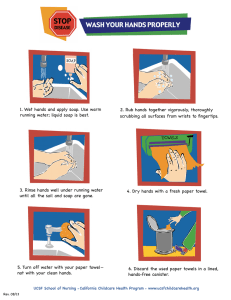
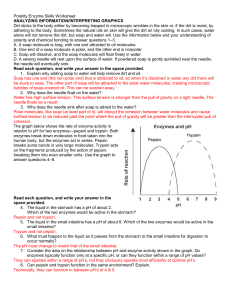
Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Worksheet NAME: Catalase and Hydrogen Peroxide Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) is a mild acid that is produced in our bodies through natural process that benefit us by fighting infections and optimizing overall cellular health. However, high concentrations of H2O2 is lethal so bodies must manage this substance. Catalase is a natural enzyme that does just this. Performed in various regions such as in the liver, catalase breaks down 2 H2O2 into 2 water (H2O) and one oxygen (O2). 1. Write a chemical reaction that summarizes this reaction. 2 H2O2 + 2 water 2H2O + O2 2. Describe how this illustrates the concept of the conservation of matter. 3. THE NUMBER OF ATOMS ON THE LEFT SIDE (4 HYDROGEN AND 4 OXYGEN) EQUALS THE NUMBER OF ATOMS ON THE RIGHT. In optimal conditions, hydrogen peroxide is broken down into water and oxygen, illustrated in the graph below. Some serious conditions can alter catalase’s activity, such as pH and temperature. 4. What does the line given represent? THE LINE REPRESENTS PRODUCTIVITY UNDER IDEAL CONDITIONS. 5. In a different color, draw in and label a new line that would represent this reaction’s production if temperature is increased by 5°F (about 2.5°C). 6. Justify this. INCREASING BY A LITTLE WON’T DESTROY THE ENZYME, BUT WILL DECREASE ITS PRODUCTIVITY 7. In a different color, draw in and label a new line that would represent this reactions production if temperature is boiled (denatured). 8. Justify this. A DENATURED PROTEIN WILL NOT FUNCTION. NO FUNCTION MEANS NO PRODUCTIVITY BECAUSE THE DENATURED PROTEIN HAS NO EFFECTIVE ACTIVE SITE. THE SUBSTATE REACTANTS WILL NOT BIND TO THE ENZYME, THEREFORE, WILL NOT BIND WITH OTHER SUBSTATE REACTANTS AND FORM NO PRODUCTS. Soap and Dirt Dirt, generally considered non-polar, sticks to the body either by becoming trapped in microscopic wrinkles in the skin or, if the dirt is moist, by adhering (sticking) to the natural oils of our skin. Sometimes the natural oils on skin will give the dirt an oily coating. In such cases, water alone will not remove the dirt, but soap and water will. Use the information below and your understanding of polarity and chemical reactions to answer the following questions. a. A soap molecule is long, with one non-polar end attracted to non-polar oil molecules and the other polar end attracted to polar water molecules. b. Soap will dissolve and will float freely in water if there is no dirt or oil. c. Soap is attracted to and will bind with oil particles (sometimes where dirt is trapped). d. The product of soap molecules and oils are micelles (pictured below). Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. 1. What is the difference between polar and non-polar? POLAR = MOLECULE HAS AN UNEVEN DISTRIBUTION OF CHARGE ACROSS THE WHOLE OF TH MOLECULE NON-POLAR = MOLECULE HAS A (relatively) EVEN DISTRIBUTION OF CHARGE ACROSS THE ENTIRETY OF THE MOLECULE 2. Why does soap dissolve in water? (like when you put detergent into the sink water) SOAP WILL DISSOLVE IN WATER BECAUSE OF THE PART OF THE SOAP MOLECULE THAT IS POLAR WILL INTERACT WITH OTHER POLAR MOLECULES, LIKE WATER. 3. Why does dirt stick to soap, but not to water? DIRT (NONPOLAR) WILL STICK TO THE NONPOLAR REGIONS OF A SOAP MOLECULE, HOWEVER WATER HAS NO NONPOLAR REGION SO THE DIRT WILL AVOID WATER. 4. Write what you believe would be the chemical reaction of soap and oil in the correct form. SOAP + OIL MICELLE 5. How does dirt and soap come into contact with each other? RANDOMLY, THE SOAP’S NONPOLAR REGION WILL STICK TO THE NONPOLAR DIRT PARTICLES AS IT’S DISSOLVING IN WATER. 6. What are two ways you could improve the activity of soap in any “cleaning” situation? SIMPLY PUT, ADD ENERGY BY EITHER HEATING THE WATER OR SCRUBBING (BOTH OF WHICH WE LEARN PRETTY EARLY ON… WASHING IN WARM/HOT WATER OR SCRUBBING WITH SOMETHING ABRASIVE (adding friction) WORKS BETTER THAN WASHING IN COLD WATER) Pepsin and Trypsin in Digestion The graph shows the rate of enzyme activity in relation to pH for two enzymes—pepsin and trypsin. Both enzymes break down molecules in food taken into the human body, but the enzymes act in series, meaning one after the other. Pepsin breaks some bonds in very large macromolecules forming fragments. Trypsin then acts on the fragments produced by the action of pepsin, breaking them into even smaller units. Once the fragments are small enough they will be absorbed into the blood stream and finally into cells. Use the graph to answer following questions. Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. 1. Write 2 different chemical reactions that would best summarize the two major reactions taking place in this scenario. PEPSIN + LARGE MOLECULE FRAGMENTS TRYPSIN + FRAGMENTS SMALLER UNITS (implied that these units can be absorbed by our cells) 2. The liquid in the stomach has a pH of about 2. Which of the two enzymes would be active in the stomach? PEPSIN 3. The liquid in the small intestine has a pH of about 8. Which of the two enzymes would be active in the small intestine? TRYPSIN 4. What must happen to the liquid as it passes from the stomach to the small intestine for digestion to occur normally? THE pH MUST BE INCREASED SOMEHOW 5. Consider the data on the relationship between pH and enzyme activity shown in the graph. Do enzymes typically function only at a specific pH, or can they function within a range of pH values? THEY FUNCTION IN A RANGE OF pHs THOUGH THERE IS AN OPTIMAL pH FOR EACH (INDICATIVE OF THE HIGHEST RATE OF REACTION) 6. Can pepsin and trypsin function in the same environment? Explain. THEY CAN BUT BOTH WOULD FUNCTION AT LESS THAN OPTIMAL LEVELS. THE pH WOULD BE BETWEEN 4 AND 5 IN THIS CASE. THIS IS OF COURSE LESS THAN OPTIMAL FOR EITHER ENZYME.