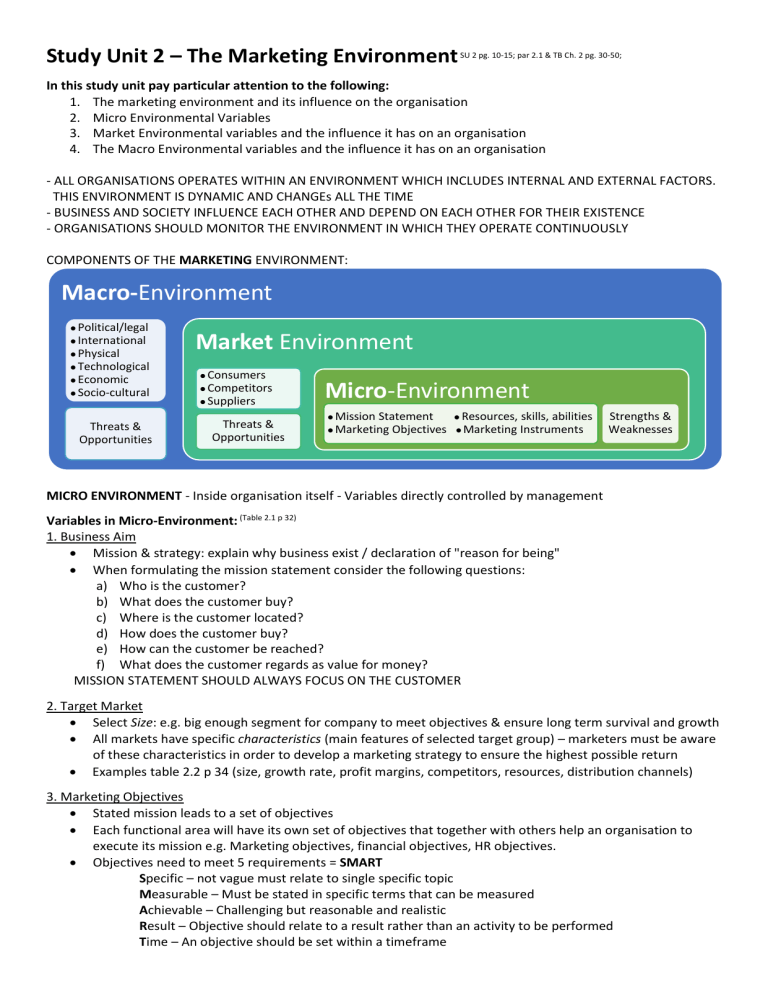
Study Unit 2 – The Marketing Environment SU 2 pg. 10-15; par 2.1 & TB Ch. 2 pg. 30-50; In this study unit pay particular attention to the following: 1. The marketing environment and its influence on the organisation 2. Micro Environmental Variables 3. Market Environmental variables and the influence it has on an organisation 4. The Macro Environmental variables and the influence it has on an organisation - ALL ORGANISATIONS OPERATES WITHIN AN ENVIRONMENT WHICH INCLUDES INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL FACTORS. THIS ENVIRONMENT IS DYNAMIC AND CHANGEs ALL THE TIME - BUSINESS AND SOCIETY INFLUENCE EACH OTHER AND DEPEND ON EACH OTHER FOR THEIR EXISTENCE - ORGANISATIONS SHOULD MONITOR THE ENVIRONMENT IN WHICH THEY OPERATE CONTINUOUSLY COMPONENTS OF THE MARKETING ENVIRONMENT: Macro-Environment Political/legal International Physical Technological Economic Socio-cultural Threats & Opportunities Market Environment Consumers Competitors Suppliers Threats & Opportunities Micro-Environment Mission Statement Marketing Objectives Resources, skills, abilities Marketing Instruments Strengths & Weaknesses MICRO ENVIRONMENT - Inside organisation itself - Variables directly controlled by management Variables in Micro-Environment: (Table 2.1 p 32) 1. Business Aim Mission & strategy: explain why business exist / declaration of "reason for being" When formulating the mission statement consider the following questions: a) Who is the customer? b) What does the customer buy? c) Where is the customer located? d) How does the customer buy? e) How can the customer be reached? f) What does the customer regards as value for money? MISSION STATEMENT SHOULD ALWAYS FOCUS ON THE CUSTOMER 2. Target Market Select Size: e.g. big enough segment for company to meet objectives & ensure long term survival and growth All markets have specific characteristics (main features of selected target group) – marketers must be aware of these characteristics in order to develop a marketing strategy to ensure the highest possible return Examples table 2.2 p 34 (size, growth rate, profit margins, competitors, resources, distribution channels) 3. Marketing Objectives Stated mission leads to a set of objectives Each functional area will have its own set of objectives that together with others help an organisation to execute its mission e.g. Marketing objectives, financial objectives, HR objectives. Objectives need to meet 5 requirements = SMART Specific – not vague must relate to single specific topic Measurable – Must be stated in specific terms that can be measured Achievable – Challenging but reasonable and realistic Result – Objective should relate to a result rather than an activity to be performed Time – An objective should be set within a timeframe There are different types of objectives: See detail on TB pg. 36-37 Business/Long term objectives – 8 major areas: Market Standing (Sell what & to whom) Productivity (input/output ratio) Innovation Physical & Financial Resources Profitability Manager Performance & Development (Quality of mngr.) Worker Performance & Attitude (e.g. output per employee) Public & Social Responsibility Functional/ Short term objectives Profit (max profit/ROI) Customer Orientation (satisfy needs/wants) Survival & Growth (keep up with changing demands) Sales & Market Share ( by differentiation/new lines/location) Efficiency Motive Marketing Instruments Objectives 4. Resources, Skills and Abilities Used to take advantage of external opportunities / counter threats Internal analysis: review org.'s strengths, weaknesses & capabilities of finance, facilities, product knowledge Examples are capital, skills, structures, systems, knowledge 5. Marketing instruments/marketing mix (4 P's) Use of marketing instruments is determined by the specific target market •Best product (quality, size) to meet needs of market •Must reflect value perceived by consumer •Customers buying patterns •Distribution Channels Produc t /Servic e Place Price Promo -tion •Best communication method to reach specific market MARKET ENVIRONMENT – Forces outside the business. Influenced/partially controlled by management Variables in Market Environment: 1. Suppliers Businesses/individuals who provide resources the business needs to produce goods & services Having the right supplier may mean the difference between success and failure Supply of materials & services is N.B: directly influences business' profit & price charged to the customer 2. Customers Focal point of every business : their needs; purchasing power; behaviour patterns (in-depth analysis) A MARKET CAN BE DEFINED AS CONSISTING OF PEOPLE WITH NEEDS WHO HAVE MONEY TO SPEND AND IS WILLING TO SPEND THAT MONEY There are 5 types of customer markets (TB p 40) a) Consumer Markets: individuals/households who buy goods/services for personal consumption b) Industrial / B2B Markets: org.'s buy goods/services for further processing/use in manufacturing process c) Reseller Markets: buy goods/services and resell them at a profit d) Government Markets: government agencies buy goods to produce public service/transfer to others e) International Markets: foreign buyers (incl. consumers, producers, resellers & governments) 3. Competitors Define competition: situation in a market where several businesses offer similar kinds of products or services and compete for the business patronage of the same customers Competitive Market Structures: (TB p 41) Monopoly Oligopoly One Competitor Few Competitors No real substitutes Few differentiated / homogeneous products Complete Control Control much of supply Monopolistic Competition Perfect Competition Many Competitors Unlimited Competitors Many products, little differentiation Many differentiated products No Influence on price / supply THE MACRO ENVIRONMENT – External forces in-/directly influencing individual org. – Org. has no influence/control. Variables in the macro environment Macro environment is dynamic – it changes rapidly and impact of such change can be felt very quickly 1. Political & Legal (Institutional Environment) Political stability / government decisions: one of the most N.B influencers of the marketing environment International law and regulations will also effect how organisations do business in other counties 2. International Environment What happens in world almost immediately reported and markets reacts to these events instantaneously. Sourcing suppliers is much easier than in the past – organisations are not limited to local suppliers only It is important to understand relevant regulations and conditions of all countries you do business in. Also be aware of cultural differences that may impact trade 3. Physical Environment Natural resources are not available in infinite quantities – businesses must be aware of limitations Availability of raw materials used in manufacturing will have an effect on supply of a product 4. Technological environment Technological innovations can be described as the process that expands people’s capacity. It originates in research and development of enterprises and the state It results in new machinery and products and also new processes, methods and management approaches. This bring about changes in the environment 5. Economic environment Inflation The Business Cycle Monetary Policy Interest rates Economic environment Exchange Rate Unemploy ment Consumer Income 6. The Socio-cultural Environment Impacts marketing techniques, media used, types of ads., organisational structures, products designed and offered for sale across all types of businesses and industries Social trends directly affect marketing strategies Trends include – demographics, lifecycles, cultural values, and sub cultural influencers THE SWOT ANALYSIS Helps managers identify internal strengths and weaknesses as well as external opportunities and threats ENVIRONMENTAL SCANNING Measurement; projection and evaluation of change in different environmental variables Importance of environmental analysis: 1. Helps business capitalise on early opportunities 2. Early signal of impending problems or threats 3. Sensitises business to changing needs and wants of customers 4. Objective info about SWOT 5. Improves image of business by showing it is sensitive and responsive to environment






