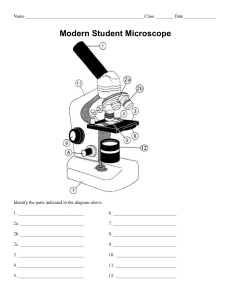
Name: ____________________________________ Grade & Section: _________________ Activity #__ The Scientific Method The scientific method is a process for experimentation that is used to explore observations and answer questions. The scientific method is used in all sciences— including chemistry, physics, geology, and psychology. The scientists in these fields ask different questions and perform different tests. However, they use the same core approach to find answers that are logical and supported by evidence. Objectives 1. Identify the steps of the scientific method 2. Use the scientific method to create an experiment in their daily life. List the steps of the Scientific Method In the space provided. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. In the space provided, use the Scientific Method to solve the following problems. Follow the step-by-step process you wrote above to find a solution. Write your answer in PARAGRAPH FORM and be sure to write in COMPLETE SENTENCES. Observation 1: One morning you wake up and discover that your radio no longer works. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________. Observation 2: You take all of your books home from school and promptly finish your homework. The next morning you wake up and cannot find your bag with your books in it. Your brother has a backpack that looks very similar to yours. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. What is a hypothesis? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Why do we need to learn scientific method? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Conclusion: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Name: _________________________________ Grade & Section: ____________________ Activity # __ What Solutions do You Find in Your Home? Objectives: Describe the observable characteristics or properties of common solutions found at home or in stores; Present the data gathered in table form to show the different properties of common solutions. Products or Solutions Found at Home or in Stores Characteristics Solutions Found in Nature Characteristics Question: Why is solution important to our daily lives? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Conclusion: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Name: __________________________________ Grade & Section: ___________________ Activity #__ Elements, Compounds & Mixtures All matter is made of elements that are fundamental substances that cannot be broken down by chemical means. An element is a substance that cannot be further reduced as to simpler substances by ordinary processes. In essence, an element is a substance consisting of one type of atom. A compound is a pure substance composed of two or more different atoms chemically bonded to one another. That means that it cannot be separated into its constituents by mechanical or physical means and only can be destroyed by chemical means. A mixture is a material containing two or more elements or compounds that are in close contact and are mixed in any proportion. For example, air, sea water, crude oil, etc. Objectives: 1. Distinguish and describe the three types of matter: elements, compounds, mixtures. 2. Identify whether the substance is an element, compound or mixture Materials: Activity paper and ballpen Procedure: Classify each of the materials below. Elements: 1. A pure substance containing only one kind of ____________. 2. An element is always uniform all the way through (homogeneous). 3. An element _____________ be separated into simpler materials (except during nuclear reactions). 4. Over 100 existing elements are listed and classified on the ____________________. Compounds: 1. A pure substance containing two or more kinds of _______________. 2. The atoms are _________________ combined in some way. Often times (but not always) they come together to form groups of atoms called molecules. 3. A compound is always homogeneous (uniform). Compounds ___________________ be separated by physical means. Separating a compound requires a chemical reaction. 4. The properties of a compound are usually different than the properties of the elements it contains. Mixtures: 1. Two or more ________________ or _________________ NOT chemically combined. 2. No reaction between substances. 3. Mixtures can be uniform (called ________________________) and are known as solutions. 4. Mixtures can also be non-uniform (called ________________________). 5. Mixtures can be separated into their components by chemical or physical means. 6. The properties of a mixture are similar to the properties of its components. Part 2: Classify each of the following as elements (E), compounds (C) or Mixtures (M). ____Diamond(C) ____Uranium (U) ____Krypton (K) ____Wood ____Sugar (C6H12O6) ____Milk ____Iron (Fe) ____A dog ____Air ____Gasoline ____Alcohol (CH3OH) ____Salt ____Water ____Pizza ____Gold (Au) Conclusion: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Name: __________________________________ Grade & Section: ___________________ Activity #__ Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous Mixture A homogeneous mixture has the same uniform appearance and composition throughout. A heterogeneous mixture consists of visibly different substances or phases. Direction: Classify the following types of matter as either homogeneous or heterogeneous. 1. Carbonated soft drink (w/ bubbles) 2. Chocolate chip ice cream 3. Salad 4. Corn syrup 5. Soil 6. Aluminum foil 7. Black coffee 8. Sugar & water 9. Air (with smog) 10. Paint 11. Rubbing alcohol 12. Full fat milk 13. Beach sand 14. Pure air 15. Chunky spaghetti sauce Pure Substances vs. Mixtures Direction: Classify the following as pure substances (element or compound) or mixtures. 1. Sodium 11. Iron 2. Water 12. Salt water 3. Soil 13. Chocolate chip ice cream 4. Coffee 14. Nitrogen 5. Oxygen 15. Eggs 6. Isopropyl Alcohol 16. Blood 7. Carbon dioxide 17. Table salt 8. Cake batter 18. Nail polish 9. Air Mixture 19. Milk 10. Chicken noodle soup 20. Soda Questions: 1. What is the difference between a homogeneous and a heterogeneous mixture? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. 2. Are all solutions homogeneous mixtures? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. 3. Can homogeneous mixtures be separated into their components? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Conclusion: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Name: __________________________________ Grade & Section: ___________________ Activity #__ Solutions A solution is a mixture of two or more substances. The substance that dissolves the others is the solvent. The substance that dissolve into the solvent are solutes. Direction: Choose the letter of the definition that best matches each term. A. _______ 1. Solution a. capable of being dissolved _______ 2. Solute b. solution with water as the solvent _______ 3. Solvent c. substance that is dissolved in a solution _______ 4. Soluble d. substance that dissolves in water to form a solution that conducts an electric current _______ 5. Alloy e. solid solution containing two or more metals _______ 6. Aqueous solution f. homogeneous mixture of two or more substances in a single physical state _______ 7. Electrolyte g. substance that does the dissolving in a solution B. Answer each of the following questions in the space provided. Describe the properties of a solution ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Give two examples of solutions in nature and explain why each is important. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Conclusion: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Name: __________________________________ Grade & Section: ___________________ Activity #__ Unsaturated, Saturated and Supersaturated Solutions An unsaturated solution contains less than the maximum amount of solute. A saturated solution contains the maximum quantity of solute that dissolves at that temperature. A supersaturated solution contain more solute than is possible to be dissolved. Supersaturated solutions are unstable and temporary. Procedures: 1. You add the first packet of sugar, and stir until it all dissolves with no sugar settled on the bottom. 2. You add a second packet of sugar and it takes a little more time for the sugar to dissolve. After stirring for a minute, you realize that there are still some sugar crystals at the bottom of the glass. 3. After tasting your tea, you decide it is still not sweet enough and add more sugar. However, it all settles at the bottom, and regardless of how much you stir, the crystals stay at the bottom of the cup. Q1. What can you do to help the sugar crystals dissolve? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Direction: Identify which type of solution was created in each step. Steps for Sweetening Iced Tea Type of Solution 1. Add one packet of sugar. All of the sugar crystals dissolved with none settled on the bottom. 2. Add second packet of sugar. Not all of the sugar crystals and a few settled on the bottom. 3. Add third packet of sugar. None of the sugar crystals dissolved and all settled on the bottom. To dissolve the sugar, you do the following: a. Heat up the tea to dissolve the sugar. b. Cool it back down so you can drink it. Conclusion: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Name: __________________________________ Grade & Section: ___________________ Activity #__ The Microscope Objectives: 1. Label the parts of the microscope and 2. Describe the functions of each parts A.) Base Knob D.) Diaphragm G.) Stage Clips J.) Eyepiece WORD BANK B.) Fine Adjustment E.) Light Source H.) Coarse Adjustment Knob K.) Objective Lenses C.) Arm F.) Stage I.) Nosepiece Please match the parts of the microscope with their function. Put the letter next to the part of the microscope that fits the description. 1. Eyepiece: _____ A – This part holds the objective lenses and is able to rotate to change magnification. 2. Base: _____ 3. Nosepiece: _____ 4. Stage: ______ 5. Coarse Adjustment Knob: _____ 6. Diaphragm: ______ 7. Stage Clips: ______ 8. Fine Adjustment Knob: ______ 9. Objective Lenses: ______ 10. Arm: _____ 11. Light Source: _____ B – This part of the microscope adjusts the amount of light that reaches the specimen (1 = least to 5 = most). C – This part moves the stage slightly to help you sharpen or “fine” tune your view of the specimen. D – Where you look into the microscope. This part allows you to view the image on the stage and contains the ocular lens. E – This part is used to support the microscope when carried. F – Part of the microscope that supports the slide being viewed. G – These are used to hold the slide into place. H – The bottom part of the microscope I – This part of the microscope is found on the nosepiece and range from low to high power. J – This part moves the stage up and down to help you get the specimen into view. K – This part of the microscope projects light upwards to allow you to see the specimen. Questions: 1. What is a microscope? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. 2. What is the function of a microscope? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Conclusion: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Name: __________________________________ Grade & Section: ___________________ Activity #__ Making Simple Slides Objectives: Prepare a simple slide at home State the correct way of carrying a microscope from one place to another Materials: Clear Scotch tape A few granules of salt, sugar, ground coffee, sand, or any other grainy material compound microscope Procedures: 1. To make a slide, tear a 2 ½-3” long piece of Scotch tape and set it sticky side up on the kitchen table or other work area. 2. Fold over about ½” of the tape on each end to form finger holds on the sides of the slide. 3. Next, sprinkle a few grains of salt or sugar in the middle of the sticky part of the slide. You can repeat this with the other substances if you like, just be sure to label each slide you make with an ink pen or permanent marker so you will know what’s on the slides. Questions: 1. Describe how and with what you are to clean the lens of the microscope. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. 2. List four things that you are to do when you are finished using the microscope. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. 3. What is the correct way of carrying a microscope from one place to another? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Conclusion: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Name: __________________________________ Grade & Section: ___________________ Activity #__ Levels of Organization of Living Things Objectives: Describe the biological levels of organization from the smallest to highest level Living things are highly organized and structured, following a hierarchy that can be examined on a scale from small to large. The atom is the smallest and most fundamental unit of matter. The bonding of at least two atoms or more form molecules. The simplest level of organization for living things is a single organelle, which is composed of aggregates of macromolecules. The highest level of organization for living things is the biosphere; it encompasses all other levels. The biological levels of organization of living things arranged from the simplest to most complex are: organelle, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, ecosystem, and biosphere. Direction: Identify where the following picture belongs. Questions: Why it is that cell is considered to be the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. What do you think will happen to the tissues, organs, and organ systems if these cells were injured or diseased? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. If the tissues, organs, and organ systems were injured or diseased, what do you think will happen to the organism? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Conclusion: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Name: __________________________________ Grade & Section: ___________________ Objectives: Activity #__ The Plant Cell Describe plant cell Identify the parts and function of the plant cell Use the word bank to answer the questions and label the drawing below. A. ribosome E. nucleus I. cytoskeleton B. mitochondria F. vacuole J. cell wall C. cell membrane G. Golgi body K. cytoplasm D. nucleolus H. chloroplast L. lysosome M. endoplasmic reticulum 1. ____ uses the energy of sunlight to produce glucose during photosynthesis 2. ____ provides strength and shape to the cell; network of protein fibers 3. ____ control center of the cell; contains DNA 4. ____ surrounds the internal cell parts; controls the passage of materials in and out 5. ____ vesicle that contains substances that break down materials 6. ____ produces energy 7. ____ provides rigid structure and protection; made of cellulose 8. ____ vesicle that provides storage of water and other materials; if full, provide support 9. ____ packages and transports proteins from the ER to other parts of the cell 10. ____ ER; passageways that transport proteins within the cell 11. ____ everything inside of the cell membrane except for the nucleus 12. ____ composed of protein and RNA; involved in ribosome production 13. ____ where proteins are made in the cells; the dots Questions: Describe the shape of the plant cell. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. What is the function of a. cell wall ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. b. chloroplast ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Conclusion: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Name: __________________________________ Grade & Section: ___________________ Activity #__ The Animal Cell Objectives: Describe the animal cell Identify the parts and function of the animal cell Compare and contrast the similarities and differences of both plant cell and animal cell. Use the word bank to answer the questions and label the drawing below. A. cell membrane E. nucleus I. rough endoplasmic reticulum B. mitochondria F. vacuole J. ribosome C. Golgi body G. cytoplasm K. smooth endoplasmic reticulum D. lysosome H. nucleolus L. nuclear membrane 1. ____ A double layer that supports and protects the cell. Allows materials in and out. 2. ____ Contains digestive enzymes that destroy damaged organelles and invaders. 3. ____ Jelly-like fluid that surrounds and protects the organelles. 4. ____ The control center of the cell. Contains the DNA 5. ____ Surrounds the nucleus. 6. ____ A round structure in the nucleus that makes ribosomes. 7. ____ Stores food and water. 8. ____ Processes and packages materials for the cell. 9. ____ The “Powerhouse”. Breaks down food to produce energy in the form of ATP. 10. ___ Builds and transports substances through the cell. Has ribosomes on it. 11. ___ Builds and transports substances through the cell. Does not have ribosomes. 12. ___ Helps make protein for the cell. For the chart below, place a check in the box if the cell has that component. Organelle Plant Animal Cell Wall Chloroplast Ribosome Mitochondria Vacuole DNA Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Questions: 1. What cell parts are found in both cells? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. 2. Which cell parts are present only in animal cells? _____________________________________________________________________________. 3. Which cell parts are present only in plant cells? _____________________________________________________________________________. Conclusion: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Name: __________________________________ Grade & Section: ___________________ Activity #__ Reproduction Objectives: Identify how the offspring of the two types of reproduction differ. Direction: Identify the organism’s mode of reproduction. Vegetative Propagation Spore Formation 1. ____________________________________ 2. ____________________________________ Budding Fertilization 3. ____________________________________ 4. ____________________________________ Conjugation Regeneration 5. ____________________________________ 6. ____________________________________ Questions: What are the different modes of reproduction? ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Give two (2) examples of organisms types that go through a. asexual reproduction ______________________________________________________________________________ b. sexual reproduction _____________________________________________________________________________________ Arrange the following characteristics. 2 parents needed Limited ability to adapt Involves specialized sex cells Offspring genetically identical to parents 1 parent needed Adaptable to environmental change Lots of energy needed Involves somatic cells Does not need much energy Offspring are a genetic mix of both parents Slow Quick Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Conclusion: ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________.