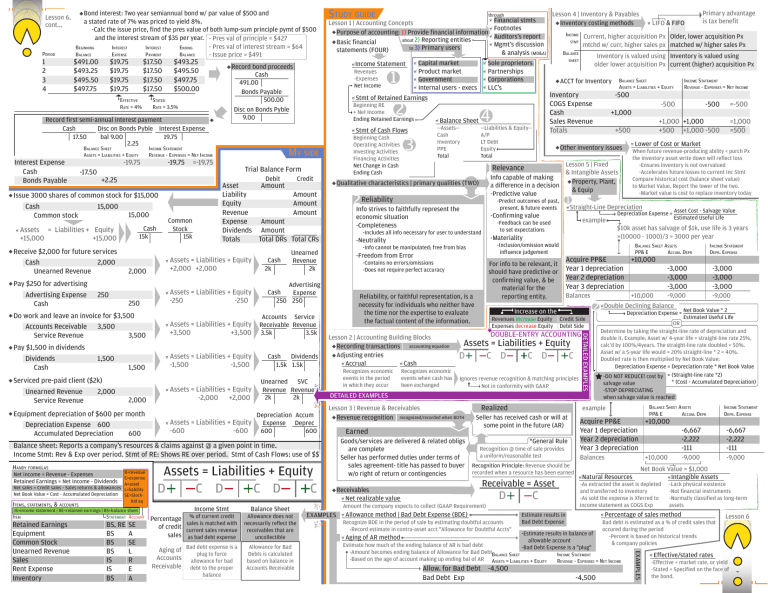
Lesson 6, cont... PERIOD 1 2 3 4 Bond interest: Two year semiannual bond w/ par value of $500 and a stated rate of 7% was priced to yield 8%. -Calc the issue price, find the pres value of both lump-sum principle pymt of $500 and the interest stream of $35 per year. - Pres val of principle = $427 - Pres val of interest stream = $64 BEGINNING INTEREST INTEREST ENDING EXPENSE PAYMENT BALANCE BALANCE - Issue price = $491 $491.00 $493.25 $495.50 $497.75 $19.75 $19.75 $19.75 $19.75 $17.50 $17.50 $17.50 $17.50 EFFECTIVE RATE = 4% $493.25 $495.50 $497.75 $500.00 STATED RATE = 3.5% Record first semi-annual interest payment Disc on Bonds Pyble Interest Expense Cash bal 9.00 19.75 17.50 2.25 BALANCE SHEET ASSETS = LIABILITIES + EQUITY Interest Expense Cash Bonds Payable -19.75 Issue 3000 shares of common stock for $15,000 15,000 Cash 15,000 Common stock Cash 15k Assets = Liabilities + Equity +15,000 +15,000 Pay $250 for advertising Advertising Expense Cash Common Stock 15k Asset Amount Liability Equity Revenue Expense Amount Dividends Amount Totals Total DRs Assets = Liabilities + Equity +2,000 +2,000 250 Assets = Liabilities + Equity -250 -250 Pay $1,500 in dividends Dividends Cash Assets = Liabilities + Equity -1,500 -1,500 1,500 2,000 Equipment depreciation of $600 per month Depreciation Expense 600 600 Accumulated Depreciation Assets = Liabilities + Equity -2,000 +2,000 Cash 2k Credit R=revenue E=expense A=asset Net sales = Credit sales - Sales returns & allowances L=liability Net Book Value = Cost - Accumulated Depreciation SE=Stockhld eq Net income = Revenue - Expenses Retained Earnings = Net Income - Dividends ITEMS, STATEMENTS, & ACCOUNTS IS=income statement | RE=retained earnings | BS=balance sheet -Freedom from Error Dividends Cash 1.5k 1.5k Unearned SVC Revenue Revenue 2k 2k Depreciation Accum Assets = Liabilities + Equity Expense Deprec 600 600 -600 -600 STATEMENT ACCOUNT Retained Earnings Equipment Common Stock Unearned Revenue Sales Rent Expense Inventory BS, RE BS BS BS IS IS BS SE A SE L R E A Aging of Bad debt expense is a plug to force Accounts allowance for bad Receivable debt to the proper balance Allowance for Bad Debts is calculated based on balance in Accounts Receivable Depreciation Expense = Asset Cost - Salvage Value Estimated Useful Life Acquire PP&E +10,000 Year 1 depreciation Year 2 depreciation Year 3 depreciation Balances 2 Increase on the Credit Side Debit Side Realized *General Rule Recognition @ time of sale provides a uniform/reasonable test Recognition Principle: Revenue should be recorded when a resource has been earned Receivable = Asset D C Allowance method | Bad Debt Expense (BDE) Recognize BDE in the period of sale by estimating doubtful accounts -Record estimate in contra-asset acct "Allowance for Doubtful Accts" -3,000 -3,000 -3,000 +10,000 -9,000 Double Declining Balance -9,000 Depreciation Expense = Net Book Value * 2 Estimated Useful Life OR Determine by taking the straight-line rate of depreciation and double it. Example: Asset w/ 4-year life = straight-line rate 25%, calc'd by 100%/4years. The straight-line rate doubled = 50%. Asset w/ a 5-year life would = 20% straight-line * 2 = 40%. Doubled rate is then multiplied by Net Book Value: Depreciation Expense = Depreciation rate * Net Book Value -DO NOT REDUCE! cost by = (Straight-line rate *2) * (Cost - Accumulated Depreciation) salvage value -STOP DEPRECIATING when salvage value is reached BALANCE SHEET ASSETS PP& E ACCUM. DEPR INCOME STATEMENT DEPR. EXPENSE Acquire PP&E +10,000 Year 1 depreciation Year 2 depreciation Year 3 depreciation -6,667 -2,222 -111 -6,667 -2,222 -111 Balances -9,000 -9,000 +10,000 Natural Resources Net Book Value = $1,000 Intangible Assets -As extracted the asset is depleted and transferred to inventory -As sold the expense is Xferred to income statement as COGS Exp -Lack physical existence -Not financial instruments -Normally classified as long-term assets Percentage of sales method Estimate results in Bad Debt Expense Bad debt is estimated as a % of credit sales that occured during the period -Percent is based on historical trends & company policies -Estimate results in balance of Aging of AR method allowable account Estimate how much of the ending balance of AR is bad debt -Bad Debt Expense is a "plug" -Amount becomes ending balance of Allowance for Bad DebtBALANCE SHEET INCOME STATEMENT -Based on the age of account making up ending bal of AR ASSETS = LIABILITIES + EQUITY REVENUE - EXPENSES = NET INCOME Allow. for Bad Debt -4,500 Bad Debt Exp INCOME STATEMENT DEPR. EXPENSE -3,000 -3,000 -3,000 example Seller has received cash or will at some point in the future (AR) Amount the company expects to collect (GAAP Requirement) EXAMPLES Lower of Cost or Market When future revenue-producing ability < purch Px the inventory asset write down will reflect loss -Ensures inventory is not overvalued -Accelerates future losses to current Inc Stmt Compare historical cost (balance sheet value) to Market Value. Report the lower of the two. -Market value is cost to replace inventory today BALANCE SHEET ASSETS PP& E ACCUM. DEPR DETAILED EXAMPLES Receivables Net realizable value =1,000 =500 $10k asset has salvage of $1k, use life is 3 years =(10000 - 1000)/3 = 3000 per year Ignores revenue recognition & matching principles Not in conformity with GAAP Goods/services are delivered & related obligs are complete Seller has performed duties under terms of sales agreement- title has passed to buyer w/o right of return or contingencies =-500 +1,000 +1,000 +500 +1,000 -500 +500 example DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING Earned -500 Straight-Line Depreciation Assets = Liabilities + Equity D C D C D C Lesson 3 | Revenue & Receivables Revenue recognition recognized/recorded when BOTH Assets = Liabilities + Equity D C D C D C Balance Sheet Income Stmt Allowance does not Percentage % of current credit sales is matched with necessarily reflect the of credit current sales revenue receivables that are sales as bad debt expense uncollectible Recognizes economic events when cash has been exchanged -500 +1,000 1 For info to be relevant, it should have predictive or confirming value, & be material for the reporting entity. Revenues increase Equity Expenses decrease Equity INCOME STATEMENT REVENUE - EXPENSES = NET INCOME -500 -Inclusion/omission would influence judgement Reliability, or faithful representation, is a necessity for individuals who neither have the time nor the expertise to evaluate the factual content of the information. Recognizes economic events in the period in which they occur BALANCE SHEET ASSETS = LIABILITIES + EQUITY Other inventory issues -Feedback can be used to set expectations -Contains no errors/omissions -Does not require perfect accuracy Lesson 2 | Accounting Building Blocks Recording transactions accounting equation Adjusting entries Accrual Cash Inventory COGS Expense Cash Sales Revenue Totals -Materiality -Info cannot be manipulated; free from bias Advertising Cash Expense 250 250 ACCT for Inventory -Confirming value -Includes all info necessary for user to understand Unearned Revenue 2k Inventory is valued using Inventory is valued using older lower acquisition Px current (higher) acquisition Px SHEET Lesson 5 | Fixed & Intangible Assets Property, Plant, a difference in a decision & Equip -Predictive value economic situation -Completeness -Neutrality BALANCE -Predict outcomes of past, present, & future events Primary advantage is tax benefit Current, higher acquisition Px Older, lower acquisition Px mtchd w/ curr, higher sales px matched w/ higher sales Px STMT Relevance 1Info capable of making 2InfoReliability strives to faithfully represent the Total CRs Accounts Service Receivable Revenue 3.5k 3.5k 4 --Liabilities & Equity-A/P LT Debt Equity Total LIFO & FIFO -4,500 EXAMPLES ITEM 3 Balance Sheet --Assets-Cash Inventory PPE Total Qualitative characteristics | primary qualities (TWO) Amount Amount Amount Balance sheet: Reports a company's resources & claims against @ a given point in time. Income Stmt: Rev & Exp over period. Stmt of RE: Shows RE over period. Stmt of Cash Flows: use of $$ HANDY FORMULAS Sole proprietors Partnerships Corporations LLC's Capital market Product market Government Internal users - execs INCOME DETAILED EXAMPLES Assets = Liabilities + Equity +3,500 +3,500 1,500 Beginning Cash Operating Activities Investing Activities Financing Activities Net Change in Cash Ending Cash Trial Balance Form Do work and leave an invoice for $3,500 Accounts Receivable 3,500 3,500 Service Revenue Serviced pre-paid client ($2k) Unearned Revenue 2,000 Service Revenue 2 MY SIDE =-19.75 Financial stmts Footnotes Auditors's report Mgmt's discussion & analysis (MD&A) Stmt of Retained Earnings Stmt of Cash Flows 2,000 250 1 Beginning RE + Net Income Ending Retained Earnings Debit +2.25 Receive $2,000 for future services Cash 2,000 Unearned Revenue Income Statement Revenues -Expenses Net Income Lesson 4 | Inventory & Payables Inventory costing methods through Lesson 1 | Accounting Concepts Purpose of accounting: 1) Provide financial information about 2) Reporting entities Basic financial to 3) Primary users statements (FOUR) Record bond proceeds Cash 491.00 Bonds Payable 500.00 Disc on Bonds Pyble 9.00 INCOME STATEMENT REVENUE - EXPENSES = NET INCOME -19.75 -17.50 STUDY GUIDE Lesson 6 Effective/stated rates -Effective = market rate, or yield -Stated = Specified on the face of the bond.


