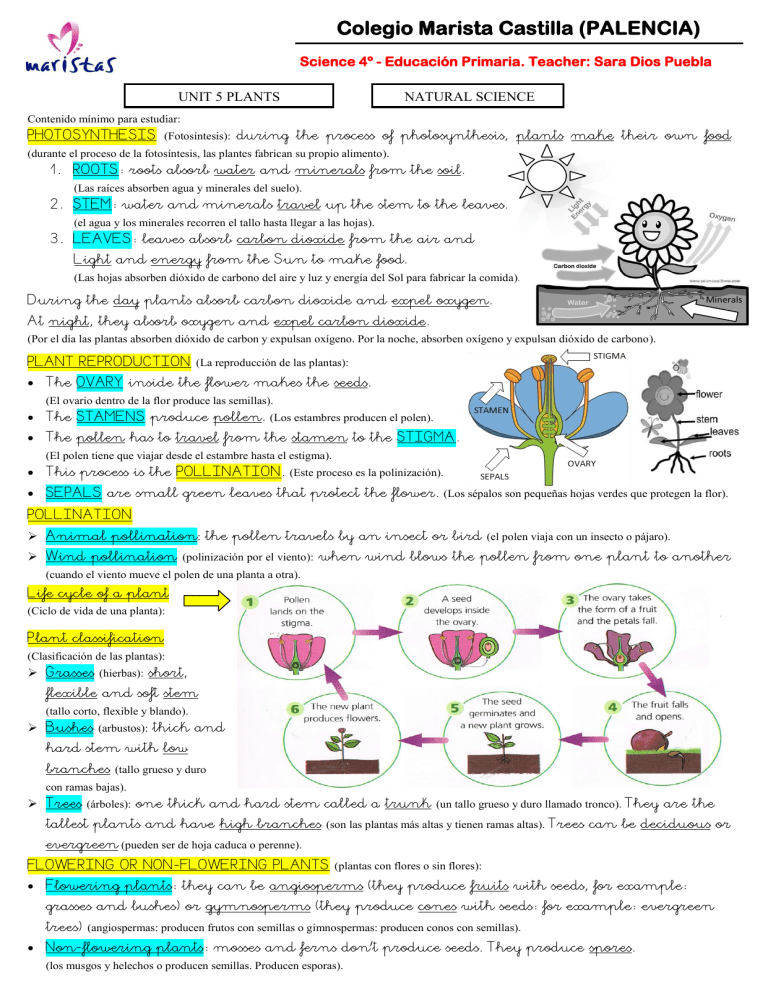
Colegio Marista Castilla (PALENCIA) Science 4º - Educación Primaria. Teacher: Sara Dios Puebla UNIT 5 PLANTS NATURAL SCIENCE Contenido mínimo para estudiar: PHOTOSYNTHESIS (Fotosíntesis): during the process of photosynthesis, plants make their own food (durante el proceso de la fotosíntesis, las plantes fabrican su propio alimento). 1. ROOTS: roots absorb water and minerals from the soil. (Las raíces absorben agua y minerales del suelo). 2. STEM: water and minerals travel up the stem to the leaves. (el agua y los minerales recorren el tallo hasta llegar a las hojas). 3. LEAVES: leaves absorb carbon dioxide from the air and Light and energy from the Sun to make food. (Las hojas absorben dióxido de carbono del aire y luz y energía del Sol para fabricar la comida). During the day plants absorb carbon dioxide and expel oxygen. Minerals At night, they absorb oxygen and expel carbon dioxide. (Por el día las plantas absorben dióxido de carbon y expulsan oxígeno. Por la noche, absorben oxígeno y expulsan dióxido de carbono). PLANT REPRODUCTION (La reproducción de las plantas): The OVARY inside the flower makes the seeds. (El ovario dentro de la flor produce las semillas). The STAMENS produce pollen. (Los estambres producen el polen). The pollen has to travel from the stamen to the STIGMA. (El polen tiene que viajar desde el estambre hasta el estigma). This process is the POLLINATION. (Este proceso es la polinización). SEPALS are small green leaves that protect the flower. (Los sépalos son pequeñas hojas verdes que protegen la flor). POLLINATION Animal pollination: the pollen travels by an insect or bird (el polen viaja con un insecto o pájaro). Wind pollination (polinización por el viento): when wind blows the pollen from one plant to another (cuando el viento mueve el polen de una planta a otra). Life cycle of a plant (Ciclo de vida de una planta): Plant classification (Clasificación de las plantas): Grasses (hierbas): short, flexible and soft stem (tallo corto, flexible y blando). Bushes (arbustos): thick and hard stem with low branches (tallo grueso y duro con ramas bajas). Trees (árboles): one thick and hard stem called a trunk (un tallo grueso y duro llamado tronco). They are the tallest plants and have high branches (son las plantas más altas y tienen ramas altas). Trees can be deciduous or evergreen (pueden ser de hoja caduca o perenne). FLOWERING OR NON-FLOWERING PLANTS (plantas con flores o sin flores): Flowering plants: they can be angiosperms (they produce fruits with seeds, for example: grasses and bushes) or gymnosperms (they produce cones with seeds: for example: evergreen trees) (angiospermas: producen frutos con semillas o gimnospermas: producen conos con semillas). Non-flowering plants: mosses and ferns don’t produce seeds. They produce spores. (los musgos y helechos o producen semillas. Producen esporas).