Genitically modified plants From: http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools
advertisement

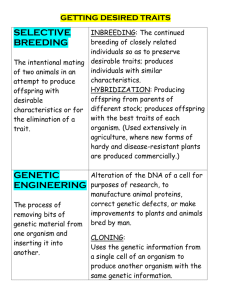
Genitically modified plants Word box How it works Certain enzymes can cut pieces of DNA from one organism, and join them into a gap in the DNA of another organism. This means that the new organism with the inserted genes has the genetic information for one or more new characteristics. For example, the organism might produce a useful substance, or be able to carry To carry out : effectuer out a new function. We say that the organism has been genetically modified. Genetic modification works in animals, plants and microorganisms. For example, Crop : culture new genes can be transferred to crop plants to make GM crops. Some GM crops are resistant to certain herbicides (weed killers) while others are resistant to insect pests or need less water to grow up. Genetic engineering : génie One biotechnology applied to food crops is genetic engineering. Genetic génétique engineering is the process in which either a desired gene of an organism is isolated, spliced out of the surrounding genetic sequence, cloned using laboratory techniques, and inserted into the host organism which is being modified (see Traits = Characteristics figure below). The host crop then displays the desired manifestations of the gene. This means that scientists can modify a plant so that it displays traits from other plants, such as greater leaf area or a different color. Genetic engineering can also refer to the removal of a specific gene from the DNA of the target crop, which then Selective breeding = artificial prevents the plant from manifesting that gene. Using this technique, genetic selection: engineers can select for certain phenotypes, and the processes related to said traits, without having to undergo selective breeding within a population. Genetic Process by which humans use engineering takes less time than selective breeding, and in some cases is able to animal breeding and plant carry out genetic changes that would not occur naturally. breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits by choosing which typically animals or plant males and females will sexually reproduce and have offspring together. Domesticated animals are known as breeds, while plants are known as varieties or cultivars. (Opposite is natural selection...) The process of genetic modification through isolation of a gene and insertion into the genetic sequence of a host organism There are strong arguments for and against genetic modification of crop plants. GM crops generally have increased yields, useful for feeding a growing Yield: production, récolte population. Maize, the crop with the highest global production, annually sustains losses on the order of 15 percent of potential yield attributable to drought. As the climate changes as a consequence of global warming, some climates will become more arid, increasing drought and resulting in up to 10 million more lost tons of Drought: sécheresse maize per year. It has been estimated that 25 percent of these losses may be resolved by genetically modifying maize to be more drought tolerant. However, some people are excited by the almost limitless possibilities of genetic modification, while others believe the process is unethical and should be banned. There are concerns about the effect of GM crops on wild flowers and insects, and To harm: nuire à whether eating GM food may harm human health. From: http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/aqa/geneticvariation/reproductionrev5.shtml and: http://12.000.scripts.mit.edu/mission2017/genetically-modified-crops/