7. A ___ consumer eats primary consumers.
13. Eagles, killer whales, lions and tigers are all examples of ___.
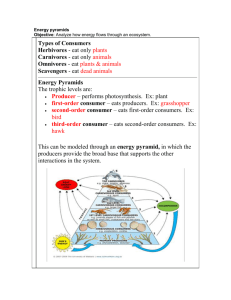
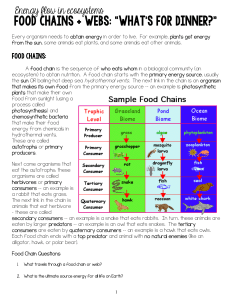
14. The ___ of an arrow in a food chain points toward the
organism doing the eating.
15. The bacteria in hydrothermal vents use the ___ found in the
vents to create energy.
17. These producers form the basis of most marine food chains.
21. Earthworms, fungi and bacteria are all examples of ___.
23. ___ are marine habitats that sunlight cannot reach.
25. This is the dry matter found in living things.
26. The chemical process that producers use to create their own
food from the energy of the Sun.
27. ___ in hydrothermal vents form the basis of vent food chains.
1. Organisms at the base of all food chains that make their own
food.
2. A ___ consumer eats tertiary consumers.
3. This is a sequence of feeding relationships showing what
organism eats another.
Name: ____________________________________
Date: _____________________________________
Across
FOOD CHAINS, TROPHIC
LEVELS
and ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS
Crossword Puzzle
Down
4. Rabbits, grasshoppers, squirrels, tadpoles and deer are all
examples of ___.
5. This is the position that an organism occupies in a food chain.
6. An organism that breaks down detritus and forms nutrients.
8. These are substances needed by organisms for growth and
repair.
9. This is the waste matter and remains of once living organisms.
10. Organisms that cannot make their own food so they must
consume other living things for food.
11. Only ___% of energy is transferred from one trophic level to
the next.
12. A ___ consumer eats secondary consumers.
14. A consumer that is not hunted by anything else for food.
16. A ___ consumer eats producers.
18. This is the ultimate source of all energy for most food chains.
19. ___% of energy is lost during the transfer from one
trophic level to the next.
20. A pyramid of ___ represents trophic levels in terms of the
population of organisms at each trophic level.
22. This is a group of interconnected food chains.
24. A pyramid of ___ always decreases in size as you move up
trophic levels