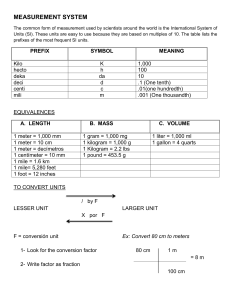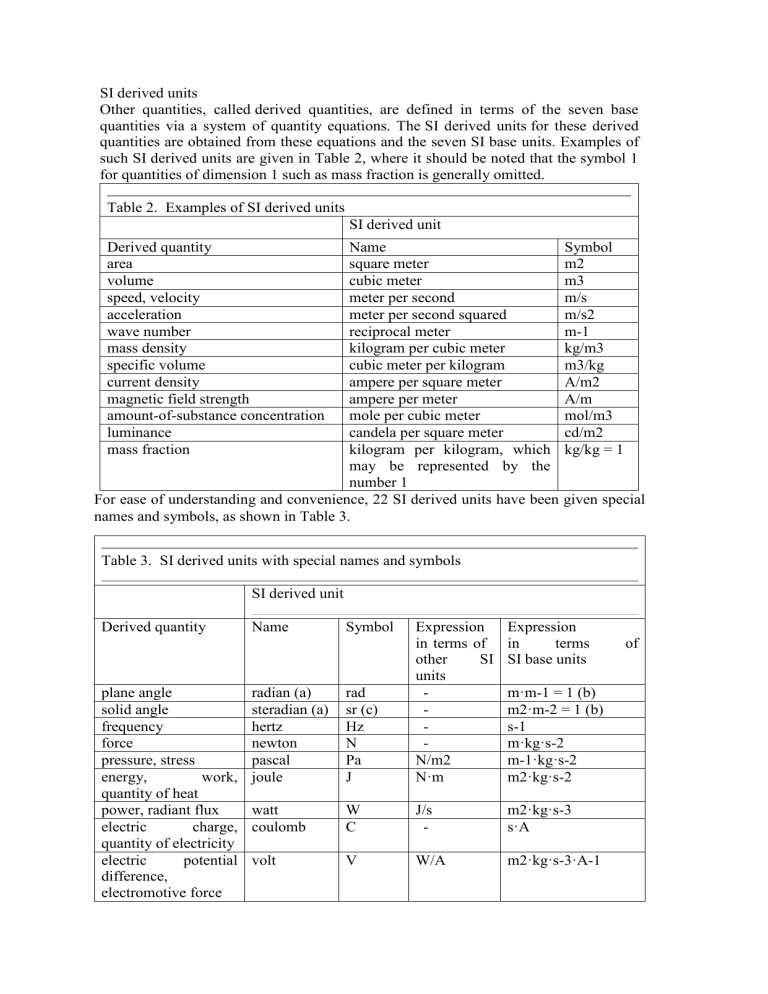
SI derived units Other quantities, called derived quantities, are defined in terms of the seven base quantities via a system of quantity equations. The SI derived units for these derived quantities are obtained from these equations and the seven SI base units. Examples of such SI derived units are given in Table 2, where it should be noted that the symbol 1 for quantities of dimension 1 such as mass fraction is generally omitted. Table 2. Examples of SI derived units SI derived unit Derived quantity area volume speed, velocity acceleration wave number mass density specific volume current density magnetic field strength amount-of-substance concentration luminance mass fraction Name Symbol square meter m2 cubic meter m3 meter per second m/s meter per second squared m/s2 reciprocal meter m-1 kilogram per cubic meter kg/m3 cubic meter per kilogram m3/kg ampere per square meter A/m2 ampere per meter A/m mole per cubic meter mol/m3 candela per square meter cd/m2 kilogram per kilogram, which kg/kg = 1 may be represented by the number 1 For ease of understanding and convenience, 22 SI derived units have been given special names and symbols, as shown in Table 3. Table 3. SI derived units with special names and symbols SI derived unit Derived quantity plane angle solid angle frequency force pressure, stress energy, work, quantity of heat power, radiant flux electric charge, quantity of electricity electric potential difference, electromotive force Name Symbol radian (a) steradian (a) hertz newton pascal joule rad sr (c) Hz N Pa J Expression in terms of other SI units N/m2 N·m Expression in terms SI base units watt coulomb W C J/s - m2·kg·s-3 s·A volt V W/A m2·kg·s-3·A-1 m·m-1 = 1 (b) m2·m-2 = 1 (b) s-1 m·kg·s-2 m-1·kg·s-2 m2·kg·s-2 of capacitance electric resistance electric conductance magnetic flux magnetic flux density inductance Celsius temperature farad ohm siemens weber tesla henry degree Celsius lumen lux a becquerel F S Wb T H °C C/V V/A A/V V·s Wb/m2 Wb/A - m-2·kg-1·s4·A2 m2·kg·s-3·A-2 m-2·kg-1·s3·A2 m2·kg·s-2·A-1 kg·s-2·A-1 m2·kg·s-2·A-2 K luminous flux illuminance activity (of radionuclide) absorbed dose, gray specific energy (imparted), kerma dose equivalent (d) sievert catalytic activity katal lm lx Bq cd·sr (c) lm/m2 - m2·m-2·cd = cd m2·m-4·cd = m-2·cd s-1 Gy J/kg m2·s-2 Sv kat J/kg m2·s-2 s-1·mol