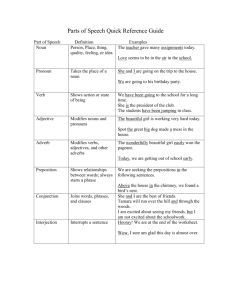
BSEE 23: Structure of English BSEE 23: Structure of English Module 1 Traditional Grammar: Categories and Functions Introduction: In traditional grammar, words are assigned to grammatical categories (called parts of speech) on the basis of their semantic properties (i.e. meaning), morphological properties (i.e. the range of different forms they have) and syntactic properties (i.e. word-order properties relating to the positions they can occupy within sentences): a set of words which belong to the same category thus have a number of semantic, morphological and syntactic properties in common. The most tangible elements of a language are its words. You’ve heard people say “There’s no such word” or “What does the word lollapalooza mean?” Someone doing a crossword puzzle may have asked you, “What’s a three-letter word for excessively?” We say one person likes to use “two-bit” words and another has a preference for “four-letter” words. In these BSEE 23: Structure of English instances, people have clear notions of what a word is. The ability to use any word in a sentence requires knowledge of its lexical category. Even young children must know the category of every word they use—which ones are verbs, nouns, or adjectives. Of course the child’s knowledge is unconscious, and even a grammarian’s child wouldn’t ordinarily know the names of the categories. Pre-Assessment: I want you to read the article written in the box. Then, identify the nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs and prepositions. Write your answer in the table below. We found this place accidentally and have been returning almost weekly. We just love it. It is so simple and yet so wonderful and the staff is great. They are always smiling and just so nice. There is almost always a line. A must! (Review of the Fry Bread House in Phoenix, slightly adapted) Nouns Pronouns Verbs Adjectives Adverbs Conjunctions Prepositions Learning Points: Categories can be divided into two main classes: lexical and functional. 1. Lexical/substantive categories (=categories whose members are content words) are the nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs and prepositions. The differences between the first and second category, nouns and verbs in terms of morphological, syntactical and semantical characteristics are summarized in Table 1 below. BSEE 23: Structure of English Table 1. Differences Between N(oun) and V(erb) Noun (N) Verb (V) Morphology (/mɔːrˈfɒlədʒi/) a. have grammatical morphemes or inflections (plural – s or possessive ‘s) * the study of words, how they are formed, and their relationship to other words in the same language e.g. girl – girls, girl vs girl’s with a few exceptions e.g child – children, mouse – mice a. –s of third person singular present tense verbs e.g. Jelyn jogs every morning. * analyzes the structure of words and parts of words such as stems, root words, prefixes, suffixes b. – ed of the past tense of the verbs e.g. Jelyn jogged yesterday morning. b. have derivational morphemes- c. –en of the past participle mark nouns derived from other part of e.g. He has written a novel. speech like –ity, -ness, -ation, -er, -ion, -ment d. – ing of the present participle e.g. He is reviewing his lesson right e.g. teach-teacher, sad- sadness now. involve-involvement e. end in –ize, -ate Marked noun or verb is one which is Marked verb or form is one which is not typical, common, or regular. not typical, common, or regular. Children, mice, bacteria Unmarked form is one that is typical, Unmarked or regular form of the common or regular. simple past ends in –ed. Which of the following plural nouns is Which of the following simple past an unmarked form? verb forms is a marked form? A. bacteria C. students A. dreams C. weighted B. sheep D. woman B. kept D. wrote Syntax * the arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences in a language a. may follow the/a/an and this/that/ these/those a. may follow an auxiliary e.g. have gone, will submit e.g. a laptop, the article, this video that bag/ these book reviews/ those ladies b. may be modified by an adverb e.g. She spoke softly. b. may be modified by adjective e.g. courageous woman c. may be followed by a noun or preposition and noun e.g. The cat jumped off the counter. c. may be followed by preposition e.g on time, with that guy Semantics * the study meaning language a. name of person, place, event, 0f Some linguists include “idea” to in account for abstract nouns denotes an action, event, state of being BSEE 23: Structure of English Let’s also take a look at the difference between the third and fourth lexical category, Adjectives and Adverbs in Table 2. Table 2. Differences Between A(djectives) and A(dverb) Morphology Syntax Adjectives (Adj) a. end in –ous,-ary, -al, -y,-ic e.g. gorgeous, ordinary, multifunctional, naughty, static Adverbs (Adv) a. end in –ly in many cases, -wise,ways e.g sad-sadly b. can be participles e.g. boring It is such a long, boring flight. I was really bored during the flight. b. have no ending like fast, now a. modify noun e.g. voracious reader a. the only kind of word that which could be used to end sentences like the word badly e.g. He worded the statement badly. b. occur after verb be to complete the sentence e.g. They may be tired/ill/unhappy etc. Semantics c. denote a gradable property which can be exist in varying degrees like very/ rather/ somewhat e.g. She is very happy. b. modify V, Adj, or Adv e.g. I will eat later. V Adv The place was strangely quiet. Adv Adj He is almost always busy. Adv Adv a. denote states or attributes e.g. unkempt, zealous, clumsy, petite a. denote the manner in which an action is performed Preposition(P) is the fifth and final lexical/substantive category. Many prepositions have the semantic property of marking location (cf. in, on, off, inside, outside, under, above, below). They have the syntactic property that a preposition (with the appropriate kind of meaning) can be modified by right in the sense of ‘completely’, or by straight in the sense of ‘directly’ (as with the preposition down in He fell right down the stairs and the preposition to in He went straight to bed). Prepositions have the morphological property that they are invariable/uninflected forms (e.g. the preposition off has no past tense form *offed, no superlative form *offest, and so on). 2. Functional categories (= categories whose members are function words) 1. Determiner (D) 2. Quantifier (Q) Definite article the Demonstrative determiners This/that/these/those Denoting expressions of quantity some, all, no, any, each, every, BSEE 23: Structure of English most, much, many. 3. Pronoun (PRN) Antecedent Indefinite article a which quantifies over a single identity ‘stand in place of’ (the meaning of the prefix pro) or ‘refer back to’ noun expressions Refers back to noun Personal Pronoun 4. Auxiliary Verb Article “a” I, me, we, us, you, he, him, she, her, it, they, them Marking grammatical properties like Alex has/had (done) the activity. tense, aspect, voice or mood He is/was (doing) the assignment. (perfect /progressive aspect) The letters are/were delivered (passive) voice auxiliary He really does/did (say a lot) (an expletive or dummy) auxiliary 5. Coordinator (C) Relatively simple and categories or phrases can/could/may/might/will/would/ shall/should join similar You can eat your cake with a spoon or fork. (both nouns) Coordinators such as and, but, or for, My dog enjoys being bathed but nor join two elements of the same kind hates getting his nails trimmed. (both verb phrases) Anne is an actress. Normally, she acts and sings. (both verbs) Complementizer A conjunction which complement clause marks a I know that he is there. I am doubtful that he is there. Learning Tasks: 1. Directions: Read the short article. Then, identify the lexical Categories (nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions) in the given text. Write your answer in Table 1. 1 point for each word The most common symptoms of COVID-19 are fever, dry cough, and tiredness. Other symptoms that are less common and may affect some patients include aches and pains, nasal congestion, headache, conjunctivitis, sore throat, sore throat, loss of taste or smell or a rash or discoloration of fingers or toes. These symptoms are usually mild and begin gradually. Some people become infected but only have very mild symptoms. BSEE 23: Structure of English Noun symptoms Verb are Adjective Adverb Preposition 2. Functional Categories Using the same text, identify the functional categories( determiners, quantifiers, pronoun and coordinators). Use the table for your answer. 1 point for each word. Determiners The Quantifiers Pronouns Coordinator BSEE 23: Structure of English References: Gelderen, Elly Van (2010). An Introduction to the Grammar of English. John Benjamin Publishing Co. Amsterdam. The Netherlands Celce-Murcia, Marianne & Larsen-Freeman. The Grammar Book: An ESL/EFL Teacher’s Course. 2nd Edition. Heinle, Heinle Publishers https://www.slideshare.net/midnightphantom26/chapter-2-grammatical-metalanguage Prepared by: DIOSALYN T. GALANG, MAEd Asst. Professor 3 Reviewed by: LEAH C. NAVARRO, EdD Chairperson, TED Approved by: MAT M. NUESTRO, MEM Director, Curriculum and Instruction