TEACHERS GUIDE
Participation in Government
The Mount Academy
Unit One: Foundations of American Government
Student Name:
Section:
Working Relentlessly to Ensure that 100% of Students will Graduate in June, 2020!
September 2, 2019
WELCOME BACK
Students,
It is my sincere honor and privilege to be your teacher for Participation in
Government and Economics this year. It is hard to imagine, and beyond exciting to think about the fact that all of you are Seniors in High School. College applications, scholarships and Graduation are right around the corner. I am here to not only help you succeed academically, but to make sure you have as enjoyable a year as possible. Should you ever need anything, I am always available. My contact information is at the end of this letter. This will be the third year I am having some of you, and the second year for the others. I am looking forward to continuing to build our relationships both in and outside the classroom.
We will be doing work every day in this class- from September through June.
There will be no excuses, and you are expected to be in class every day both physically and mentally. Participation will be of the utmost importance as this class will be very focused on discussion of current and past political events.
You are taking this class at the best time- a Presidential Election year. The next few months will truly define our countries history, and I am excited to work through all of the excitement with all of you!
Please fill out the Student Survey on the following page. These surveys allow me to better get to know you, and allow you to let me know how I can most assist you this year, as well as your own goals for the coming ten months. The Parent/Guardian Survey should be returned to me by Friday, September 5 th .
You will receive points toward your grade for the completion of both.
Looking forward to spending this year with all of you,
September 3, 2019
2
World’s Smallest Political Quiz
3
September 4, 2019
Objective: SWBAT define government and describe the basic powers every government holds.
Do Now: (3 min)
Think about your daily life- list at least five things that the government provides for you:
1.
School
2.
Metro Cards
3.
Reduced lunch
4.
Public housing
5.
Fire/Police men
Vocabulary: (8 min)
1. Government: the institution through which society makes and enforces laws and policies
2. Democracy: a form of government where the supreme power rests with the people
(US)
3. State: a body of people, living in a defined territory with the power to make and enforce laws without permission from a higher authority
4. Public Policy: the things that a government decides to do, ranging from education to health care to transportation
Recall: The United States Government is broken up into three branches- describe what each branch does and who/what makes up the Branch:
1. Executive:
2. Legislative:
3. Judicial:
The Purpose of Government
“We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish
Justice, insure domestic tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote the general welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America.” –Preamble to the
Constitution
1. According to the Preamble, name three things that the Government is responsible for
(in your own words)
4
Representative Barbara Jordan: Rep. Jordan was the first African American women to be elected to the Texas Legislature. She spoke at the 1976 Democratic National
Convention and said the following:
“A nation is formed by the willingness of each of us to share in the responsibility for upholding the public good. A government is invigorated when each of us is willing to participate in shaping the future of this nation. Let each person do his or her own part. If one citizen is unwilling to participate, all of us are going to suffer. For the American idea, though it is shared by all of us, is realized in each one of us.”
1. How do Jordan’s expectations for Americans relate to the basic ideas that underline our democracy?
2. Do you agree or disagree with her statement? Why or why not?
Daily Assessment:
1. What is the difference between a government and a state?
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
2. Who holds the power in a dictatorship? How is this different or similar to who holds the power in a democracy?
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
3. What is the purpose of a Constitution?
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
5
September 5, 2019
Objective: SWBAT identify the various forms of government
Vocabulary:
1. Autocracy: one single person holds unlimited political power
2. Oligarchy: a government where the power to rule is held by a small, usually self appointed elite group
3. Federal Government: a government where the power is divided between a central government and local governments
4. Free Enterprise system: private ownership and decisions v. government decisions
5. Mixed Economy: Free Enterprise + government participation to protect the public
What makes something a Free Enterprise System?
1. Private Ownership
2. Individual Initiative
3. Profit
4. Competition
Direct Democracy v. Representative Democracy
1. Direct Democracy: every citizen or member of a specific group gets to vote for laws
2. Representative Democracy: citizens elect representatives to vote for them (US)
Quote Analysis:
“The legitimate object of government, is to do for a community of people, whatever they need to have done, but can not do, at all, or can not, so well do, for themselves- in their separate, and individual capacities”- Abraham Lincoln, 1854
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
6
How does the political cartoon above show the idea of an oligarchial government?
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
Think, Pair, Share
Prompt: “Many people have suggested using the Internet to create a direct democracy in the United States where every citizen could vote.”
Think : Take five minutes to write down your opinion and thoughts silently and independently:
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
Pair : Select a partner who is sitting near you. You will each have two minutes to share your thoughts on the prompts.
Share: We will then have a class discussion
7
September 8, 2019
Objective: SWBAT explain the six basic principles of the Constitution
The Constitution: The Constitution is a brief, straightforward document that had guided
American government for over 200 years. Its authors wrote the Constitution based on the principles that political power resides with the people, and that the National Government should be limited and divided into three branches to limit of the power of any one of those three branches.
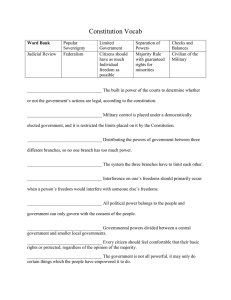
Six Basic Principles:
1. Popular sovereignty
“all political rests with the people”
The National Government gets its power from the people
2. Limited Government
A government can only do the things the people have given it power to do
3. Separation of Powers
Power is divided between the three branches- Executive, Legislative and Judicial
4. Checks and Balances
Each of the three branches can “check” the power of the other two branches
5. Judicial Review
The ability for the Courts to declare laws unconstitutional
Example of Checks and Balances
6. Federalism
The division of power between the National and state governments
Checks and Balances…A Closer Look: For the following examples, I want you to say which branch is checking which branch.
Example: The President can veto a law
Answer: Executive checks Legislative
1. Courts can declare laws Unconstitutional
2. Congress can remove Judges
3. The Senate appoints/rejects Judicial nominees
4. Congress can override a Presidential veto
5. Congress can impeach a President
6. The President appoints Supreme Court Judges who serve a life sentence
7. Congress can create lower Courts
8
8. The President can pardon someone who has been convicted of a crime
9. The Senate can reject presidential nominations of federal officials
10. The President submits the Federal Budget to the Congress
11.
What do you think…
Some people consider the Judicial Branch to be the least democratic of the three branches of government because federal judges are not elected and cannot be easily removed. How can voters and their elected representatives check the power of the judicial branch?
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
9
September 9, 2019
Objective: SWBAT describe main way the Constitution can be formally changed/amended
SWBAT identify at least five of the 27 amendments that have been added to the
Constitution
Vocabulary:
1. Amendment: a change or addition to the Constitution
2. Bill of Rights: the first ten amendments to the Constitution that protect individual freedoms and rights
How 26 of the 27 Amendments Came to Be:
1. An amendment is proposed by a 2/3 vote in the House and Senate
2. It is then ratified (passed) by ¾ of the States
Recall: We discussed many of the most significant amendments to the Constitution last year. Before we go over some of them, and then discuss new ones, let’s see what you remember. Write down what you recall about each of the following amendments.
1 st
: freedom of speech, press and religion
2 nd : right to bear arms
5 th
: right to remain silent
13 th
: freed the slaves
14 th
: made former slaves citizens
15 th
: voting rights- male, citizen, 21+
19 th
: women suffrage
22 nd
: limit on Presidential terms
27 th : Congress cannot pass laws increasing their own salary
Two Ways to Look at the Constitution:
1. Original Intent- think about what the original writers were thinking
2. Living Constitution- time changes, and the Constitution should be read in a different way
Evaluate the Quotes:
“This provision is made in a Constitution, intended to endure for ages to come, and consequently, to be adapted to the various crises of human affairs.” – John Marshall,
Chief Justice of the Supreme Court
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
10
“I would look for justices of the Supreme Court who understand that our Constitution is a living and breathing document, that it was intended by our founders to be interpreted in the light of the constantly evolving experience of the American people.”- Al Gore, 2000
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
“There’s the argument of flexibility and it goes something like this: The Constitution is over 200 years old and societies change. It has to change with society, like a living organism, or it will become brittle and break. But you would have to be an idiot to believe that; the Constitution is not a living organism; it is a legal document. It says something and doesn't say other things . . . [Proponents of the living constitution want matters to be decided] not by the people, but by the justices of the Supreme Court . . .
They are not looking for legal flexibility, they are looking for rigidity, whether it's the right to abortion or the right to homosexual activity, they want that right to be embedded from coast to coast and to be unchangeable” –Justice Scalia, US Supreme Court
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
Mini Quiz:
1. The Bill of Rights was added to the United States Constitution to
1. provide the president with the power to enforce the laws
2. protect individuals' civil liberties
3. establish a presidential cabinet
4. guarantee voting privileges to all citizens
2. The major reason the Bill of Rights was added to the United States Constitution was to
1. limit the power of state governments
2. protect individual liberties against abuse by the federal government
3. provide for equal treatment of all people
4. separate powers between the three branches of government
3. The adoption of the Bill of Rights (1791) addressed Antifederalist criticism of the new Constitution by
1. providing for an indirect method of electing the president
2. protecting citizens from abuses of power by the national government
3. allowing the national government to coin money
4. establishing a process for impeaching federal officials
4. "The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the states, are reserved to the states respectively, or to the people."
--10th amendment
This part of the Bill of Rights was intended to
1. give the people the right to vote on important issues
2. assure the same rights to citizens of all states
3. limit the powers of the Federal Government
4. limit the power of the states over their citizens
11
September 10, 2019
Objective: SWBAT define federalism and explain why the Framers chose this system of government
Vocabulary:
1. Federalism: division of power between the national and state/local governments
2. Delegated powers: the powers granted to the National Government by the Constitution
Delegated Powers: There are three types of delegated powers:
1. Expressed Powers
Powers that are spelled out in the Constitution
Examples: raise an army, grant patents, collect taxes
2. Implied Powers:
Powers that are suggested by the Constitution
Examples: building highways, ending discrimination in public places
3. Inherent Powers:
Powers that the National Government are presumed to have
Examples: immigration
Voices on Government:
“The Founding Fathers divided power between the federal government and the states.
The constitutional principle of federalism- embodied in the Tenth Amendment- raises two fundamental questions that policy makers should answer: What should government be doing? And what level of government should do it? Everything flows from them.
That’s why federalism is at the heart of democracy.” o Senator Fred Thompson (Republican, Tennessee)
First, put Senator Thompson’s comments in your own words…what was he saying?
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
Secondly, use the above quote to answer the following question:
How do you think Senator Thompson would respond to the following statement: “State and local governments are often in a better position than the Federal Government to respond to the peoples concerns.”
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
12
Powers Reserved to the States:
The 10 th
Amendment gives the States the power to create and enforce laws that are not specifically given to the National Government in the Constitution
Examples :
1. Cannot sell alcohol to people under 21
2. Those under 18 cannot get married without parental permission
Concurrent Powers: These are powers that the state and National Government both hold
Examples:
1. Collect taxes (you pay state and federal taxes)
2. Establish courts (state courts and federal courts)
Mini Quiz:
1. Federalism is best described as the
1. authority to make and enforce decisions based on a written constitution
2. difference in the function of the public and private sectors of the economy
3. divisions of power between a national government and state governments
4. use of checks and balances between the three branches of government
2. Which statement is an example of the system of federalism?
1. Cabinet members are appointed by the president.
2. Revenue bills must begin in the House of Representatives.
3. The national government coins money, but states cannot.
4. The president can negotiate treaties, but the Senate has the power to ratify them.
3. Federalism is a term used to define the division of power between the
1. president and the vice president
2. Senate and the House of Representatives
3. national and state levels of government
4. three branches of the federal government
4. The principle of federalism contained in the Constitution of the United States is most consistent with the idea of Speaker (Circle your answer)
Speaker A:
A leader is not ultimately responsible to the people but to God, from whom the leader derives the right to govern.
Speaker B:
Each citizen is entitled to a voice in government. Therefore, government should be run by those representatives elected directly by the citizens so that the will of the citizens is expressed.
Speaker C:
History has taught us that the concentration of political power leads to the abuse of that power. Therefore, power should be divided among national, state, and local governments.
13
September 11, 2019
STUDY GUIDE!
Make sure you can define the following terms:
1. Federalism:
2. Division of Powers:
3. Delegated Powers:
4. Expressed Powers:
5. Implied Powers:
6. Reserved Powers:
7. Concurrent Powers:
You will be asked to choose five of the following to answer tomorrow:
1. List five Constitutional Amendments and what they do (can be bullet points)
2. Name the three branches of government, and describe what each one does.
3. What are checks and balances? Give one example of checks and balances in action.
4. What is the difference between a Government and a State?
5. What makes something a “free enterprise system”? You must name at least three characteristics.
14
6. What is the difference between a direct and indirect democracy? Which is the United
States?
7. There are six basic principles of the Constitution- name and explain three.
Need anything while you are studying?
15