marie-tharp-pioneered-mapping-the-bottom-of-the-ocean-6decades-ago-scientists-are-still-learning-about-earths-last-frontier-142451 Seafloor Spreading Theory Harry Hess together with Robert Dietz suggested an explanation to the continental drift theory. This is the Seafloor spreading Theory, process by which new ocean sea floor is formed near the mid-ocean ridge and moves outward. Hot less dense material from below the earth’s crust rises towards the surface at the mid – ocean ridge. 14 What is It Subduction As new ocean floor is created by sea-floor spreading at the midoceanic ridges it is consumed at the subduction zones where the lithosphere sinks under the asthenosphere https://www.medellin.unal.edu.co/~rrodriguez/geologia /ofiolitas/Introduction%20to%20Plate%20Tectonics.htm Findings that support Seafloor Spreading Theory: 1. Rocks are younger at the mid-ocean ridge. 2. Rocks far from the mid-ocean ridge are older. 3. Sediments are thinner at the ridge. 4. Rocks at the ocean floor are younger than those at the continents. https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seafloorspreadingtheorydiscu ss3-160802131934/95/seafloor-spreading-theory-discuss-3-31638.jpg?cb=1516545491 Harry Hess observed that the rate of formation of new seafloor at the mid-ocean ridge is not always as fast as the destruction of the old seafloor at the subduction zone. This explains why the Pacific Ocean is getting smaller and why the Atlantic Ocean is getting wider. If the subduction zone is faster than the seafloor spreading, the ocean shrinks. He published his theory in History of Ocean Basins (1962), and it came to be called "seafloor spreading." 15 In the early 1960s, dating of ocean-core samples showed that the ocean floor was younger at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge but progressively older in either direction, confirming the reality of seafloor spreading. What’s More To further understand the idea of Harry Hess, perform the activity below to learn about the other evidence of Seafloor Spreading Theory. Modeling Sea Floor Spreading Materials Cardboard Procedure Scissors Paper Colored pencil or crayons Part 1 1. To create a working model of sea floor spreading, follow the model seen below (Figure 1). The base is best if made from poster board or card stock. The width and length of the base are not critical, as long as they are at least 12 cm wide and 30 cm long. Cut 3 slits, each slightly more than 8 cm wide. One slit needs to be in the center, and the other two at either end of the base, at least 4 cm in from the ends. Label the slits A and B at either end. 2. Cut out the plate strips and place them back-to-back (marked sides together with number 1 at the top) and tape the end as indicated (at the end nearest number 7.) 3. Shade alternating strips to represent the reversals of the earth’s magnetic field. Be sure that the shading on either side of the strip match the alternate side. 4. Put the two strips up through the bottom slit and then off to the slits at either end of the base. (Figure 2.) 5. Thread the two strips through the center slit of the base, keeping the taped edge at the bottom. Pull the “North American Plate” strip down through slit “A” and the “Eurasian Plate” strip through slit “B”. 16 6. Push the strips up from below until you can see numbers 3, 4, and 5 on top of the base. Templates for plate strips 1. What does the center slit in the model represent? 2. What do the strips of paper represent? 3. Based on your understanding of Seafloor Spreading, does the earth get bigger? Why or Why Not? 17 Lesson 3 Evidence of Plate Movements: Magnetic Reversal What’s New Magnetic Reversal Magnetic Reversal also called magnetic ‘flip’ of the Earth. It happens when the North Pole is transformed into a South Pole and the South Pole becomes the North Pole. This is due to the change in the direction of flow in the outer core. What is It Paleomagnetism confirms the seafloor spreading hypothesis Geomagnetic field switches from reversed polarity to normal polarity on irregular basis Iron crystals in magma incorporate Earth’s new magnetic orientation Iron-rich sediment particles align with geomagnetic field like compass needles http://www.eniscuola.net/en/2017/01/09/at-theorigin-of-rocks-the-secrets-of-paleomagnetism/ Geologists used magnetometers to conduct studies in the 1950’s and were amazed that polarity had reversed many times in the past. Two or more plates pull apart. Molten material rises through Rift Zone. Newest magma on either side of rift. Like conveyer belts, the newer crust travels away from the center on each side. Oceanic crust records reversed and normal polarity episodes. https://www.whoi.edu/oceanus/feature/paving-theseafloor-151-brick-by-brick/ 18 What I Have Learned Direction: Write TRUE if the statement is correct and FALSE if the statement is wrong on the column provided for every item. No. Statement 1 2 Magnetic Reversal is also called magnetic flip. The OLDEST seafloor is located closest to the mid ocean ridge. A device used by scientists to have a clearer view of the ocean floors is called Radar. Subduction is the process by which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deep ocean trench and back into the mantle. The COOLEST seafloor temperature is located farthest from the mid ocean ridge. Year 1990 was when seafloor spreading theory was proposed. The deepest part of the ocean is called trenches. The oceanic crust expands when it reaches the continental crust. Harry Hess and Alfred Wegener proposed the theory of seafloor spreading. Changes in magnetic polarity occur because the magnetic poles switch positions. Seafloor spreading is when new seafloor is formed as magma is forced upward. Rock shapes in the mid ocean ridge is one evidence of sea floor spreading. If subduction is faster than seafloor spreading, the ocean gets wider. Youngest rocks were always at the center of the ridges. Ocean floors keep spreading, so all oceans are getting bigger. 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 19 True or False What I Can Do Make a diagram of the seafloor spreading theory showing the process of convection current. Assessment Multiple Choice. Choose the letter of the best answer. Write the chosen letter on a separate sheet of paper. ____1. In 1912, Alfred Wegener, proposed that continents were once one Large mass which he called Pangaea. What does Pangaea means? A. All continent C. All ground B. All earth D. All land ____2. Who were the two scientists who proposed the theory of seafloor spreading in the early 1960s? A. Charles Darwin and James Hutton B. F. Vine and D. Mathews C. Harry Hess and Robert Dietz D. John Butler and Arthur Smite ____3. What are the two land masses formed after the first broke of Pangaea? A. Africa and Gondwanaland C. North and South America B. Eurasia and Africa D. Gondwanaland and Laurasia 20 ____4. What evidence shows us that the continents were once one because of their shape wherein the edge of one continent matches the edge of another? A. coal deposits C. from rocks B. fossils D. the continental jigsaw puzzle ____5. If the Atlantic Ocean is widening at a rate of 3 cm per year, how far (in km) will it spread in million years? A. 3 km C. 300 km B. 30 km D. 3000 km ____6. The lithospheric plates are believed to be moving slowly. What is the driving force that facilitates this movement? A. convection current in the mantle C. magnetic force at the poles B. gravitational force of the moon D. the force of the atmosphere ____7. Which observation was NOT instrumental in formulating the hypothesis of seafloor spreading? A. depth of the ocean B. thickness of seafloor sediments C. magnetization of the oceanic crust D. identifying the location of glacial deposits ____8. If there are MORE mid-ocean ridges than subduction zones, what happens to the ocean? The ocean ___________. A. gets larger C. sinks B. gets smaller D. will not change ____9. According to the Plate Tectonics theory, what was the most visible product after the first break of Pangaea into two large land masses 40-50 million years ago? A. Himalayas C. Underwater mountain ranges B. Rift valleys D. Volcanic island arc ____10. How did Wegener describe the coal beds discovered in Antarctica? A. always frozen C. once underwater B. once near the equator D. part of Africa ____11. What strong evidence discovered by our scientist that Earth's magnetic reversal had been happening in the past? A. The Earth's magnetic field is fluctuating. B. The magnetic field of the Earth becomes weaker. C. The ages of the rocks on the ocean floor are constantly changing. D. The magnetic reversal occurrence is supported by magnetic patterns in magnetic rocks found on the ocean floor. 21 ____12. What theory tells us that hot dense material from below earth‘s crust rises towards the surface of the mid-ocean ridge? A. Continental drift C. Seafloor spreading B. Hess D. Sea spreading ____13. If all the inner layers of the Earth are firm solid, what could have happened to Pangaea? It would have A. remained as a supercontinent. B. slowly disappeared in the ocean. C. become as it is today. D. stretched and covered the whole world. ____14. What can you say about the rate of movement of materials coming out from the mid-oceanic ridge and the materials sinking in the subduction zone? A. The rising of the materials from the ridge is slower than in the subduction zone. B. The movement of the materials in both ridge and subduction zone is the same. C. The rising of the materials from the ridge is faster than in the subduction zone. D. There is no much movement of materials happening in both the ridge and subduction zone. ____15. Where can you find the youngest ocean floor? A. at the middle of the ridge C. away from the mid-ocean ridge B. at the subduction zone D. near the mid ocean ridge 22 Additional Activities You are an archaeologist, and you were tasked to give lecture to a group of young tourists explaining how pieces of shell-like stones can be found on a cliff when there is neither ocean nor sea nearby. Your lecture should include what fossils are and how they reached locations through plate movements. Use models from readily available materials at the site such as paper, sticks, leaves, stones, or pebbles which will allow you to show how these fossils were transported to places. The tour organizer will provide feedback on your lecture based on the accuracy and clarity of your explanations, and organization of presentation. Rubric for evaluating essay Categories 1 Introduction There is no clear introduction, main point not established Content Conclusion Essay generally needs little explanation. Unorganized content. Significant errors in grammar and spelling Does not include concluding statement 2 Includes an opening statement but does not adequately introduce the topic; main points unclear Essay is lacking in a majority of areas. Frequent errors in grammar and spelling 3 Includes an opening statement. Topic adequately introduced; main points clear 4 Introduction is inviting and organized well; the topic is introduced in an engaging way to hook readers; main points are clear and connected to the content Essay is above adequate in most areas. Write clearly but there are few errors in grammar and spelling Essay is exceptional in every way. Write clearly and well organized content with minimal errors in grammar and spelling Conclusion not connected to the content presented Includes a concluding statement and it is connected to the content presented Includes a concluding statement and it is connected to the content presented. Written in an engaging way 23 24 What I Learned Post- Assessment 1. T 2. F 3. F 4. T 5. T 6. F 7. T 8. F 9. F 10.T 11.T 12.T 13.F 14.T 15.F 1. B 2. C 3. D 4. D 5. D 6. A 7. D 8. D 9. A 10.B 11.D 12.D 13.A 14.B 15.A What’s More Pre- Assessment 1. A 2. C 3. A 4. A 5. C 6. A 7. C 8. B 9. B 10.C 11.B 12.C 13.C 14.A 15.A Answer Key References Map of Continents (Online Image). Retrieved July 3, 2021 from https://www.123rf.com/photo_58785150_stock-vector-seven-continentsworld-map-asia-africa-north-and-south-america-antarctica-europe-andaustralia-detai.html Glaciation (Online Image). Retrieved July 3, 2021 from https://www.geolsoc.org.uk/Plate-Tectonics/Chap1-Pioneers-of-PlateTectonics/Alfred-Wegener/Glacial-Deposits-from-Permo-CarboniferousGlaciation Continental Jigsaw (Online Image). Retrieved July 3, 2021 https://educatorpages.com/site/Riversideschoolscience/pages/platetectonics from Mountain Ranges (Online Image). Retrieved July 3, 2021 from https://sites.google.com/site/platetectonicsamyg/theory-of-continentaldrift/mountain-ranges - evidence from rocks Fossils (Online Image). Retrieved July 3, 2021 https://phys.org/news/2016-04-fast-die-young-life-history.html from University of Utah. Types of Fosills (Online Image). Retrieved July 3, 2021 from http://publish.illinois.edu/alfredwegener/evidence/ Alfred Wegener (Online Image). Retrieved July 3, 2021 https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/1002814/view/alfred-lotharwegener-german-geophysicist-and-meteorologist from http://publish.illinois.edu/alfredwegener/evidence/ Continent (Online Image). Retrieved July 3, https://www.thinglink.com/scene/716674018916171777 2021 from Subduction (Online Image). Retrieved July 3, 2021 from https://www.medellin.unal.edu.co/~rrodriguez/geologia/ofiolitas/Introducti on%20to%20Plate%20Tectonics.htm Magnetic reversal (Online Image). Retrieved July 3, 2021 https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seafloorspreadingtheorydiscuss3160802131934/95/seafloor-spreading-theory-discuss-3-31638.jpg?cb=1516545491 from Earth’s magnetic filed (Online Image). Retrieved July 3, 2021 from http://www.eniscuola.net/en/2017/01/09/at-the-origin-of-rocks-thesecrets-of-paleomagnetism/ 25 Magnetic reversal (Online Image). Retrieved July 3, 2021 from https://www.whoi.edu/oceanus/feature/paving-the-seafloor-151-brick-bybrick/ Seafloor Spreading (Online Image). Retrieved July 3, 2021 from https://theconversation.com/marie-tharp-pioneered-mapping-the-bottomof-the-ocean-6-decades-ago-scientists-are-still-learning-about-earths-lastfrontier-142451 https://www.troup.org/userfiles/929/My%20Files/Science/MS%20Science /6th%20Science/Geology/geological_events/model_seafloor_spreading_all.p df?id=21566 https://www.fusd1.org/cms/lib/AZ01001113/Centricity/domain/883/es% 20labs/Sea%20Floor%20Spreading%20Activity.docx 26 For inquiries or feedback, please write or call: Department of Education - Bureau of Learning Resources (DepEd-BLR) Ground Floor, Bonifacio Bldg., DepEd Complex Meralco Avenue, Pasig City, Philippines 1600 Telefax: (632) 8634-1072; 8634-1054; 8631-4985 Email Address: blr.lrqad@deped.gov.ph * blr.lrpd@deped.gov.ph SCIENCE 10 LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET MODULE 5: EVIDENCE OF PLATE MOVEMENTS Name:_______________________ Grade & Section _______ Score: ______ Most Essential Learning Competency: Enumerate the lines of evidence that support plate movement. Directions: Complete the puzzle with words related to the plate movements. Vertical box with shades completes question 10. 1. Father of Plate Tectonic Theory 2. Two plates collide this is called_____________ boundary. 3. Cycle of heating, rising, cooling and sinking is a _________current. 4. Layer of the Earth where convection current occurs. 5. Branch of geology that deals with the movements that shape the Earth’s crust. 6. Landmass that broke 200 million years ago and which means “All Earth” in Greek word. 7. Largest tectonic plate does not contain a continent. 8. Scientists are now able to track the movement of tectonic plates using_______. 9. Portion of the Earth that moves in tectonic plates 10.Mystery word: scientists who study earth processes such as earthquakes, landslides, floods and volcanic eruptions. Directions: Answer the question briefly. You are an oceanographer and you want to investigate the top of Mid Atlantic Ridge because you heard that it is rich in mineral deposits. What scientific issues should you consider?