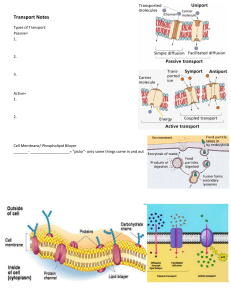
NAME_______________ DATE Composition of the Cell Membrane and Functions The cell membrane is also called the ____________ membrane and is made of a phospholipid____________ .The phospholipids have a hydrophilic (water attracting) ____________and two hydrophobic (water repelling) ____________ . The head of a phospholipid is made of an alcohol and a ____________group, while the tails are chains of ____________. Phospholipids can move ___________ and allow water and other ___________ molecules to pass through into or out of the cell. This is known as simple ____________ because it does not require _____________ and the water or molecules are moving____________ the concentration gradient. Another type of lipid in the cell membrane is _CHOLESTERAL that makes nym?rane more fluid. Embedded in the phospholipid bilayer OTEINS_ that also aid in diffusion and in cell recognition. Proteins called _INTEGRAL_ proteins go all the way thFöüUh¯fhe bilayer, while _PERIPHERAL_ proteins are only on one side. Integral proteins are also called _CHANNEL_ proteins. Large molecules like _LIPIDS_ or carbohydrates use proteins to help move across cell membranes. Some of the membrane proteins have carbohydrate _RECEPTORS_ attached to help cells in recognize each other and certain molecules. List 4 functions of the cell or plasma membrane: a. b. c. Cell membranes help organisms maintain homeostasis by controlling what substances may enter or leave cells _exchange materials such as food, water, & wastes with its environment _water, oxygen, & carbon dioxide can move in and out freely 1 d. is semi-permeable or selectively permeable only allowing certain molecules to pass through Correctly color code and identify the name for each part of the cell membrane. Letter Name/Color Phospholipid bilayer Letter Name/Color Peripheral protein (red) Integral protein (pink) Fatty acid tails (orange) Phosphate heads (yellow) Cholesterol (blue) Glycoprotein (green) Glycolipids (purple) C E 2 Match the cell membrane structure or its function with the correct letter from the cell membrane diagram. Letter Structure/Function Letter Structure/Function Attracts water Helps maintain flexibility of membrane Repels water Make up the bilayer Involved in cell-to-cell Help transport certain materials across the cell recognition membrane Osmosis and Tonicity Define osmosis. _MOVEMENT OF WATER DOWN CONCENTRATION GRADIENT_ In which direction does water move across membranes, up or down the concentration gradient? _________________ Define these 3 terms: a. isotonic b. Hypertonic c. hypotonic 3 Use arrows to show the direction of water movement into or out of each cell. WATER WATER 100% Match the description or picture with the osmotic condition: Isotonic C solution with a lower solute concentration A solution in which the solute concentration is the same A condition plant cells require A condition that animal cells require When a red blood cell bursts (cytolysis). When a plant cell loses turgor pressure (Plasmolysis) A solution with a higher solute concentration A plant cell with good turgor pressure A solution with a high water concentration 4 Label the tonicity for each solution (isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic): H20 H20 HYPO rso HYPER H20 H20 HYPO Hypo Hypn Transport Requiring Energy What type of transport is represented by the following picture? ACTIVE What energy is being used? ATP In which direction (concentration gradient), is the movement occurring? AGAINST(UP) Color the internal environment of the cell yellow. Color and Label the transport proteins red and the substance being moved blue. OUTSIDE CELL One type of active transport is called the _Na/K pump which helps muscle cells contract. This pump uses _ENERGY to move ions UP the concentration gradient. The protein that is used to pump the ions through is called a CARRIER protein and it changes its SHAPE to move the ions across the cell membrane. Label and color the carrier proteins red and the ions green. 6