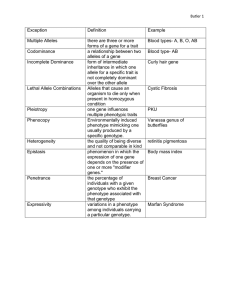
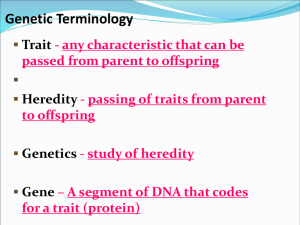
Warm Up 1) A child is born with blue eyes even though BOTH his parents have brown eyes. How is this possible? 2) Can two blue eyed parents have a brown eyed child? Explain why or why not. Genetics: The study of heredity Heredity = the passing of traits from parents to offspring The Incredibles Heredity = the passing of traits from parents to offspring Trait = A feature or characteristic of a person Physical appearance Behavior tendencies Predisposed to medical conditions A person’s traits are influenced by: their genetic inheritance environmental factors What is a trait? Where are these traits located? DNA! The DNA “carries” the traits that make you who you are! Trait = a feature or characteristic of a person Physical appearance Genetics: Environment: hair color hair texture eye color face shape smile shape Trait = a feature or characteristic of a person Physical appearance Genetics: genes determine natural hair color Environment: hair color hair texture eye color face shape smile shape Trait = a feature or characteristic of a person Physical appearance Genetics: genes determine natural hair color Environment: sun or hair dyes change hair color hair color hair texture eye color face shape smile shape Trait = a feature or characteristic of a person Behavior tendencies Genetics: Environment: Trait = a feature or characteristic of a person Behavior tendencies Genetics: genes determine the tendency to use a certain hand Environment: Trait = a feature or characteristic of a person Behavior tendencies Genetics: genes determine the tendency to use a certain hand Environment: can learn to use the opposite hand Trait = a feature or characteristic of a person Predisposed to medical conditions Genetics: Environment: Trait = a feature or characteristic of a person Predisposed to medical conditions Genetics: genes determine a risk of heart disease Environment: Trait = a feature or characteristic of a person Predisposed to medical conditions Genetics: genes determine a risk of heart disease Environment: eating healthy foods and exercising can reduce risk Trait = a feature or characteristic of a person Phenotype = a person’s version of a trait “physical appearance” hair color: black hair texture: straight eye color: blue Practice List 3 genetic traits Dash has. List Dash’s phenotype for each trait. Trait = a feature or characteristic of a person Gene = part of a person’s DNA that influences a trait Eye color gene Face shape gene Hair color gene Gene = part of a person’s DNA that controls a trait Alleles= different versions of a gene Eye color gene: brown allele Eye color gene: blue allele Practice List 3 possible alleles for the hair color gene. Are there other possibilities for hair as well? Hair color gene Alleles = different versions of a gene Dominant Allele Represented by a capital letter Example: B for brown eyes Recessive allele Represented by a lowercase letter Example: b for blue eyes Alleles = different versions of a gene All people have 2 alleles for every gene (one from each parent) Allele of eye color gene from dad Allele of eye color gene from mom Alleles = different versions of a gene All people have 2 alleles for every gene (one from each parent) Genotype = a person’s combination of alleles “genetic makeup” Allele of eye color gene from dad Allele of eye color gene from mom Genotype = a person’s combination of alleles A person may inherit 2 of the same alleles = purebred 2 dominant alleles = purebred dominant Example: B and B Genotype = Phenotype = Mom Dad E E Child Genotype = a person’s combination of alleles A person may inherit 2 of the same alleles = purebred 2 dominant alleles = purebred dominant Example: B and B Genotype = BB Phenotype = Mom Dad E E Child Genotype = a person’s combination of alleles A person may inherit 2 of the same alleles = purebred 2 dominant alleles = purebred dominant Example: B and B Mom Genotype = BB Phenotype = brown eyes E Child Dad E Genotype = a person’s combination of alleles A person may inherit 2 of the same alleles = purebred 2 recessive alleles = Mom Dad e e Child Genotype = a person’s combination of alleles A person may inherit 2 of the same alleles = purebred 2 recessive alleles = purebred recessive Example: b and b Genotype = Phenotype = Mom Dad e e Child Genotype = a person’s combination of alleles A person may inherit 2 of the same alleles = purebred 2 recessive alleles = purebred recessive Example: b and b Genotype = bb Phenotype = Mom Dad e e Child Genotype = a person’s combination of alleles A person may inherit 2 of the same alleles = purebred 2 recessive alleles = purebred recessive Example: b and b Genotype = bb Phenotype = blue eyes Mom Dad e e Child Alleles = different versions of a gene A person may inherit 2 different alleles = hybrid Dominant allele masks recessive allele Example: B and b Genotype = Mom Dad E e Child Phenotype = -or- Mom Dad e E Child Alleles = different versions of a gene A person may inherit 2 different alleles = hybrid Dominant allele masks recessive allele Example: B and b Genotype = Bb Mom Dad E e Child Phenotype = -or- Mom Dad e E Child Alleles = different versions of a gene A person may inherit 2 different alleles = hybrid Dominant allele masks recessive allele Example: B and b Genotype = Bb Mom Dad E e Child Phenotype = brown eyes -or- Mom Dad e E Child Practice Brown hair (B) is dominant to blond hair (b). Genotype purebred dominant purebred recessive hybrid Phenotype Practice Brown hair (B) is dominant to blond hair (b). Genotype purebred dominant purebred recessive hybrid BB Phenotype Brown hair Practice Brown hair (B) is dominant to blonde hair (b). Genotype Phenotype purebred dominant BB Brown hair purebred recessive bb Blond hair hybrid Practice Brown hair (B) is dominant to blond hair (b). Genotype Phenotype purebred dominant BB Brown hair purebred recessive bb Blond hair hybrid Bb Brown hair Which genotypes are purebred? Which is hybrid? Practice Right-handedness (R) is dominant to left-handedness (r). What genotype(s) could a right-handed person have? RR or Rr What genotype(s) could a left-handed person have? rr Practice In pea plants, green peas (G) are dominant to yellow peas (g). What would be the genotype of a: -purebred green pea? GG -hybrid green pea? Gg -yellow pea? gg Hands on Practice: Make sure you have a Punnet square worksheet Step 1: Identify the parent genotypes Homozygous (2 of the same) dominant – RED – capital R Homozygous recessive – WHITE – lower case r Hands on Practice Step 2 – place the parents genotypes in place to be crossed R = red r = white Hands on Practice Step 3 – combine the genotypes for each box R = red r = white Hands on Practice Step 4 – write the Write out the genotypes and phenotypes for all offspring Hands on Practice Genotypes: 25% homozygous dominant (RR), 50% heterozygous (Rr), 25% homozygous recessive (rr) Phenotypes: 75% Red flowers and 25% white flowers Hands on Practice Check point question: Could you ever have pink flowers?