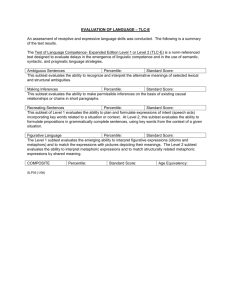
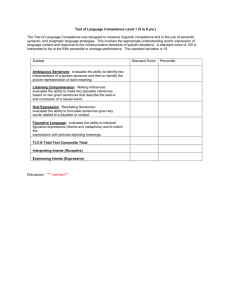
Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals – 4th UK edition (CELF 4 UK) : The norm referenced scores allow you to compare the child’s performance to the performance of other students of the same age. A subtest standard between seven and thirteen is considered within normal limits. A score below seven is considered below average and a score above thirteen is considered above average. The core language and index scores have a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. Two thirds of all typically language developing children will score between 85 and 115. Percentile ranks are also used to demonstrate the child’s language attainments in comparison to 100 children of the same age. The 50th percentile is average. A child who obtains a percentile rank of 99 is achieving at the highest level when compared to his peers. A child with a percentile rank of 1 is performing at the lowest level when compared to other children of the same age. Table 1. Relationship Between CELF scores, Deviations from the Mean, and Percentile Ranks. __________________________________________________________________ Subtest Standard Deviations Percentile Rank Standard Score from the Mean ___________________________________________________________________ 19 +3 99 16 + 2 98 13 +1 84 10 7 0 Mean -1 50 16 4 -2 2 1 -3 1 _____________________________________________________________________ A core language score is derived by testing on 4 subtests. This core language score is a general measure of language ability that quantifies a student’s overall language performance Subtest Concepts and Directions Recalling Sentences Formulated Sentences Word Classes-. Total Core Language Score (Mean = 100) Standard Score (Mean = 10) Percentile Rank . The receptive language index score measures listening and auditory comprehension. Different subtests are computed according to the child’s age. Subtest Concepts and Directions Word Classes-receptive Sentence Structure Receptive-Language Score (Mean = 100) Standard Score(Mean = 10) Percentile Rank The expressive language index score is an overall measure of the student’s expressive language skills. Subtest Word Structure Recalling Sentences Formulated Sentences Expressive-Language Score (Mean = 100) Standard Score(Mean = 10) Percentile Rank The language content index score measures aspects of semantic development including vocabulary, concept and category development interpretation of factual and inferential information and the ability to create meaningful and correct sentences. Subtest Concepts and Directions Expressive Vocabulary Sentence Structure Language Content (Mean = 100) Standard Score(Mean = 10) Percentile Rank The language structure index score is an overall measure of receptive and expressive components of interpreting and producing sentence structure. Subtest Word Structure Recalling Sentences Formulating Sentences Sentence Structure Language Structure Standard Score (Mean = 10) Percentile Rank The language memory index score is a measure of the ability to recall spoken directions, formulate sentences with given words, and identify semantic relationships. Subtest Concepts and Directions Recalling Sentences Formulated Sentences Language Memory (Mean = 100) Standard Score(Mean = 10) Percentile Rank Appendix 1 The individual subtests of the CELF 4 that were administered are detailed below: The Concepts and directions subtest assesses the ability to interpret, recall and carry out commands of increasing length and complexity. Concepts assessed would include sequential (beginning, first, last), inclusion (and/but, neither) and location (next to, right/left). A low score on this subtest may be compensated for by adapting the length and complexity of instructions. The Recalling Sentences subtest requires the child to repeat sentences of increasing structural complexity and has a dependence on auditory memory. A low score on this subtest may be compensated for by allowing the child extra time to process and respond, use of visuals or scripts. Formulating Sentences subtest evaluates the ability to formulate simple, compound and complex sentences. The child with a low score on this subtest can be helped by pre-teaching, modelling and guiding language activities. The Word classes subtests assesses ability to grasp the relationships between pairs of words including opposites (e.g. smooth, rough), words having part-whole relationship (whisker-cat) or having similar meaning (fast, quick). This can also be extended to include an assessment of the child’s ability to explain the logical relationships between associated words. Word Structure subtest evaluates the student’s ability to apply word structure (grammatical markers) rules to words/phrases. These structures can be taught systematically. Sentence Structure this subtest evaluates the student’s ability to interpret spoken sentences of increasing length and complexity and to select the correct picture that represents the sentence. Expressive vocabulary assesses the child’s ability to name illustrations of people objects and actions. Word Definitions: Evaluates the examinees ability to analyse and define words Number repetition: evaluates the student’s ability to repeat random number sequences of graduated length forwards and backwards. Understanding spoken paragraphs: evaluates the student’s ability to focus attention listen to paragraphs of increasing length understand oral text and answer questions about the content. Sentence Assembly: evaluates the student’s ability to formulate grammatically acceptable sentences and transform given words. Semantic relationships: evaluates the student’s ability to interpret sentences. Familiar Sequences: Evaluates the ability to manipulate and sequence auditory/verbal information as quickly as possible. This task places a heavy demand on attention, processing speed and working memory. Appendix 2: Relationship to the curriculum and classroom activities.