---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Electromagnetism
•
Produced by electric charges. Force between particles or charged objects
•
Electricity and magnetism together form the electromagnetic force and are one of the fundamental forces in nature
•
There is a force called a weak force) a force that works during the dissolution of beta in
nuclear decay
•
Strong force found inside the nucleus of the atom to hold the components of the nucleus
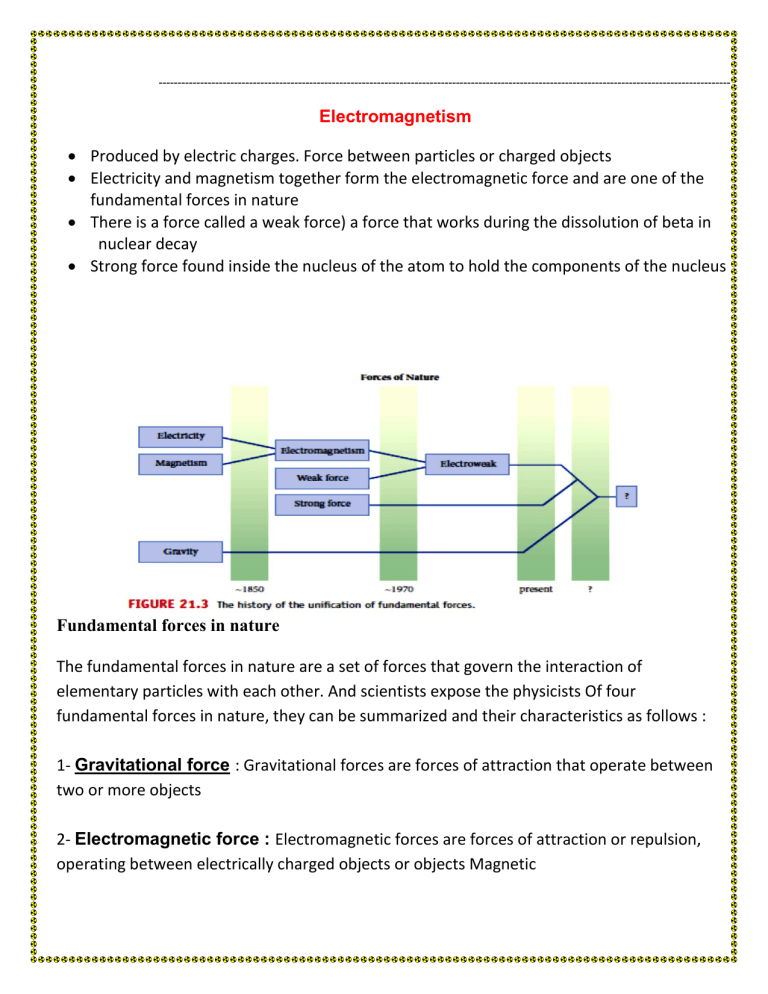
Fundamental forces in nature
The fundamental forces in nature are a set of forces that govern the interaction of elementary particles with each other. And scientists expose the physicists Of four fundamental forces in nature, they can be summarized and their characteristics as follows :
1- Gravitational force : Gravitational forces are forces of attraction that operate between two or more objects
2- Electromagnetic force : Electromagnetic forces are forces of attraction or repulsion, operating between electrically charged objects or objects Magnetic
3- Extreme nuclear force : Forces within the atomic nucleus. It works to coherent its components and overcome the electrical repulsion force between protons The secret of its success in keeping protons together in the nucleus of an atom is due to the fact that they are stronger than electromagnetic force
4- Weak nuclear force : This force is responsible for the radioactivity associated with decomposition of subatomic bodies
2.1 Electric charge
•
Electric charge is the physical property of matter.
•
There are two types of electric charge: positive and negative (commonly carried by protons and electrons respectively).
Symbol of charge ( q )
The unit of electric charge is the coulomb ( C).
1C= A s
One coulomb is an extremely large unit of charge
Elementary charge(e) : the charge on a single electron is 1.602×10 -19 C. (The magnitude of the charge of an electron)
q e
= - e (q e
: electron charge)
Proton :- ( another basic particle of atoms )
The same magnitude of electron but it’s positive charge ( q p
= +e)
A proton is composed of two up quarks (each with charge ( +2/3 e) and one down quark with charge ( – 1/3 e) To be a proton charge
-The electrically neutral neutron (hence the name!) is composed of an up quark and two down quarks, To be a neutron charge the charge, q , of any object can be expressed in terms of the sum of the number of protons,
N p
, minus the sum of the number of electrons, N e
, that make up the object q= e(N p
-N e
)
1 How many electrons in 1.00 C of charge :
2What is the number of electrons traveling from electroscope charged with positivecharge if its net charge equal 7.5 × 10 -11 C :
3 What is the charge of an electroscope if the number electrons Surplus it 4.8 × 10 8 e
4- How many electrons must be removed from a neutral object to leave a net charge of
0.500 µC?
Example (1.1)
If we wanted a block of iron of mass 3.25 kg to acquire a positive charge of 0.100 C, what fraction of the electrons would we have to remove?



