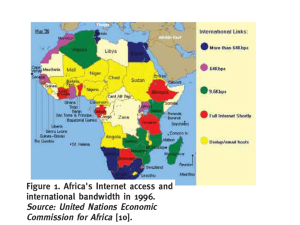
VSAT Dr.Ir.Joko Suryana Introduction • Satellite Communication is a technology of data transmission whether one-way data broadcasting or two-way interactive using frequency as a medium. Consist of : • Space Segment or Satellite ( eg. Measat, Intelsat, Inmarsat ) • Ground Segment or earth station which includes Antenna, Outdoor Unit, Inter Facility Link, Indoor Unit and Customer Premises Equipment. • VSAT is a satellite-based communications service that offers flexible and reliable communications solutions including Enterprise Wide Networking with high reliability and a wide reach that extend even to remote sites. Why VSAT? VSAT networks provides: • Reliability in transmission of data (data, voice, video) • Allocation of resources to different users (bandwidth, amplification power) • Fixed network solutions at reasonable price (eg. voice channel at 3-15 cents/min.) • Provide point-to-multipoint (broadcast), multipoint-topoint (data collection), point-to-point communications and broadband multimedia services. • Serviced in land area which are difficult to install (remote locations ,water areas). • An ability to have direct access to users and user premises. VSAT Characteristic and Advantage • Reliability: reliable satellite transmission of data, voice and video between an unlimited number of geographically dispersed sites or from these sites to headquarters • Flexibility: The VSAT networks offer enormous expansion capabilities; On the other hand, VSATs offer unrestricted and unlimited reach. Additional VSATs can be rapidly installed to support the network expansion to any site, no matter however remote. • Network Management: Network monitoring and control of the entire VSAT network is much simpler than a network of leased lines, easily integrates end-to-end monitoring and configuration control for all network subsystems. • A low mean-time to repair - few hours, compare to leased lines which extends up to a few days. Essentially, lesser elements imply lower MTTR. Uptime of up to 99.5 percent is achievable on a VSAT network. This is significantly higher than the typical leased line uptime of approximately 80-85%. VSAT Characteristic and Advantage • Cost: VSAT network offers significant savings over 2-3 years timeframe. The service charges depend on the bandwidth which is allocated to the network in line with customer requirements. • Link Budgets: RF equipment would cater to the requirements of the network topology and satellite modems in use. The link Budget estimates the ground station and satellite EIRP (Effective Isotropic Radiated Power) required. Calculations of signal levels through the system to ensure the quality of service should normally be done, prior to the establishment of a satellite link. VSAT Services • Interactive real time application: – Point of Sale/retail/Banking (eg. ATM) – Corporate data • Telephony – Rural : individual subscribers – Corporate Telephony • Intranet, Internet and IP infrastructure – Multimedia delivery (eg. video streaming) – Interactive distance learning/ training • Direct-to-home – Broadband Internet access for consumers and businesses Satellite Communication Concept C Band – 6/4GHz Ku Band -14/12GHz Ka Band – 30/20GHz Uplink 6 GHz HPA Downlink 4 GHz LNA Up Converter Down Converter Satellite Modem Satellite Modem CPE CPE PSTN Transmitting Earth Receiving Earth Station Station PSTN Note : HPA – High Power Amplifier (Earth station equipment that amplifies the transmit RF signal. ) CPE – customer premises equipment ( eg. Telephone, PABX, Ethernet hub, host server, etc.) VSAT Communication Concept C Band – 6/4GHz Ku Band -14/12GHz Ka Band – 30/20GHz Uplink 6 GHz HPA Downlink 4 GHz LNA Up Converter Down Converter Satellite Modem Satellite Modem CPE CPE PSTN Transmitting Earth Receiving Earth Station Station PSTN Hub System VSAT Station Equipment VSAT specification Antenna diameter: 0.6m – 3.8m Traffic Capacity : 9.6Kbps – 2Mbps Frequency Bands : C-band (4-6Ghz), Ku-Band (12-14Ghz), Ka-Band (20-30Ghz) Use of satellite : Geo-stationary satellite (36,000km above equator) Network: Point-to-point Configuration : Point-to-multipoint Equipment List : – Antenna; – Outdoor Unit (High Power Amplifier (HPA), Low Noise Amplifier (LNA), SolidState Power Amplifier (SSPA)) – Indoor Unit (chassis) Note : • Antenna size is used to describe the ability of the antenna to amplify the signal strength; • Outdoor unit (ODU) is connected through a low-loss coaxial cable to the indoor unit (IDU) called IFL (Interfacility Link). Typical VSAT system • Up- converters and High Powered Amplifiers (HPA) • antenna varies - antenna size describe the • Radio Frequency Terminal (RFT) is mounted on the antenna used for converting and amplifyingability the signal of thebefore antenna to amplify the signal frame and interconnected to the feed-horn + Low Noise transmitting to the feed-horn. strength Amplifiers (LNA) + down-converters. • Extended C band, down converter receives the signal • feed-horn directs transmitted power to • LNAs – minimize signal noise. Noise temperature is parameter at 4.5 to 4.8GHz and the up converter converts it to antenna dish or collects the received power from used to describe the performance of an LNA. 6.725 to 7.025GHz. it. VSAT ODU and ISU : Equipment Outdoor Unit Feed Assembly Indoor Unit Typical value for ODU ( VSAT ) Hub Antenna Typical value for ODU ( Hub ) Network Components Skystar 360E Typical Hub Configuration VSAT Budget VSAT Topology • STAR - the hub station controls and monitors can communicates with a large number of dispersed VSATs. Generally, the Data Terminal Equipment and 3 hub antenna is in the range of 6-11m in diameter. Since all VSATs communicate with the central hub station only, this network is more suitable for centralized data applications. • MESH - a group of VSATs communicate directly with any other VSAT in the network without going through a central hub. A hub station in a mesh network performs only the monitoring and control functions. These networks are more suitable for telephony applications. • HYBRID Network - In practice usually using hybrid networks, where a part of the network operates on a star topology while some sites operate on a mesh topology, thereby accruing benefits of both topologies. VSAT Network Architectures One Way • One-Way – Receive Only – High Bit-Rate DVB Compliant Outbound – Inbound Return Channel via Dial-Up Modem – Can be used with existing infrastructure • Example: Harmonic’s CyberStreamTM Baseband Equipment Satellite DVB Modulator LAN DVB Receiver RFT IP Encapsulator VSAT TVRO Antenna TCP/IP ACK’s NACK’s Router Internet Modem/ISDN Return VSAT Network Architectures Two-Way Star Topology • • • All VSATs Communicate via a Single Hub Network is Independent of Existing Infrastructure VSAT Antenna Size dependent upon Power and Gain of Hub Antenna – Also Upon Inbound Bitrate, ODU Power and Satellite Footprint • • Contention Based Access – Usually TDMA or FTDMA Typical Ping Times Approximately 650-700ms VSAT VSAT VSAT Hub VSAT VSAT VSAT VSAT VSAT VSAT Network Architectures Two-Way Mesh Topology • • • • • • VSATs communicate directly with each other Some systems require initial signaling via the Hub Larger Antennas, Higher Power required at the VSAT Smaller Antenna, Lower Power required at the Hub Used extensively in Telephony Networks Delay minimized on VSAT to VSAT Calls VSAT VSAT VSAT VSAT VSAT VSAT VSAT Topology What is VSAT Accessing Scheme? The objective of VSAT networks: - is to maximize the use of common satellite and other resources amongst all VSAT sites. The method: - by optimizing the use of satellite capacity, and spectrum utilization in a flexible and costeffective manner ( referred as satellite access schemes.) - or we can call as VSAT technology. Type of VSAT technology TDMA Time-division Multiple Access VSAT TECHNOLOGY SCPC Single-carrier per Channel PAMA Pre-Assigned Multiple Access FDMA Frequency Division Multiple Access FDMA DAMA Demand Assigned Multiple Access CDMA Code Division Multiple Access TDMA (time-division multiple access) • When numerous remote sites communicate with one central hub, this design is similar to packet-switched networks. • Because of competition with one another for access to the central hub, it restrict the maximum bandwidth to most cases is about 19.2 kbps. • all VSATs share satellite resource on a time-slot basis. • Usually used in STAR topology as a transmission technique. • Offered to domestic needs. TDMA (time-division multiple access) Copyright Maxis The VSAT Hub communicates with all dispersed VSATs (typically a 1.8-meter diameter parabolicshaped dish) on an outgoing channel of up to 512kbps based on the TDM scheme. The incoming or return channel from the dispersed VSATs uses the TDMA channel technology that enables a large number of the respective VSATs to share this single return channel. The incoming routes typically operate at 128kbps, and can go up to a maximum bandwidth of 256kbps. TDMA (time-division multiple access) Copyright Maxis Petrol stations, information providers, retail chains, financial institutions and any large corporation that requires transfers of low to medium rate data applications between its head office and, local and outstation branch offices. Example of Point of Sales (POS transactions), Credit Card Verification, Reservations Systems Financial and Banking applications (teller, loans, ATM) etc. SCPC (single-carrier per channel) • SCPC-based design provides a point-to-point technology, making VSAT equivalent to conventional leased lines. • dedicated bandwidth of up to 2 Mbps • Usually use in an international VSAT services in Asia-Pacific. SCPC (single-carrier per channel) Copyright Maxis In the Hub-to-Remote configuration, one end of the VSAT link (normally the customer's HQ) is connected to the 11-meter VSAT Hub (Earth Station) via a terrestrial leased line. A VSAT antenna at the remote end or the distant end (normally the branch office) of the VSAT link is then interconnected to the VSAT hub via the satellite. SCPC (single-carrier per channel) Copyright Maxis VSAT links with a Remote-to-Remote configuration bypass the VSAT Hub and has a stand-alone VSAT antenna at both ends of the link. Typical VSAT antenna size ranges from 1.8m to 2.4m. FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access) • oldest method for channel allocation • the satellite channel bandwidth is broken into frequency bands for different earth stations • the earth stations must be carefully power-controlled to prevent the microwave power spilling into the bands for the other channels. Here, all VSATs share the satellite resource on the frequency domain only. 3 type: • PAMA (Pre-Assigned Multiple Access); • DAMA (Demand Assigned Multiple Access); and • CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access). PAMA (Pre-Assigned Multiple Access); • the VSATs are pre-allocated a designated frequency. Equivalent of the terrestrial (land based) leased line solutions. • PAMA solutions use the satellite resources constantly. Therefore, no call-up delay in the interactive data applications or high traffic volumes. • PAMA connects high data traffic sites within an organization. DAMA (Demand Assigned Multiple Access); • The network uses a pool of satellite channels, which are available for use by any station in that network. • On demand, a pair of available channels is assigned, so that a call can be established. Once the call is completed, the channels are returned to the pool for an assignment to another call. • Since the satellite resource is used only in pro-portion to the active circuits and their holding times, this is ideally suited for voice traffic and data traffic in batch mode. • DAMA offers point-to-point voice, fax, data requirements and supports video-conferencing. Satellite connections are established and dropped only when traffic demands them. CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) • Under this, a central network monitoring system allocates a unique code to each of the VSATs. Enabling multiple VSATs to transmit simultaneously and share a common frequency band. • The data signal is combined with a high bit rate code signal which is independent of the data. • Reception at the end of the link is accomplished by mixing the incoming composite data/code signal with a locally generated and correctly synchronized replica of the code. • Since this network requires that the central network management system co-ordinates code management and clock synchronization of all remote VSATs, STAR topology is the best one. • Mainly used for interference rejection or for security reasons in military systems. Contoh Penerapan Contoh Penerapan Contoh Penerapan Contoh Penerapan Contoh Penerapan Contoh Penerapan Contoh Penerapan Thanks