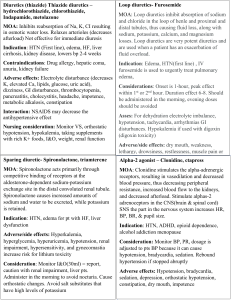
History of Present Illness 81F with HTN, hyperlidemia, p.Afib, h/o V Tach s/p ICD in 2004, COPD Increased SOB, exertional dyspnea for 3 days. PND + Orthopnea + Pedal edema + Denied CP/lightheadedness/palpitation Denied fever/cough Been compliant with her meds. Past History Medical Surgical HTN Right hip replacement Hyperlipidemia Appendectomy Paroxysmal A Fib Partial hysterectomy H/o Vtach s/p ICD Cataract surgery Chronic HF COPD Mild pulmonary HTN Family / Social History FH No premature CAD SH Denied smoking / ETOH Lives with husband Sedentary lifestyle Allergies/Meds Meds Amiodarone ASA EC 81 mg daily Toprol XL 100 mg daily Cozaar 100 mg daily Lasix 80 mg daily Lipitor 20 mg daily K-Dur 20 mEq daily Fosamax, Inspira, Lexapro Allergies Sulfa Allergies/Meds Meds ASA EC 325 mg daily Toprol XL 100 mg daily Monopril 20 mg bid Norvasc 5 mg daily Lasix 100 mg daily Lipitor 10 mg daily Clonidine 0.2 mg bid Cardura 4 mg daily Avodart 0.5 mg daily Lantus 18 units daily Humulog SS Synthroid Sulfa Allergies Physical Examination Vitals: BT 37 RS: BP 98/70 R 30 P 66, regular SpO2 77% on RA GA: Decreased bs lung bases Scattered crackles CVS: JVD + 7 cm, AAOx3, tachypneic Regular S1 S2, no S3/S4 Talks in broken sentences SEM LPSB 2/6 HEENT: Mildly pale, anicteric sclera Dry oral mucosa. No thyroid enlargement Abd: BS+, soft, non-tender Ext: pedal edema 1+ Differential Diagnosis Cardiogenic pulmonary edema Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema COPD exacerbation Pneumonia Pulmonary embolism MI Investigation BUN/Cr CBC 32/1.6 WBC 15.7 Ca / Mg Hb/Hct 12.1/35.5 LFT - NL except TB 1.7 Plt 227 CIP CK /CKMB Chemistry 9.2 / 1.9 124/3.3 Trop I Na 138 K 4 ABG Cl 98 7.47 I 34 I 107 I 24 BNP > 3900 HCO3 26 2.2 Investigation Chest x-ray Cardiomegaly and pulmonary edema EKG SR with 1st deg AV block 78 bpm New non specific ST-T changes in inferior and lateral leads Echocardiogram EF 30% Pseudonormal pattern of LV diastolic filling Multiple segmental abnormalities (akinetic apex; hypokinetic mid posterior, lateral, septum, anterior, inferior segments.) Mild TR Mild pulm HTN Mildly dilated left atrium Diagnosis Acute decompensation of chronic HF Pulmary edema NSTEMI Definition Clinical syndrome in which patients have: Signs breathlessness, fatique, ankle swelling, etc. Symptoms tachycardia, tachypnea, rales, edema, etc. Objective evidence of structural / functional abn of heart Cardiomegaly, murmur, abn echo, raised BNP Acute Heart Failure Rapid onset of s/s of HF, resulting in the need for urgent therapy Signs and Symptoms Prior h/o heart failure or myocardial injury Dyspnea on exertion Orthopnea PND Fatique Increased edema / weight / abd. girth Elevated JVD Rales / hypoxia / tachypnea Diffuse PMI Tachycardia / arrhythmia Ventricular filling / atrial gallop (S3, S4) Peripheral edema / ascites Decreased urine output Clinical Classification Diagnosis EKG CXR Labs: CBC BMP LFT INR CIP BNP ABG Echo Various Therapies Oxygen Class 1, evidence C Keep sat >95% (or >90% in COPD pts) Non-Invasive Ventilation Class 2a, evidence B NIV with PEEP improves LV fn by reducing LV afterload. Indication: Acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema Hypertensive AHF Key points: Meta-analyses showed it reduces intubation and short term mortality. Caution in cardiogenic shock and RV failure How to use it? FiO2 0.4; PEEP 5-7.5 titrate to clinical response up to 10. Morphine Evidence for AHF is limited. Should be considered esp. in pts with Restlessness, anxiety, CP IV boluses of morphine 2.5-5 mg Caution in Hypotension Bradycardia Advanced AV block CO2 retention Loop Diuretics Class 1, evidence B Recommended in presence of symptoms secondary to congestion and volume overload Patients who are unlikely to respond to diuretics: Hypotension SBP < 90 Severe hyponatremia Severe acidosis Vasodilators Class 1, evidence B Recommended at early stage in patients who do not have: Symptomatic hypotension SBP < 90 Serious obstructive valvular ds. Key points: Decreases L,R heart filling pressure Decreases SVR Relieves pulm congestion without compromising SV / O2 demand Vasopressors Indicated only in Cardiogenic Shock after failure of inotropes + fluid challenge Vasopressor of choice : NOREPINEPHRINE (2b, C) Inotropes Use in pts with (Class 2a, evidence B) low output states Signs of hypoperfusion Congestion despite use of vasodilators and/or diuretics Key points Withdraw asap (inc oxygen demand) Increase incidence of arrhythmias Dobutamine Milrinone / enoximone Dopamine Levosimendan 2b, B 2b, B 2b, C 2a, B Cardiac glycosides Maybe useful to slow ventricular rate in AF. Produces small increase in cardiac output and reduction in filling pressure. 2b, C C Specific Treatment Strategies Decompensated chronic HF: Vasodilator + diuretics Pulmonary Edema MO + Vasodilators + Diuretics + Inotropes Hypertensive HF Vasodilator + diuretics Cardiogenic Shock Fluid challenge (250 cc in 10 min) + inotropes + norepinephrine + IABP Right HF Avoid MV; Suspect PE / RV MI Fluid challenge + inotropes AHF and ACS Early reperfusion BB / ACEI / ARB If already on ACEI/ARB -> continue If not -> start before discharge BB maybe interrupted / reduced if Unstable with low output Severe AHF Bradycardia, adv AV block, cardiogenic shock Initiate BB before discharge, after pt stabilized on ACEI / ARB. Hospital Course Started on: Dobutamine drip Lasix IV Nitropaste 9/25 -> Clinically improved. Plan to: Restart ARB Restart BB Cardiac cath