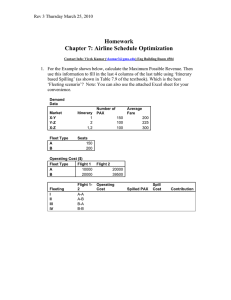
JetBlue Airways: Managing Growth Abhishek Mishra 15PGPWE 01 Santosh Pant 15PGPWE 09 Operation Strategy 2015-17 IIM R Group 5 Fact Sheet: JetBlue First to launch with more than 100 million in capital. First to offer 24 channels of live satellite free at every seat. First to broadcast the Olympics live at every seat. First to Paper less cockpit technology. First to have Security cameras. Major Competitors Americans Southwest United SWOT ANALYSIS Positive factors S Low Operating cost Strong brand Efficient employee O Industry Route & fleet expansion Creation of Airlines Alliances SWOT ANALYSIS Positive factors S Single fleet Consumer satisfaction Effective use of technology O Technological Improvements in Airplane design, operation and maintenance Deregulation of international air travel SWOT ANALYSIS Negative factors W Relative new company T Global crisis and Union Single fleet Security Concentration on middle class Increase in fuel price Fact Sheet: JetBlue First to launch with more than 100 million in capital. First to offer 24 channels of live satellite free at every seat. First to broadcast the Olympics live at every seat. First to Paper less cockpit technology. First to have Security cameras. Major Competitors Americans Southwest United PEST ANALYSIS • Political issue September11, terrorists attack Political stability Competitive Airline industry Regulatory factors PEST ANALYSIS • Economic issue Improved purchasing power Rise in Inflation Rise in oil prices PEST ANALYSIS • Social issue Greater customer awareness Increased entertainment level Security level of customers Bad services & lost baggage PEST ANALYSIS • Technological issue Beginning of e-ticketing Automated systems (cockpits) Advertisements (newly introduced animated) a) How would you describe JetBlue's operations strategy prior to the November 2005 adoption of the E190? low fares (65% lower than other competitor) and point-to-point model. Key operating principle was that flight cancellations should be avoided at all cost. Single type of plane, its fleet consisted entirely of A320. Connecting Large, typically north-eastern, US cities and more long haul flights. Reservation policy – tickets to be purchased via company’s website or through part-time employed reservation agents. Differentiation to other LCC: Comfort features such as assigned seats, leather upholstery, and satellite TV on individual screens in every seat. b) Compare the economics of the E190 and A320 for JetBlue. What are the key drivers of profitability for each type of plane? CASM (Cost per Available Seat Mile) , E190 is 12% higher than A320, 34% less than typical RJ. Revenue available seat mile (RASM), E190 is higher than A320. From Exhibit 9, we could calculate E190 RASM is about 30% higher than A320. Key drivers of profitability of E190 Owing to greater range and seating capacity relative to RJ’s E-190 could target wider range of profitable destinations. Higher utilisation of 10 to 11 hours a day compared to an average of 8 hours per day for RJs. Higher RASM, easy to get breakeven point because of the low capacity of passenger. (break even load of 75% to 80% was much lower on E-190 than A320). Lower acquisition costs. ($30-40 Million). Increase the range of choices available to JetBlue passengers by feeding customers to connecting A320 flights. Key drivers of profitability of A-320 Larger capacity. (150 against 100 of E-190). High fuel efficiency. Medium & Long-haul routes. Standardized training & Servicing Processes: A320 was a proven plane that had served as basis for JetBlue’s operations. The company had developed a high level of comfort with it. c) Do you agree with JetBlue's decision to add the E190 to its fleet? Be prepared to state the rationale for your decision. Yes we do agree to this.. Since E190 feed customers to connecting A320 flights, it resulted in higher loads and improved economics for JetBlue. Transfers at focus cities would also improve the utilization of existing airport facilities, increasing productivity and reducing downtime for airport crew members. This synergy between the E190 and A320 resulted in utilization of E190s of 10 to 11 hours a day, significantly more than average of 8 hours per day for RJs. Number of passengers required for a flight to meet the typical “breakeven” load of 75% to 80% was much lower on the E190 than the A320, E190 made it easier for JetBlue to introduce service in new markets. c) How should JetBlue slow down the growth of its fleet? Should it cut growth in A320 capacity, E190 capacity, or both ? JetBlue should slow down the growth of its fleet. This cut should be across both in A320 and E-190 planes. Reasons: E190 as a unique plane that could be used as an engine for future growth. A320 is a proven aircraft around which JetBlue had standardized its training and operating activities. In addition, E190 and A320 could inter-activate utilization. So it is not fit to cut growth in only A320 capacity or E190 capacity. Thank you