Cardiomyopathies
advertisement

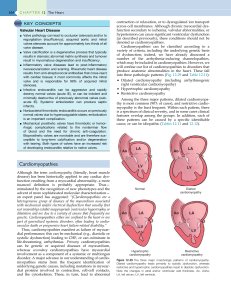
• A 40 years old gentleman comes in OPD with two years history of worsening dyspnea on exertion. He also experiences shortness of breath in midnight while lying flat for which he has to get up to catch his breath. • He’s never had chest pain. There has been occasional dry cough with dyspnea but no history of sputum or wheezing. • What is the likely cause of his dyspnea? Heart Failure • Failure: Inability to perform the expected function • Function of Heart: – Left Heart: To perfuse the body organs – Right heart: To receive blood from body and promptly send it to lungs DR M NAEEM AFZAL FCPS, Dip-DIABTES (UK) ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR EAST MEDICAL WARD MAYO HOSPITAL/KING EDWARD MEDICAL UNIVERSITY, LAHORE Definition • Heart failure is a complex syndrome that can result from any structural or functional cardiac disorder that impairs the ability of the heart to function as a pump to support a physiological circulation. HFpEF HFrEF • A 40 years old gentleman comes in OPD with two years history of worsening dyspnea on exertion. He also experiences shortness of breath in midnight while lying flat for which he has to get up to catch his breath. • He’s never had chest pain. There has been occasional dry cough with dyspnea but no history of sputum or wheezing. • He also has history of sudden cardiac death in his family. • What are the likely causes of his heart failure? Causes of heart failure • Hypertension • Myocardial ischemia/infarction • Valvular heart disease (Obstructive/Regurgitant) • What is left? • Muscle itself History • Progression of disease (Acute or chronic?) • Associated features (ischemic chest pain, palpitations) • Family history of cardiac illness or sudden cardiac death • Occupational/Exposure history • History of systemic diseases Investigations??? • • • • • ECG CXR PA view Cardiac Enzymes Echocardiography Pro-BNP levels Cardiomyopathies • Disorders characterized by morphologically and functionally abnormal myocardium in the absence of any other disease that is sufficient, by itself, to cause the observed phenotype. • Primary (Genetic/Acquired) • Secondary to systemic diseases Examination • Pulse, Blood pressure • JVP, edema • Apical impulse (location, character) • Heart sounds & Murmurs • Systemic examination (Lungs, Joints, Skin, Muscles) Dilated Cardiomyopathy (DCMP) DILATED CARDIOMYOPATHY Major Causes of Dilated Cardiomyopathy Myocarditis • Inflammation of heart muscles • Acute/subacute presentation of heart failure and elevated cardiac enzymes (with normal coronaries) • Clinically behaves as dilated cardiomyopathy • Viruses/bacteria/drugs/Immune Peri-Partum cardiomyopathy • Last trimester of pregnancy up to six months post-partum • Increased maternal age, increased parity, twin pregnancy, malnutrition, pre-eclampsia • Cardiac function usually recovers overs weeks to months Other important causes • Alcohol, Cocaine, amphetamines • Thiamine deficiency (beware; it may also occur in high users of highly processed food) • Chemotherapeutic agents • Hyperthyroidism Takutsubu cardiomyopathy • Stress induced cardiomyopathy – Sudden intense emotional or physical stress • Apical ballooning syndrome • May cause sudden death • EF may recover with time RESTRICTIVE CARDIOMYOPATHY Restrictive Cardiomyopathy • Diastolic heart failure • Infiltration of elements in ventricular muscles • Apical impulse at normal position • Preserved EF HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy HCM with or without outflow obstruction • Jerky pulse, S4 gallop • Crescendo/Decres cendo systolic ejection murmur. Its intensity increases with Valsalva. • Holosystolic apical blowing murmur of mitral regurgitation Risk factors for sudden death in HOCM The ultimate fate • Every cardiomyopathy ultimately turns into dilated cardiomyopathy • “Heart failure is not a disease; it is a final common pathway”. Summary QUESTIONS ???