Electrolysis Worksheet-1452167276
advertisement

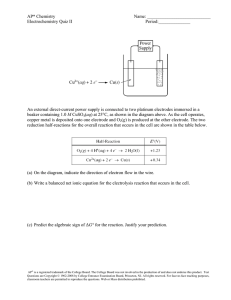
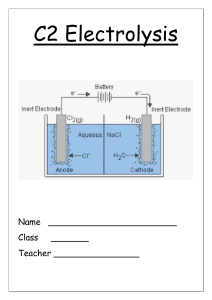
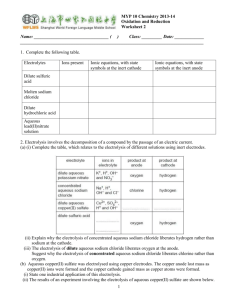
Name:……………………………………………………. Date: …………………… Electrolysis Worksheet This worksheet accompanies Electrolysis Summary. 1. a) Complete the sentences using words from the box below. Electrolysis is the process of breaking down an ionic substance using …………………. The broken down substance is called the …………………. Ionic substances contain charged particles called ………………. The electrolyte also contains positive and negative ions. During electrolysis, the negative ions travel to the positive electrode and ………………… electrons. This process is called …………………. The positive ions travel to the negative electrode and ………………… electrons. This process is called …………………. In addition, ………………… form at the negative electrode and non-metals form at the positive electrode. lose metals oxidation non-metals reduction electrolyte gain electricity ions b) Complete these equations for the electrolysis of lead bromide. i) lead bromide → ………………… ii) PbBr2(l) → ………………… iii) At the negtaive electrode: Pb2+ + 2e- → ……… iv) At the positive electrode: ………Br - → Br2 + 2e2. How can the products of the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution be used? Draw lines between the boxes on the left and the boxes on the right to match each product to its use. chlorine margarine hydrogen soap sodium hydroxide plastic © Boardworks Ltd 2011 1 Name:……………………………………………………. Date: …………………… 3. What products are formed at each of the electrodes during the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution? Label the diagram below. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………… © Boardworks Ltd 2011 …………………… 2 Name:……………………………………………………. Date: …………………… 4. Write a word equation to show the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution: …………………………………… ………………………………………… 5. a) Explain what happens to the negatively-charged chloride ions during electrolysis. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… c) Electrode equation: …………………………………… ……...……………………………………… d) Explain what happens to the positively-charged hydrogen ions during electrolysis. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… e) Electrode equation: ………………………………….. …………………………..…..……………… 6. Explain what happens to the sodium and hydroxide ions after electrolysis. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… © Boardworks Ltd 2011 3