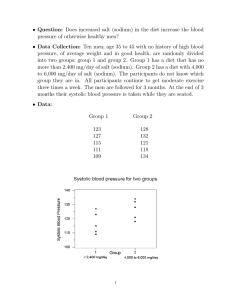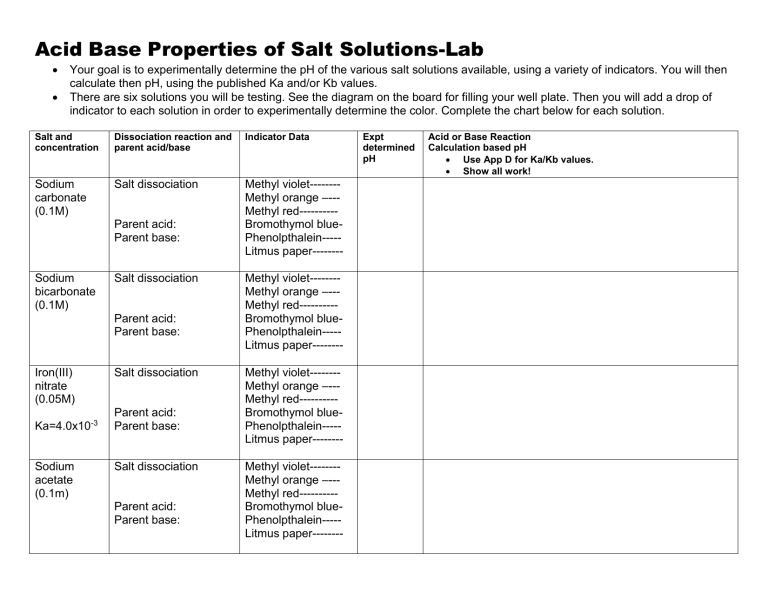
Acid Base Properties of Salt Solutions-Lab Your goal is to experimentally determine the pH of the various salt solutions available, using a variety of indicators. You will then calculate then pH, using the published Ka and/or Kb values. There are six solutions you will be testing. See the diagram on the board for filling your well plate. Then you will add a drop of indicator to each solution in order to experimentally determine the color. Complete the chart below for each solution. Salt and concentration Dissociation reaction and parent acid/base Indicator Data Sodium carbonate (0.1M) Salt dissociation Methyl violet-------Methyl orange –--Methyl red---------Bromothymol bluePhenolpthalein----Litmus paper-------- Parent acid: Parent base: Sodium bicarbonate (0.1M) Salt dissociation Parent acid: Parent base: Iron(III) nitrate (0.05M) Ka=4.0x10-3 Sodium acetate (0.1m) Salt dissociation Parent acid: Parent base: Salt dissociation Parent acid: Parent base: Methyl violet-------Methyl orange –--Methyl red---------Bromothymol bluePhenolpthalein----Litmus paper-------Methyl violet-------Methyl orange –--Methyl red---------Bromothymol bluePhenolpthalein----Litmus paper-------Methyl violet-------Methyl orange –--Methyl red---------Bromothymol bluePhenolpthalein----Litmus paper-------- Expt determined pH Acid or Base Reaction Calculation based pH Use App D for Ka/Kb values. Show all work! Ammonium chloride (0.1M) Salt dissociation Parent acid: Parent base: Sodium chloride (0.1M) Salt dissociation Parent acid: Parent base: water xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Methyl violet-------Methyl orange –--Methyl red---------Bromothymol bluePhenolpthalein----Litmus paper-------Methyl violet-------Methyl orange –--Methyl red---------Bromothymol bluePhenolpthalein----Litmus paper-------xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx A few questions: 1) Consider the difference in the pH (both expt and calculated) for the carbonate and bicarbonate solutions. Explain their difference pH in terms of Ka/Kb values. 2) Which ions are always spectators in A/B chemistry? Put this in terms of the parent acid and base. 3) Which ions from a salt tend to increase the pH of a solution? Put this in terms of the parent acid and base. 4) Which ions from a salt tend to decrease the pH of a solution? Put this in terms of the parent acid and base.