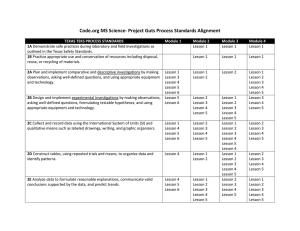
3D Science Teaching & Workshop Thinking Strategies -
advertisement
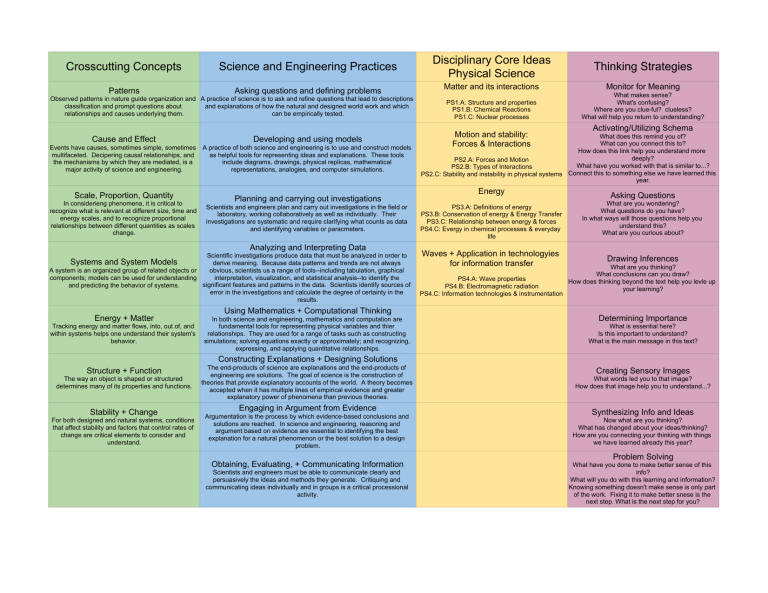
Crosscutting Concepts Science and Engineering Practices Disciplinary Core Ideas Physical Science Thinking Strategies Patterns Asking questions and defining problems Matter and its interactions Monitor for Meaning PS1.A: Structure and properties PS1.B: Chemical Reactions PS1.C: Nuclear processes What makes sense? What's confusing? Where are you clue-ful? clueless? What will help you return to understanding? Observed patterns in nature guide organization and A practice of science is to ask and refine questions that lead to descriptions classification and prompt questions about and explanations of how the natural and designed world work and which relationships and causes underlying them. can be empirically tested. Cause and Effect Developing and using models Events have causes, sometimes simple, sometimes multifaceted. Decipering causal relationships, and the mechanisms by which they are mediated, is a major activity of science and engineering. A practice of both science and engineering is to use and construct models as helpful tools for representing ideas and explanations. These tools include diagrams, drawings, physical replicas, mathematical representations, analogies, and computer simulations. Scale, Proportion, Quantity In considerieng phenomena, it is critical to recognize what is relevant at different size, time and energy scales, and to recognize proportional relationships between different quantities as scales change. Planning and carrying out investigations Scientists and engineers plan and carry out investigations in the field or laboratory, working collaboratively as well as individually. Their investigations are systematic and require clarifying what counts as data and identifying variables or paracmeters. Analyzing and Interpreting Data Scientific investigations produce data that must be analyzed in order to Systems and System Models derive meaning. Because data patterns and trends are not always obvious, scientists us a range of tools--including tabulation, graphical A system is an organized group of related objects or interpretation, visualization, and statistical analysis--to identify the components; models can be used for understanding significant features and patterns in the data. Scientists identify sources of and predicting the behavior of systems. error in the investigations and calculate the degree of certainty in the results. Energy + Matter Tracking energy and matter flows, into, out of, and within systems helps one understand their system's behavior. Using Mathematics + Computational Thinking In both science and engineering, mathematics and computation are fundamental tools for representing physical variables and thier relationships. They are used for a range of tasks such as constructing simulations; solving equations exactly or approximately; and recognizing, expressing, and applying quantitative relationships. Motion and stability: Forces & Interactions Activating/Utilizing Schema What does this remind you of? What can you connect this to? How does this link help you understand more deeply? PS2.A: Forces and Motion What have you worked with that is similar to...? PS2.B: Types of Interactions PS2.C: Stability and instability in physical systems Connect this to something else we have learned this year. Energy PS3.A: Definitions of energy PS3.B: Conservation of energy & Energy Transfer PS3.C: Relationship between energy & forces PS4.C: Evergy in chemical processes & everyday life Waves + Application in technologyies for information transfer Asking Questions What are you wondering? What questions do you have? In what ways will those questions help you understand this? What are you curious about? Drawing Inferences What are you thinking? What conclusions can you draw? PS4.A: Wave properties How does thinking beyond the text help you levle up PS4.B: Electromagnetic radiation your learning? PS4.C: Information technologies & instrumentation Determining Importance What is essential here? Is this important to understand? What is the main message in this text? Constructing Explanations + Designing Solutions Structure + Function The way an object is shaped or structured determines many of its properties and functions. Stability + Change For both designed and natural systems, conditions that affect stability and factors that control rates of change are critical elements to consider and understand. The end-products of science are explanations and the end-products of engineering are solutions. The goal of science is the construction of theories that provide explanatory accounts of the world. A theory becomes accepted when it has multiple lines of empirical evidence and greater explanatory power of phenomena than previous theories. Engaging in Argument from Evidence Argumentation is the process by which evidence-based conclusions and solutions are reached. In science and engineering, reasoning and argument based on evidence are essential to identifying the best explanation for a natural phenomenon or the best solution to a design problem. Obtaining, Evaluating, + Communicating Information Scientists and engineers must be able to communicate clearly and persuasively the ideas and methods they generate. Critiquing and communicating ideas individually and in groups is a critical processional activity. Creating Sensory Images What words led you to that image? How does that image help you to understand...? Synthesizing Info and Ideas Now what are you thinking? What has changed about your ideas/thinking? How are you connecting your thinking with things we have learned already this year? Problem Solving What have you done to make better sense of this info? What will you do with this learning and information? Knowing something doesn't make sense is only part of the work. Fixing it to make better snese is the next step. What is the next step for you?