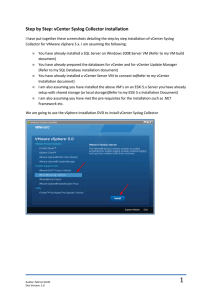
VSVC5635 vSphere vCenter Single Sign-on Best Practices Josh Gray, VMware Justin King, VMware Jonathan McDonald, VMware #VSVC5635 vSphere Deployment Best Practices – vCenter Server 5.1 What is vCenter Single Sign-On vCenter Single Sign-On 5.1 • Architecture • Deployment Configurations • Database • 5.1 Architectural References • Single vCenter Server • Multiple vCenter Servers (Local) • Multiple vCenter Servers (Remote) Deployment Best Practices and Recommendations • Deployment / Installation / Upgrading / Availability Challenges / Lesson Learned with Single Sign-On 5.1 vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 (NEW) • What's New with vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 • Deployment Configurations 2 vSphere Deployment Best Practices – vCenter Server 5.1 What is vCenter Single Sign-On vCenter Single Sign-On 5.1 • Architecture • Deployment Configurations • Database • 5.1 Architectural References • Single vCenter Server • Multiple vCenter Servers (Local) • Multiple vCenter Servers (Remote) Deployment Best Practices and Recommendations • Deployment / Installation / Upgrading / Availability Challenges / Lesson Learned with Single Sign-On 5.1 vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 (NEW) • What's New with vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 • Deployment Configurations 3 What is: vCenter Single Sign-On Server Authentication Services for the vSphere Platform A component of vCenter Server vCenter Single Sign-On creates an authentication domain where users are trusted to access available resources (vCenter etc) • no longer log into vCenter directly* Multiple identity sources (Active Directory, OpenLDAP etc) Provides Secure Token Exchange vCloud (SAML 2.0) between solutions Director When you access an SSO enabled vCenter vCenter Single Sign On (SSO) solution the solution will request an extension to SAML 2.0 Token TTL First component to touch vCO (regardless or install/upgrade) Design before implementing!! 4 What Components Have Integrated With SSO? 2014 2013 Inventory Service VSM Partners vCenter SRM Web Client VCD * SSO Others VCO Log Browser VCOPS VDP * VCD is partially integrated with SSO, only provider side logins can be integrated with SSO 5 How Does vCenter Single Sign On Work? AD AD (Domain 1) (Domain 1) 3 Open LDAP Authenticate 2 1 Issue Token (user, pswd) Login (user, pswd) Token 5 vCenter 1 6 3 Authenticate Local OS users Local OS Sign On vCenter Single OS Login (Token) Authenticate SSO users Data 4 Web Client 3 Login (Token) 6 vCenter 2 Login (Token) 7 VCO Login (Token) 8 vShield Login (Token) 9 vCloud Director vCenter Single Sign On Server Registry of Single Sign-On enabled solutions One time manual registration of vCenter 5.0 needed for discovery by vSphere Web Client. (5.1 Only) Linked Mode required to provided a single pane of glass view across geographically separate vCenter’s Linked Mode: • Sharing of Permissions • Sharing of Roles • Sharing of Licenses 7 vSphere Deployment Best Practices – vCenter Server 5.1 What is vCenter Single Sign-On vCenter Single Sign-On 5.1 • Architecture • Deployment Configurations • Database • 5.1 Architectural References • Single vCenter Server • Multiple vCenter Servers (Local) • Multiple vCenter Servers (Remote) Deployment Best Practices and Recommendations • Deployment / Installation / Upgrading / Availability Challenges / Lesson Learned with Single Sign-On 5.1 vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 (NEW) • What's New with vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 • Deployment Configurations 8 vCenter Single Sign-On 5.1 Configurations Basic vCenter Single Sign-On Most common deployment option Inventory Svc (VMware recommended) This is a single standalone instance of the SSO server that supports the connectivity of Active Directory, OpenLDAP, Local Operating System and SSO embedded users and groups This typically would be local to the vCenter Server Web Client SSO Server (Basic) vCenter Server Host or VM vCenter Server Used by the vCenter Server Simple Install option Preinstalled with the vCenter Server Appliance 9 VC Database SSO Database vCenter Single Sign-On 5.1 Configurations Primary vCenter Single Sign-On Used for advanced configurations Inventory Svc vCenter Server • vCenter SSO High Availability (SSO HA) • Local Copy at Remote Sites (Multisite) Web Client Installable version of SSO (Windows Only) SSO Server (Primary) vCenter Server Host or VM Selected with the Individual Installer Supports the connectivity of • Active Directory • OpenLDAP • SSO embedded users and groups Does not support the use of local Database operating system user accounts Only one Primary node can exist in a single SSO environment 10 vCenter Single Sign-On 5.1 Configurations vCenter Server Inventory Svc Web Client vCenter Server Inventory Svc Web Client vCenter Single Sign-On HA Backup (SSO HA) Provides failover of vCenter SSO server Centralized vCenter SSO server for multiple local vCenter Servers vCenter Server 1 vCenter Server 2 Load Balancer Select with the Individual Installer Third Party Load Balancer + configuration + Support Complex to setup • Update SSL certificates SSO Server (Primary) SSO Server (HABackup) Host or VM Host or VM • Repointing of vCenter components No Protection of Shared Database Limited Functionality when failed over • Administration lost • No service restarts Availability – Same as vCenter Server Shared Database 11 • vSphere HA, vCenter Heartbeat vCenter Single Sign-On 5.1 Configurations vCenter Single Sign-On MultiSite New York Local Authentication • Removes additional risk (WAN) • Maintains same SSO security domain Required for Linked Mode Inventory Svc Selected with the Individual Installer Does not provide site redundancy Web Client Primary SSO Server vCenter Server Manual Steps required to maintain synchronization of SSO users/groups/polices etc Los Angeles Inventory Inventory Svc Svc vCenter Server Web Client Multi Site SSO Server vCenter Server 12 2. Install IS, VC in NY 3. Install Multisite SSO in LA 4. Replicate SSO from NY to LA vCenter Server 1. Install Primary SSO in NY 5. Install IS, VC in LA 6. Replicate SSO in LA to NY 7. Repeat steps 3-6 for each site Miami Local Databases Inventory Svc vCenter Server Web Client Multi Site SSO Server vCenter Server vCenter Single Sign-On Database 1. vCenter Single Sign-On • Hard naming requirements (RSA) • Schema Scripts provided on ISO • SQL Authentication required • JDBC connection Supported Databases • Oracle • Oracle 10g (rel2) / Oracle 11g (rel1-rel2) • Microsoft SQL Server • SQL Server 2005 (SP4) / 2008 (SP1-SP3) / 2008 R2 (SP1-SP2) / SQL Server 2012 • Embedded vPostgres (vCenter Appliance only) 13 14 vSphere Deployment Best Practices – vCenter Server 5.1 What is vCenter Single Sign-On vCenter Single Sign-On 5.1 • Architecture • Deployment Configurations • Database • 5.1 Architectural References • Single vCenter Server • Multiple vCenter Servers (Local) • Multiple vCenter Servers (Remote) Deployment Best Practices and Recommendations • Deployment / Installation / Upgrading / Availability Challenges / Lesson Learned with Single Sign-On 5.1 vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 (NEW) • What's New with vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 • Deployment Configurations 15 Single vCenter Server Design Recommendation Use Simple Installer Inventory Svc vCenter Server Web Client Basic SSO Server vCenter Server Host or VM Installs / Upgrades core components with a single virtual machine 1. 2. 3. 4. vCenter Single Sign-On vCenter Inventory Service vCenter Server Additional install: vSphere Web Client No change to architecture All services are local Supports 1-1000 Hosts / 110,000 Virtual Machines Distributed model adds VC Database SSO Database 16 unnecessary complexity and recovery challenges Multiple Remote vCenter Server Design Recommendations Multiple single vCenter Server design New York Each site is independent No single pane of glass view Availability Inventory Svc vSphere HA vCenter Heartbeat vCenter Server Web Client Primary SSO Server Los Angeles New York Miami vCenter Server vCenter Server vCenter Web Client Los AngelesBasic SSO Server vCenter Server Inventory Inventory Svc Svc vCenter Server Web Client Multi Site SSO Server Linked Mode 17 vCenter Server Maintains single pane of glass Replicates Licenses, permissions and roles Inventory Svc Inventory Svc Inventory Svc Web Client Server Basic Local SSO Server Databases vCenter Server vCenter Miami Web Client Server Basic Inventory Svc SSO Server vCenter vCenter Server Web Client Server Multi Site SSO Server vCenter Server Multiple Local vCenter Server Design Recommendations Centralized SSO authentication • Same Physical location • Metropolitan / College Campus Single Centralized vSphere Web Client Availability (Required) Basic SSO Server Web Client • vSphere HA • vCenter Heartbeat Local SSO Database Simple with full functionality Database Server VCDB1,VCDB2,VCDB3 1818 vCenter Server vCenter Server vCenter Server Inventory Svc Inventory Svc Inventory Svc vCenter Server 2 vCenter Server 2 vCenter Server 2 vSphere Deployment Best Practices – vCenter Server 5.1 What is vCenter Single Sign-On vCenter Single Sign-On 5.1 • Architecture • Deployment Configurations • Database • 5.1 Architectural References • Single vCenter Server • Multiple vCenter Servers (Local) • Multiple vCenter Servers (Remote) Deployment Best Practices and Recommendations • Deployment / Installation / Upgrading / Availability Challenges / Lesson Learned with Single Sign-On 5.1 vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 (NEW) • What's New with vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 • Deployment Configurations 19 Common Issues – Login Problem / Failures Login problems are the primary problem we see with SSO Fall into several basic categories • Login fails with an STS error: • Common Causes/ troubleshooting: • vCenter SSO Service is not accessible – check networking • vCenter SSO Service is down – check services configuration • If the service cannot start: • Commonly it is database related – Check SQL connectivity and availability • Validate that passwords have not expired or changed • check imsTrace.log for errors relating 20 Common Issues – Login Problems / Failures (2) • Login fails with credentials not valid error • Common Causes • • • • • 21 Incorrect username or password specified Incorrect qualifying domain (@system-domain in this case) specified Password has expired – reset the password on the account. Account disabled or locked If none of these are working, check imsTrace.log to validate the error message for the login Common Issues – Login Problems / Failures (3) • Login fails for admin@system-domain • Similar to regular account failures. • Use the following KB to reset or unlocked from the following KB: Unlocking and resetting the vCenter Single Sign On (SSO) administrator password: http://kb.vmware.com/kb/2034608 • Example command line usage from the KB: • Always requires the master password. If lost, a reinstall is required. • To change the master password the following command can be used: 22 Best Practices for Login Problems / Failures Ensure that SSO service is started and that other teams announce any maintenance that is occurring • Most problems that GSS sees here are related to service being inaccessible • This includes Database and more importantly networking Always make sure that the admin@system-domain master password is recorded • This is the password which is set during the initial installation • As long as you have the master password, there is a way to get into the system • Think of this password as one which is similar to an Active Directory recovery password 23 Common Issues – Domain trusts 5.1 GA, A, B – No domain trusts function. • Many domain topologies exist VMware Development working to ensure that all trusts are available and function with SSO Cause: • SSO 5.1.x uses LDAP binds rather than native Windows API calls 24 Common issues - Permissions As long as authentication is successful permissions can cause unexpected problems after login completes SSO administrator is admin@system-domain vCenter administrator is whatever is specified in the installer • By default this will be the administrators group on the vCenter server If you don’t have permissions you may see: 25 Common issues – Permissions (2) Cause for this is that roles are by default separated vCenter log (vpxd.log) will show a vim.fault.NoPermission error Login with the appropriate administrator account and add permissions if desired 26 Best Practices – Permissions Configure a domain group for access by default rather than a user • This will ensure that many users have access rather than a single user • Allows for other users to still login if an account is locked out inadvertently Be sure to note down the group that was configured as the administrator access to vCenter during installation • With the vCenter linux appliance root has access by default Add additional SSO administrators other than admin@systemdomain • By adding separate users if an account expires, you can unlock the account by logging in with another user account 27 Best Practice - Local OS Accounts Recommendation: Move the use of local OS accounts in vCenter to SSO identity sources or embedded SSO user accounts Benefit: Depending on the architecture deployed the use of local OS accounts will more than likely be unavailable to vCenter server Tip: Setup a local SSO group and add AD/SSO users and or groups and apply vCenter permissions to the SSO group 28 Common Issues - Certificates Certificates are used for security for SSO • All VMware components use certificates for communication • If a certificate is invalid or expired, SSO will reject communication • All services which are registered into SSO need a valid certificate Installs to vCenter 5.1, will fail if the certificate is invalid when upgrading • The following certificates need to be VALID to successfully upgrade to 5.1 • SSO • Inventory Service • vCenter • More information on this in KB: Upgrading to vCenter Server 5.1 fails with the error: Certificate already expired (2035413) 29 Common Issues – Certificates (2) Replacing the certificates difficult due to the number of steps VMware engineering recognized the difficulty introduced and released the SSL Certificate Automation Tool • Automates the installation and configuration of new certificates • KB to the tool: Deploying and using the SSL Certificate Automation Tool (2041600) Not a certificate authority • Will generate the certificates requests and install the resulting certificates • Will not generate the certificate, admin has to get this from the CA still 30 Create SSO Database Recommendation: Create the SSO database prior to installation Benefit: You will be asked to connect to the database during SSO install otherwise you will not be able to continue Tip: Use the scripts provided on the vCenter ISO, make sure you edit them with database location and user account passwords before executing 31 Configure SSO Before Upgrading vCenter Server Recommendation: When upgrading, install SSO then web client before other components Benefit: This will allow you to preconfigure the identity sources prior to vCenter upgrade and eliminate any login risks post install Tip: Add a domain user as an SSO admin, log out and in as the user to confirm configuration before proceeding 32 vCenter Server – Availability Recommendation: Protect the vCenter Suite, not individual components Benefit: If high availability is desired use a solution that protects all components to maintain dependencies Tip: vSphere HA and vCenter Heartbeat can protect all components whether distributed or local with same license. vDP 5.5 also restores without vCenter and also can be used 33 vSphere Deployment Best Practices – vCenter Server 5.1 What is vCenter Single Sign-On vCenter Single Sign-On 5.1 • Architecture • Deployment Configurations • Database • 5.1 Architectural References • Single vCenter Server • Multiple vCenter Servers (Local) • Multiple vCenter Servers (Remote) Deployment Best Practices and Recommendations • Deployment / Installation / Upgrading / Availability Challenges / Lesson Learned with Single Sign-On 5.1 vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 (NEW) • What's New with vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 • Deployment Configurations 34 Challenges with vCenter Single Sign-On 5.1 Active Directory Integration • Does not work effectively in multi-forest / trusted domain environments • Does not scale in environments with 15K or greater users • Administration is limited Certificates • SSL communications challenging • Difficult to change / update Installation • Database requirements / security concerns • Many installable configurations • Difficult to change / reconfigure post install • Complex Diagnostics • Troubleshooting tools – non existent 35 vSphere Deployment Best Practices – vCenter Server 5.1 What is vCenter Single Sign-On vCenter Single Sign-On 5.1 • Architecture • Deployment Configurations • Database • 5.1 Architectural References • Single vCenter Server • Multiple vCenter Servers (Local) • Multiple vCenter Servers (Remote) Deployment Best Practices and Recommendations • Deployment / Installation / Upgrading / Availability Challenges / Lesson Learned with Single Sign-On 5.1 vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 (NEW) • What's New with vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 • Deployment Configurations 36 What's New with vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 (in short) Improved architecture • Multi-master • Built-in replication • Site awareness • Multi Tenant Database vCenter Server Web Client Inventory Svc Inventory Svc Inventory Svc vCenter Server Web Client vCenter Server vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 vCenter Server SSO Site 1 vCenter Server vCenter Server SSO Site 2 • There is no Database! Installation • One simplified deployment model • Select vCenter Single Sign-On for the first or an additional vCenter Server Diagnostics • Full suite of diagnostic / Troubleshooting tools 37 Web Client vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 - Installation Prerequisites • Hostname has a FQDN an is DNS resolvable (forward/reverse) • Joined to an Active Directory domain (if integrating with Active Directory) • Windows 2008 x64 SP2 or higher (or use vCenter Appliance) 38 vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 - Installation Simple Installer • single vCenter Server environments Individual installer • multiple vCenter servers and / or advanced configurations Installer Steps 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 39 Accept License agreement (EULA) Prerequisite check summary Edit default port number 7444 (if necessary) Select Deployment placement Provide Administrator@vsphere.local password Provide a site name or select a previous site name Edit destination directory (if necessary) Summary Installation Complete Upgrading? admin@system-domain? Account becomes an alias of administrator@vsphere.local Supports Upgrade of all vCenter 5.1 configurations Previous vCenter Single Sign-On 5.1 deployment models • Fully Maintained via Upgrade • Basic • Single Sign-On High Availability • Single Sign-On Multisite New recommendations with vSphere 5.5 • Take advantage of new technology • Single virtual machine for all vCenter components** • • Distributed virtual machines add complexity • Availability / Backup & Restore • Management Easily migrate to new recommendations during upgrade ** Enterprise customers with 6 or more local vCenter servers can use a centralized instance 40 Types of Identity Sources What is an identity source? An external domain or repository of users and groups Identity Sources supported with 5.5 1. Native Active Directory (Recommended) • Uses kerberos via machine account or SPN (Load Balancer) 2. Active Directory as an LDAP server • This was done for backward compatibility to 5.1 • Not likely to be supported post 5.5 • Same limitations as in 5.1 3. OpenLDAP 4. Local Operating System 5. Single Sign-On 41 Configuring your VC Server When you configure your VC Server, make sure to set the VC Administrator as administrator@vsphere.local. DO NOT SET THE VC Administrator to be a Local OS account. Diagnostics vCenter Single Sign-On 5.5 Diagnostic Tools Perform all administration and reconfiguration from MMC Snap in • vCenter Single Sign-On services need to be running KB to troubleshoot startup issues Separate download • So we can update independently and add exciting new features 42 Replication Builtin Replication • Between each Single Sign-On server deployed in the same vSphere authentication domain Replication Partners • Review / Add / Remove / Edit Geographically Separated Single Sign-On sites • Reduce overhead • Provide Redundancy Links 43 Backup / Restore / Availability Backup / Restore • Virtual Machine** • Snapshot • Tape / Disk • vDP (now supports host level restore) • Application (KB with GA) • • • • • Registry Keys SSL Certificates (tcserver) Certificate server KDC VMDir (vdcbackup) Availability of vCenter Single Sign-On server • No different to vCenter • Why? vCenter is the primary resident of the Single Sign-On server • vSphere HA, vCenter Heartbeat **Additional step required when multiple SSO instances are configured 44 The log files provided by Single Sign On includes: vminst.log: Single Sign On installer log vim-sso-msi.log: MSI installer verbose logs for Single Sign On installation vim_ssoreg.log: Single Sign On Lookup Service log exported_sso.properties: Endpoint information about each of the Single Sign On Solution Users and identity sources extracted from previous vCenter Single Sign On 5.1.0 instance vim-openssl-msi.log: MSI installer verbose log for OpenSSL installation vim-python-msi.log: MSI installer verbose log for Python installation vim-kfw-msi.log: MSI installer verbose log for MIT Kerberos installation Single Sign On logs are grouped by component and purpose: vmdird\vdcpromo.log: Promotion and demotion operation information for the Single Sign On instance when joined or removed from a linked configurations vmdird\vdcsetupIdu.log: VMware Directory Service setup post-installation log containing information about the localhost name vmdird\vmdir.log: Health reports for the VMware Directory Service service and the Lotus VMDir database vmkdcd\vmkdcd.log: Key Distribution Center (kdc) run-time log, reports ports conflicts preventing the service from starting vmware-sso\vmware-sts-idmd.log: VMware Identity Management service run-time logs, timestamped records of user attempts when accessing Single Sign On for administrative purposes vmware-sso\vmware-sts.ldmd-perf.log: VMware Identity Management service performance counter logs vmware-sso\VMwareIdentityMgmtService.<date>.log: Commons Daemon log once the Identity Management Service has started 45 Additional Information Deprecated Functionality • NIS Identity Source • More than one default domain per Identity Provider • SMTP configuration and notification for password expiration by mail TCP Ports Used by SSO • 2012 Control interface RPC for VMDirectory • 88, 2013 Control interface RPC for the Kerberos • 2014 RPC port for all VMCA APIs • 7444 vCenter Single Sign On - HTTPS • 11711 vCenter Single Sign On - LDAP • 11712 vCenter Single Sign On - LDAPS • 12721 VMware Identity Mgmt Service 46 Single vCenter Server 5.5 Design Recommendation Use Simple Installer Inventory Svc vCenter Server Web Client SSO Server vCenter Server Host or VM VC Database 47 Installs / Upgrades core components with a single virtual machine 1. vCenter Single Sign-On 2. vSphere Web Client 3. vCenter Inventory Service 4. vCenter Server No change to architecture All services are local Supports 1-1000 Hosts / 110,000 Virtual Machines Multiple vCenter Server 5.5 (Remote) Design Recommendation Los Angeles New York Server vCenter Web Client Inventory Svc Inventory Svc Inventory Svc vCenter Miami vCenter Web Client Server Web Client Server SSO Server – vsphere.local vCenter Server SSO Site 1 vCenter Server vCenter Server SSO Site 3 SSO Site 2 Single SSO Authentication Domain By Default Each site is independent Does not provide a single pane of glass view SSO automated replication SSO Users & Groups Site awareness 48 SSO Policies Identity sources Linked Mode Maintains single pane of glass Replicates Licenses, permissions and roles Availability vSphere HA vCenter Heartbeat Multiple vCenter Server 5.5 (Local) Design Recommendations A Datacenter with 6 or more vCenter Servers Centralized SSO authentication • Same Physical location Single Centralized vSphere Web Client Availability (Required) SSO SSO Server Server Web Client Web Client • vSphere HA • vCenter Heartbeat • Network Load Balancer Database Server VCDB1,VCDB2,VCDB3 vCenter Server 5.1 vCenter Server 5.5 vCenter Server 5.5 Inventory Svc Inventory Svc Inventory Svc vCenter Server 1 vCenter Server 2 vCenter Server 3 Backwards compatible to vCenter Server 5.1 4949 The Possibilities are Endless… Los Angeles New York Miami 5050 Thank You Stay up to date with vCenter Server http://blogs.vmware.com/vsphere/ @vCenterGuy @jasper9 51 THANK YOU VSVC5635 vSphere vCenter Single Sign-on Best Practices Josh Gray, VMware Justin King, VMware Jonathan McDonald, VMware #VSVC5635