respiratory system review - allied (1)
advertisement

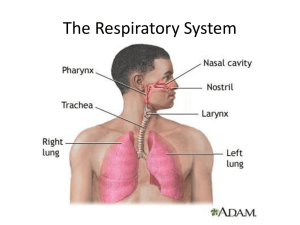
Functions of the Respiratory System Breathing process Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Enable speech production Gas exchange between blood and air Respiration external respiration - exchange of gases in lungs internal respiration - exchange of gases within cells of the body organs and tissues ventilation - movement of air External Respiration Ventilation exchange of gases in lungs Gas Exchange in pulmonary capillaries Breathing largely an involuntary activity Internal Respiration All cells require oxygen for metabolism All cells require means to remove carbon dioxide Gas exchange at cellular level External Respiration Ventilation exchange of air between lungs and atmosphere Gas Exchange in pulmonary capillaries Breathing largely involuntary activity Structures of Respiratory System upper respiratory tract nose, mouth, pharynx, epiglottis, larynx and trachea lower respiratory tract bronchial tree and lungs Nose nasal cavity nasal septum mucous membrane Traps pathogens and dirt Cilia push particles towards esophagus Moistens air NASAL SEPTUM PARTITION OR WALL CARTILAGE DIVIDES THE NOSE INTO HOLLOW SPACES CAN BE DAMAGED DUE TO TRAUMA 8 CILIA TINY HAIRLIKE STRUCTURES IN NASAL CAVITY TRAPS DIRT TRAPS PATHOGENS TRAPPED PARTICLES PUSHED TOWARD ESOPHAGUS SWALLOWED 9 Pharynx Nasopharynx oropharynx adenoids or pharyngeal tonsils palatine tonsils ( 1st phase of swallowing) laryngopharynx Larynx ( Houses vocal cords) Thyroid is housed here Epiglottis Oropharynx and laryngopharynx serve as a common passageway for both food and air Epiglottis acts as a lid or flap that covers the larynx and trachea (airway) so food does not enter the lungs. Larynx Houses vocal cords in voice box glottis (vocal apparatus)” True Vocal Cords” vocal bands or vocal cords Trachea Windpipe or airway that is 12.5cm long mucous membrane lining with cilia smooth muscle with c-shaped cartilage rings divides into two branches: bronchi no gaseous exchange Bronchi Bronchus, singular c-shaped cartilage rings with smooth muscle Bronchus divides into l & R Bronchi Bronchi divide into bronchioles terminate in air sacs called alveoli Thoracic Cavity “Thoracic “ means related to thorax Thorax ( Chest Cavity) contains: heart aorta esophagus bronchi Thymus ( Lymphoid organ) ALVEOLI Gas Exchange takes place here Alveolar wall one cell thick surrounded by blood capillaries Resemble bunches of grapes CAPILLARIES ALLOW OXYGEN & CARBON DIOXIDE TO EXCHANGE BETWEEN LUNGS & BLOOD 16 Lungs Right-3 lobes Left-2 lobes trachea PLEURA Serous membrane enclosing each lung TWO LAYERS Visceral pleura comes in contact with the lungs Parietal pleura comes in contact with the ribcage Lubricating fluid: stops friction 18 Diaphragm muscle separating chest and abdomen inspiration, diaphragm contracts and pushes down increasing thoracic space expiration, diaphragm relaxes and returns to decreases thoracic space air flows in air flows out phrenic nerve: originates in the neck (C3-C5) and passes down between the lung and heart to reach the diaphragm.Passes motor information to the diaphragm Pathologic Breathing Disorders Many Chronic Disorders Asthma ( COPD UMBRELLA) Chronic Bronchitis Emphysema Disorders Continued Asthma bronchospasms, parosysmal, productive cough, mucolytics, bronchodilators Chronic Bronchitis mucosal swelling, productive cough, chest pain expectorants, bronchodilators, steroids Emphysema barrel-chest, dyspnea, orthopnea Influenza Acute infectious respiratory disease Viral Fever, chills, headache, myalgia, anorexia Avoid aspirin in children ( can trigger Asthma) Pleural Effusions Excess fluid in pleural cavity associated with congestive heart failure, ascites, infectious lung diseases, trauma diagnosis auscultation, percussion Empyema, hydrothorax, hemothorax, pnrumothorax, pyopneumothorax thoracentesis Tuberculosis Infectious, highly communicable disease aerosol transmission primary tuberculosis immunocompromised Client requires 9 months medication regime drug resistant strains ( AIDS) Bronchopneumonia Inflammatory disease of lungs lobar, bilateral hemoptysis consolidation Pneumocystis carinii (AIDS) Cystic Fibrosis Hereditary disorder, affects exocrine glands systemic involvement lungs, pancreas, digestive tract Viscous mucus blocks bronchioles Gas exchange impaired Respiratory Distress Syndrome Surfactant decreases the surface tension of the alveoli needed for alveoli to fill with air and expand (compliance) Infant respiratory distress syndrome (hyaline membrane disease) Adult respiratory distress syndrome Oncology Primary Pulmonary Cancer Diagnosed by PET scan Smoking is leading cause of ALL TYPES OF LUNG CANCERS common site: epithelium of bronchi bronchogenic carcinoma masses form and block air passages metastasizes frequently to lymph noes, liver, bones, brain, or kidney Endotracheal Intubation passage of a tube through the mouth, pharynx, and larynx into the trachea to establish an airway.