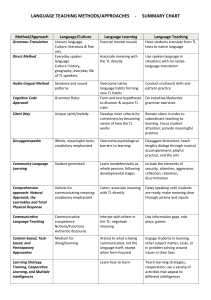
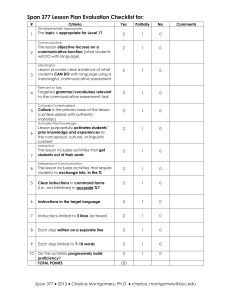
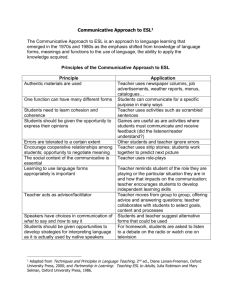
COMMUNICATIVE LANGUAGE TEACHING Inventor: This method is based partly in the theories of Brititish functional linguists such as: Firth, Halliday, and the American sociolinguistics Hymes, Gumperz and Lavob. Country U.S.A of Origin: Great Britain Theory of language: language is for communication and linguistic competence and the knowledge of forms and their meanings are part of the communicative competence. Another aspect of this knowledge is to learn the use of the language. Theory of learning: Activities that involve real communication promote learning Activities in which language is used for carrying out meaningful tasks promote learning Language that is meaningful to the learner promotes learning. Role of the teacher: the teacher facilitates the communication in the classroom, and he also acts like an adviser and a guide. Role of the student: Ss are communicators. They are actively engage in trying to make themselves understood and in understanding others. Use of the mother tongue: can be used. However, whenever possible the target language should be used. Activities: Scrambled Language Picture Role sentences Games Strip Story Play Techniques: Communicative language teaching uses almost any activity that engages learners in authentic communication. functional communication activities in which communication is involved, and social interaction activities, such as conversation and discussion sessions, dialogues and role plays. MATERIAL S o Language materials authentic to native speakers of the target language. (news paper, radio and television broadcast, menus, weather forecast, timetables). o For beginner students it is possible to use realia with out a lot of language. EVALUATIO N A teacher can informally evaluate students’ performance in his role as an adviser or co­communicator. For formal evaluation an integrative test is used which has a real communicative function. In order to assess students’ writing skill, a teacher might ask them to write a letter to a friend. Modes of interaction T­Ss, Ss­Ss, Ss­T Students’ feelings Students are given an opportunity to express their individuality by having them share their ideas and opinions on a regular basis. AREAS OF LANGUAGE EMPHASIZED Language functions might be emphasized over forms. Students work with language at the suprasentential or discourse level. STUDENTS’ ERRORS Errors of form are tolerated during fluency­based activities and are seen as a natural outcome of the development of communication skills. The teacher may note the errors during fluency activities and return to them later with an accuracy­based activity. Advantages will be more motivated by learning to communicate. Disadvantages Students Students will learn to communicate effectively. No grammar rules are presented. REFERENCES Larsen­Freeman, D. (2000). Techniques and Principles in Language Teaching. (second ed.). Oxford University Press. http://www.englishraven.com/method_communicative.html http://www.sil.org/lingualinks/languagelearning/ waystoapproachlanguagelearning/Communicativ eLanguageTeaching.htm