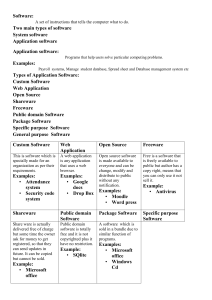
CHAPTER 8 SECURITY AND ETHICS GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP SECURITY PROTOCAL Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) are cryptographic security protocols. They are used to make sure that network communication is secure. Their main goals are to provide data integrity and communication privacy. GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP SSL (SECURE SOCKETS LAYER) SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer and, in short, it's the standard technology for keeping an internet connection secure and safeguarding any sensitive data that is being sent between two systems, preventing criminals from reading and modifying any information transferred, including potential personal details. The two systems can be a server and a client (for example, a shopping website and browser) or server to server (for example, an application with personal identifiable information or with payroll information). GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP SSL (CONT..) It does this by making sure that any data transferred between users and sites, or between two systems remain impossible to read. It uses encryption algorithms to scramble data in transit, preventing hackers from reading it as it is sent over the connection. This information could be anything sensitive or personal which can include credit card numbers and other financial information, names and addresses. GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP SSL (CONT..) When a user logs onto a website, SSL encrypts the data – only the user’s computer and the web server are able to make sense of what is being transmitted. A user will know if SSL is being applied when they see https or the small padlock in thestatus bar at the top of the screen GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP TLS TRANSPORT LAYER SECURITY Transport Layer Security, or TLS, is a widely adopted security protocol designed to facilitate privacy and data security for communications over the Internet. A primary use case of TLS is encrypting the communication between web applications and servers, such as web browsers loading a website. TLS can also be used to encrypt other communications such as email, messaging, and voice over IP (VoIP). GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP HOW DOES TLS WORK? For a website or application to use TLS, it must have a TLS certificate installed on its origin server A TLS certificate is issued by a certificate authority to the person or business that owns a domain. The certificate contains important information about who owns the domain, along with the server's public key, both of which are important for validating the server's identity. GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP A TLS connection is initiated using a sequence known as the TLS handshake. When a user navigates to a website that uses TLS, the TLS handshake begins between the user's device (also known as the client device) and the web server. During the TLS handshake, the user's device and the web server: • Specify which version of TLS (TLS 1.0, 1.2, 1.3, etc.) they will use • Decide on which cipher suites (see below) they will use • Authenticate the identity of the server using the server's TLS certificate • Generate session keys for encrypting messages between them after the handshake is complete GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP The TLS handshake establishes a cipher suite for each communication session. The cipher suite is a set of algorithms that specifies details such as which shared encryption keys, or session keys, will be used for that particular session. GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP The handshake also handles authentication, which usually consists of the server proving its identity to the client. This is done using public keys. Public keys are encryption keys that use one-way encryption, meaning that anyone with the public key can unscramble the data encrypted with the server's private key to ensure its authenticity, but only the original sender can encrypt data with the private key. The server's public key is part of its TLS certificate. (read from book also) GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP T L S I S F O R M E D O F T W O L AY E R S : record protocol: this part of the communication can be used with or without encryption (it contains the data being transferred over the internet). handshake protocol: this permits the website and the client (user) to authenticate each other and to make use of encryption algorithms (a secure session between client and website is established). GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP DIFFERENCES BETWEEN SSL AND TLS It is possible to extend TLS by adding new authentication methods. TLS can make use of SESSION CACHING which improves the overall performance compared to SSL TLS separates the handshaking process from the record protocol (layer) which holds all the data. GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP ETHICS Ethics is a set of moral principles that govern the behavior of a group or individual. GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP COMPUTER ETHICS Therefore, computer ethics is set of moral principles that regulate the use of computers. Some common issues of computer ethics include intellectual property rights (such as copyrighted electronic content), privacy concerns, and how computers affect society. Codes of ethics published by Association for computer machinery and IEEE-(Read from book pg-111) GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP THREE MAJOR AREAS WHICH COMES UNDER THE UMBRELLA OF COMPUTER ETHICS INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS PRIVACY ISSUES EFFECT OF COMPUTERS ON SOCIETY GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY Intellectual Property Rights. Intellectual property rightsrefers to a person's claim on something that they have written, invented, recorded or otherwise own. Any violation of these rights can be viewed as theft downloading or duplicating of any copyrighted digital media (i.e. music, movies or software) without proper consent, and plagiarism of any kind. It would be in your best interest to avoid these violations at all costs as many of them are not just immoral, but also illegal. GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP TEN COMMANDMENTS OF COMPUTER ETHICS Not use a computer to harm other people. Not interfere with other people's computer work. Not snoop around in other people's computer files. Not use a computer to steal. Not use a computer to bear false witness. Not copy or use proprietary software for which you have not paid. GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP TEN COMMANDMENTS OF COMPUTER E T H I C S ( C O N T. . ) Not use other people's computer resources without authorization or proper compensation. Not appropriate other people's intellectual output. Think about the social consequences of the program you are writing or the system you are designing. Always use a computer in ways that ensure consideration and respect for your fellow humans. (Written by the Computer Ethics Institute) GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP FREE SOFTWARE Free software is a program used and distributed at no charge to the user. The Free Software Foundation (FSF) developed four principles, dubbed the “four essential freedoms,” that software must abide by in order to be considered free software: • The freedom to run the program and use it for any purpose; • The freedom to study the program, including how it works, and modify it( gives users access to the source code) to meet your preferences and needs; • The freedom to freely redistribute the program to better help others • The freedom to redistribute freely any copies of your modified and adapted versions of the program to better help others. GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP FREE SOFTWARE(CONT.) Eg- F-spot,scribus,abiword etc However, most free software licenses include terms prohibiting the sale, resale or commercial use. Free software is often released for promotional purposes. For example, certain free software programs may require registration with an email address. The software owner collects these email addresses, which may be used to promote or sell other products. GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP FREEWARE Freeware is any copyrighted software, application or program that may be freely downloaded Such programs are available for use at no cost to general end users. Freeware software can be distributed as a fully operational program for an unlimited period. freeware is normally shared without including its source code. Therefore, users are unable to make any changes to it. Common examples are Adobe Reader and Skype; both programs are available for free. Another example of common freeware might be an old game, which a game developer might choose to re-release as freeware. GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP SHAREWARE The concept of shareware is similar to that of freeware in that it is originally distributed free of charge. However, unlike freeware, that cost-free period is usually only for a trial period, after which the software stops being freely available until the user pays for continued use or license GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP Freeware About Freeware refers to software that anyone can download from the Internet and use for free. Features All the features are free. Shareware Sharewares give users a chance to try the software before buying it. Most of the times, all features are not available, or have limited use. To use all the features of the software, user has to purchase the software. GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP Freeware Distribution Freeware programs can be distributed free of cost. Shareware Shareware may or may not be distributed freely. In many cases, author’s permission is needed, to distribute the shareware. Example Adobe PDF, Google Talk, yahoo messenger, MSN messenger Winzip, Cuteftp, Getright Disadvantage You can’t sell freeware software Shareware cannot be and modified software must be modified, and it may be freeware. either a cut down or temporary version. GRADE-10 COMPUTER SCIENCE CP