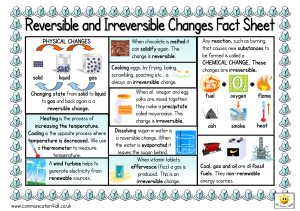
A physical property of matter is one that can be observed without changing its composition. Gold is a shiny yellow metal. Lead has a high density. Observations of these characteristics do not change the composition. A chemical property is one which is observed when matter undergoes a transformation that results in a change of composition. Gasoline will burn in air to form products which are very different from the original material. Iron will rust in moist air to form a compound called iron oxide. The fact that gasoline burns and iron rusts are therefore chemical properties. A physical change is a change in the form of matter without changing its composition. Examples of such changes are phase changes such as melting, boiling, etc. A chemical change is one that leads to a change in the composition of the matter involved. The burning of wood leads to products very different than the starting material. Physical changes are quite often reversible. Ice can be melted to form liquid water; however, water can be readily reconverted to ice. Chemical changes are usually irreversible. Gasoline can be burned to produce water and carbon dioxide, but it is not possible to reconvert these into the original material. Even though matter can undergo changes it is important to realize that in ordinary chemical reactions matter cannot be created or destroyed. We say that matter is conserved. This is one of the fundamental conservation laws. PHYSICAL CHANGE PHYSICAL CHANGE •Will change the visible appearance, without changing the composition of the material. •Can be reversible or irreversible -boil, melt, cut, bend, split, crack • A Physical change is a change in a substance that does not change what the substance is. PHYSICAL CHANGE EXAMPLES • Examples of physical change include: – Change in shape – Change in size – Change in phase • Melting (solid to liquid) • Boiling (liquid to gas) • Evaporation (liquid to gas) • Condensation (gas to liquid) • Freezing (liquid to solid) • Sublimation (solid to gas) • Deposition (gas to solid) PHYSICAL CHANGE • Physical changes might be caused by: – Grinding – Cutting – Crushing – Bending – Breaking – Heating/cool ing • (change in phase) – squishing PHYSICAL CHANGE • Evidence that a physical change has occurred might include: – Change in shape – Change in form – Change in size – Change in phase (This is always a physical change!) – Physical changes are usually reversible PHYSICAL CHANGE • What could you do to these items to cause a physical change to occur? CHEMICAL CHANGE CHEMICAL CHANGE • a property that can only be observed by changing the composition of the material. • A chemical change is a change in which a substance is changed into a different substance. (You’ve changed what it is.) CHEMICAL CHANGE • Examples of chemical changes include: – Burning – Rusting – Tarnishing – Decomposing – Polymerization CHEMICAL CHANGE • Chemical changes occur when a chemical reaction causes bonds between atoms to break or to form. CHEMICAL CHANGE – CHEMICAL REACTIONS • There are 5 types of chemical reactions that cause chemical changes to occur. CHEMICAL CHANGE – CHEMICAL REACTIONS 1. Composition reactions – Two things come together to form something new – A + B = AB – 2H2 + O2 2H2O CHEMICAL CHANGE – CHEMICAL REACTIONS 2. Decomposition reactions – 1 thing breaks apart to form 2 or more things. – AB = A + B – 2H2O 2H2 + O2 CHEMICAL CHANGE – CHEMICAL REACTIONS 3. Single replacement reactions – One atom replaces another atom – A + BC = AC + B or A + BC = AB + C – Mg + 2HCl H2 + MgCl2 CHEMICAL CHANGE – CHEMICAL REACTIONS 4. Double replacement reactions – Two chemicals switch places – AX + BY = AY + BX – 2KI + Pb(NO3)2 PbI2 + 2KNO3 CHEMICAL CHANGE – CHEMICAL REACTIONS 5. Combustion reaction – A substance combines with oxygen and releases energy. – C3H8 (propane) + 5O2 3CO2 + 4H2O CHEMICAL CHANGE – CHEMICAL REACTIONS 6. Acid-Base Reaction – This is a special kind of double displacement reaction that takes place when an acid and base react with each other. The H+ of the acid reacts with the OH – of the base forming water. HCl + NaOH NaCl = H2O CHEMICAL CHANGE: EVIDENCE • Evidence that a chemical change has occurred might include: – A color change – An odor change – Formation of a precipitate (you mix two liquids and make a solid) – Gas is formed (bubbles) – Changes in physical properties. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGE • During a chemical change energy can be released in the form of: – Heat – Light CHEMICAL CHANGE – CHEMICAL REACTIONS • When a chemical change occurs, energy is either released or absorbed. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGE HEAT • A chemical reaction that releases energy in the form of heat is called exothermic. – Heat comes OUT • Exo = out • Thermic = heat – It will feel HOT. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGE HEAT • A chemical reaction that absorbs energy in the form of heat is called endothermic. – Heat goes IN • Endo = in • Thermic = heat – It will feel COLD Classify the following as chemical change (cc), chemical property (cp), physical change (pc), or physical property (pp). 1 . _ _ _ _ H E AT CONDUCTIVITY 6. ____ S H O RT E N I N G M E LT I N G 11. _ _ _ AC I D R E S I S TA N C E 12. ___ BRITTLENESS 2 . _ _ _ _ S I LV E R TA R N I S H I N G 7. ____ EXPLODING DY N A M I T E 3. ____ S U B L I M AT I O N 8. ____ COMBUSTIBLE 4. ____ M AG NETI Z I NG STEEL 14. ___ BAKING BREAD 9 . _ _ _ _ W AT E R FREEZING 15. ___ BREAKING A BONE 5. ____ LENGTH O F M E TA L OBJECT 1 0 . _ _ _ _ WO O D BURNING 13. ___ MILK SOURING