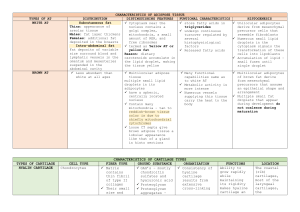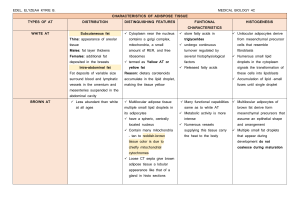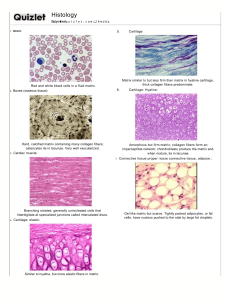
Meghan Barboza, PhD Online Course Specialized forms of Connective Tissue Cartilage Bone Blood Main Functions of Cartilage Resists compression and tension Support soft tissue Provide sliding areas for joints Foundation for bone development Principal Characteristics Form cell nests (isogenic cell groups) Consist of chondrocytes Rounded, independent cells Avascular Noninnervated Perichondrium Layer of tissue surrounding cartilage cartilage Perichondrium Two layers of dense irregular CT: Outer Layer contains perichondrial fibroblasts Inner layer is chondrogenic producing the chondroblasts/ chondrocytes http://audilab.bmed.mcgill.ca/HA/html/bc_2_E.html Perichondrium Chondroblast/Chondrocyte Both originate from mesenchyme of the inner layer of perichondrium dc423.4shared.com Secretions of Chondrocytes Collagen type 2 Collagen type 1 Fibrocartilage only Proteoglycans Glycoproteins Fluid www.studyblue.com Cartilage’s ECM Interterritorial matrix Cartilage’s ECM Interterritorial matrix Territorial matrix Cartilage’s ECM Interterritorial matrix Territorial matrix Pericellular capsule Cartilage Lacunae The space that contains the chondrocytes. Can contain multiple cells. 3 Types of Cartilage Hyaline Elastic Fibrous or fibrocartilage Differentiation based on prevailing type of fiber Hyaline Cartilage Collagen type II made by chondroblast/chondrocytes and containing chondrocytes Most common: tracheal rings, nose, joint surfaces, and site of long & short bone development Elastic Cartilage Epiglottis, external ear, Eustachian tube Similar isogenic nests Collagen type II and elastic fibers Perichondrium Fibrocartilage Intervertebral discs (inner-most), and selected ligamentous and tendinous attachments to other bones vertebra nucleus pulposus Fibrocartilage Linear isogenic nests Collagen type I No perichondrium Chondrogenesis: Appositional Growth Appositional To grow outwards Requires a perichondrium Chondrogenesis: Interstitial Growth Interstitial To grow into already occupied space Endochondral Bone Formation A combination of appositional and interstitial growth of cartilage (blue). Followed by replacement of that cartilage with bone (yellow). Check your understanding Cauliflower ear, pictured to the right, occurs when fluid accumulates under the perichondrium. What has happened to the cartilage? Will this cause pain throughout a person’s life? What is the ‘soft spot’ on a newborn’s head? What causes the condition to the right in infants? http://www.medicaldaily.com/ www.patienthelp.org