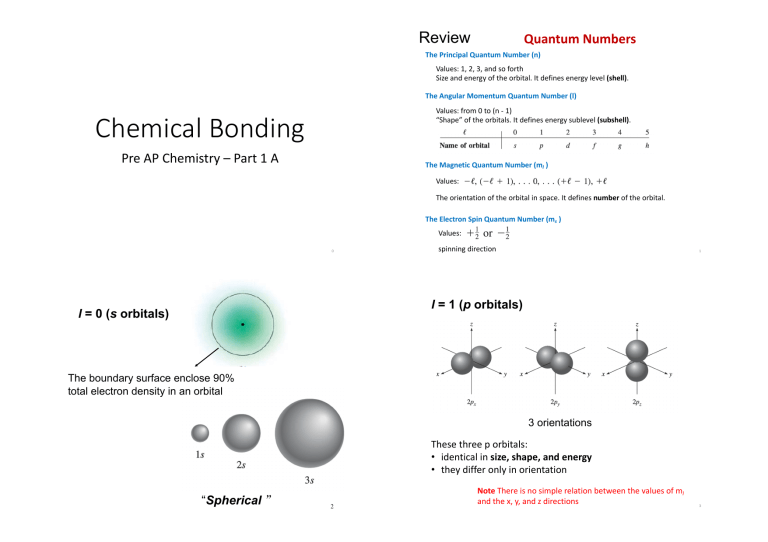
Review Quantum Numbers The Principal Quantum Number (n) Values: 1, 2, 3, and so forth Size and energy of the orbital. It defines energy level (shell). The Angular Momentum Quantum Number (l) Values: from 0 to (n - 1) “Shape” of the orbitals. It defines energy sublevel (subshell). Chemical Bonding Pre AP Chemistry – Part 1 A The Magnetic Quantum Number (ml ) Values: The orientation of the orbital in space. It defines number of the orbital. The Electron Spin Quantum Number (ms ) Values: 0 spinning direction 1 l = 1 (p orbitals) l = 0 (s orbitals) The boundary surface enclose 90% total electron density in an orbital 3 orientations These three p orbitals: • identical in size, shape, and energy • they differ only in orientation “Spherical ” 2 Note There is no simple relation between the values of ml and the x, y, and z directions 3 Energy of orbitals l = 2 (d orbitals) 5 orientations Practice List the values of n, l, and ml for orbitals in the 4d subshell. Energy depends on both n and l 4 Aufbau principle 1s < 2s <2p <3s <3p <4s <3d <4p 5 5 Hund’s Rule “Fill up” electrons from low energy orbitals to high energy orbitals. The most stable arrangement of electrons in subshells is the one with the greatest number of parallel spins. 1s < 2s < 2p < 3s < 3p < 4s < 3d < 4p …… 6 7 The Pauli Exclusion Principle If two electrons in an atom should have the same n, l, and ml values, then they must have different values of ms . Practice An oxygen atom has a total of eight electrons. Write the orbital diagram of an oxygen atom and write the four quantum numbers for each of the eight electrons in the ground state. 8 9 1 Practice Shorthand notation with noble gas core is abbreviated electronic configurations use [noble gas] e.g. for Sc, Full electron configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d1 Shorthand notation with noble gas core: [Ar]4s23d1 Practice Write the electron configuration for the following elements. 10 2 11 Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom. Chemical bond Group Atoms interact to form a chemical bond, only their outer regions are in contact, only valence electrons participate in chemical bonding. Chemical bond between two oxygen atoms e- configuration # of valence e- 1A ns1 1 2A ns2 2 3A ns2np1 3 4A ns2np2 4 5A ns2np3 5 6A ns2np4 6 7A ns2np5 7 8A ns2np6 8 12 Lewis dot symbol Lewis dot symbol of ions Each dot represents a valence electron. elements valence electron 13 Lewis dot symbol H 1 H Be 2 Be B 3 B C 4 C N 5 N O 6 O F 7 F Cation: Lewis dot symbol Na+ Na+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Anion: 14 Cl- Cl S2- S - 2- 15 Electronegativity(EN) 9.2 the ionic bond Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract toward itself the electrons in a chemical bond. Page 372 9.4 the covalent bond Page 379 Beryllium, the first member of Group 2A, forms mostly covalent compounds. relative value, no unit, e.g. electronegativity of O is 3.5. 17 16 A difference of 1.8 units or more will give a compound that is predominantly ionic. The Electronegativities of Common Elements Increasing electronegativity Increasing electronegativity e Incr • elec g n i as tiv ega n o tr ity, A pt 8 e c ex Because noble gas are very stable, they can hardly form ordinary compounds, so 8A elements are exceptions in electronegativity trend. • F has largest electronegativity among the elements. 18 19 Lattice: A regular pattern or lattice of alternating positive and negative ions Ionic compound Lewis dot symbols e.g.1 CaO Ca e.g.2 + O Ca2+ O 2- Li2O 2 Li e.g.3 + O 2Li+ O 2- Mg3N2 3 Mg + 2 N 3Mg2+ 2 N 3- 20 21 Lattice energy can be determined by coulomb’s law. Lattice Energy Lattice energy (U) is the energy required to completely separate one mole of a solid ionic compound into gaseous ions. F is attraction force F=k Q+Qr2 Q+ is the charge on the cation Q- is the charge on the anion Lattice energy + NaCl(s) → Na+(g) + Cl-(g) r is the distance between the ions → For ionic compounds, larger charge, smaller radius, greater attraction force between cation and anion, greater lattice energy. 22 23 Compare and explain lattice Energy Practice Practice Compound Lattice Energy(kJ/mol) MgF2 2957 MgO 3938 F=k Q+Qr2 Which of the following ionic compounds will have the largest lattice energy: Al2O3, MgO, CaO. Explain your answer. In blue: ionic size in pm Explain why MgO has larger lattice energy than MgF2? Because charge of O2- is larger than F-, the attraction force between Mg2+ and O2- is stronger than that between Mg2+ and F-. So MgO has larger lattice energy. 25 24 Covalent bond type: Covalent bonds • Covalent bond is generally formed between nonmetal and nonmetal. Because their electronegativity difference is small between nonmetal atoms. • Polar (covalent) bond, different nonmetal atoms • Nonpolar (covalent) bond, same nonmetal atom. Polar covalent bond • Covalent bond is formed by sharing electrons between two atoms. 26 Shared electron density is not evenly distributed, but greater electron density around one of them. e.g. HF Nonpolar covalent bond shared electron density is evenly distributed. e.g. H2 27 Why should two atoms share electrons? F + 7e- F F F F F 7e- 8e- 8e- Page 380 Lewis structure “Octet rule” • An atom except hydrogen tends to form bonds until it is surrounded by eight valence electrons. • Hydrogen atom tend to be surrounded by 2 valence electrons when forming bond. or F F Lewis structure is a representation of covalent bonding in which shared electron pairs are shown either as lines or as pairs of dots between two atoms, and lone pairs are shown as pairs of dots on individual atoms. Bonding pair/shared electron pair lone pairs lone pairs Lone pairs are not involved in covalent bond formation 28 Single bond – two atoms share one pairs of electrons H + O + H H O H 2e- 8e- or 2e- H O H single bonds Double bond – two atoms share two pairs of electrons O C O or O C O double bonds 8e- 8e- 8e- Triple bond – two atoms share three pairs of electrons N N 8e-8e- or N N triple bond Bond Lengths: Bond strength/stability: Triple bond < Double Bond < Single Bond Triple bond > Double Bond > Single30Bond 29





