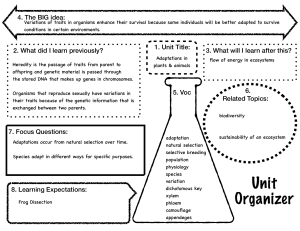
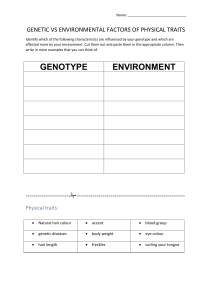
Genetic Variation Within Populations Genetic Variation is stored in a population’s Gene Pool-- The combined alleles of all of the individuals in a population. Genetic Variation comes from 2 main sources: 1. Mutation: random changes in DNA 2. Recombination: Sexual reproduction. Natural Selection Acts on Distribution of Traits. Environmental conditions can change and certain phenotypes may become an advantage. 3 Types of Natural Selection are: 1. Directional Selection: Favors phenotypes at one extreme of a traits range. 2. Stabilizing Selection: The intermediate phenotypes are favored and become the most common in the population. 3. Disruptive Selection: Both extreme phenotypes are favored. Sexual Selection: Occurs when certain traits increase mating success. These traits are not always adaptive for the survival of the individual. Artificial Selection: Humans make use of the genetic variation of plants and animals by acting as the selective agent. Humans determine which traits are favorable or not. Other Mechanisms of Evolution Gene Flow: The movement of alleles from one population to another. Founder Effect: Is genetic drift that occurs after a small number of individuals colonize a new area. The gene pools of these populations are often different from the larger populations. Evolution through Natural Selection is Not Random Mutation and genetic drift cannot be predicted, they are random events. These random events are sources of genetic diversity. However, natural selection, which acts on diversity, is not random. Individuals with traits that are better adapted to their environment have a better chance of surviving and reproducing that do individuals without these traits. Convergent Evolution: Evolution toward similar characteristics in unrelated species. Divergent Evolution: When closely related species evolve in different directions. Different adaptations for different environments. Coevolution: the process in which two or more species evolve in response to each other. The RED QUEEN THEORY Extinction: The elimination of a species from Earth. Background Extinction: Occur continuously but at a very low rate. Mass Extinction: Much more rare. Operate at the global level. The fossil record confirms there have been 5 mass extinctions in the last 600 million years.