t the t tech hnica al ti times s
advertisement
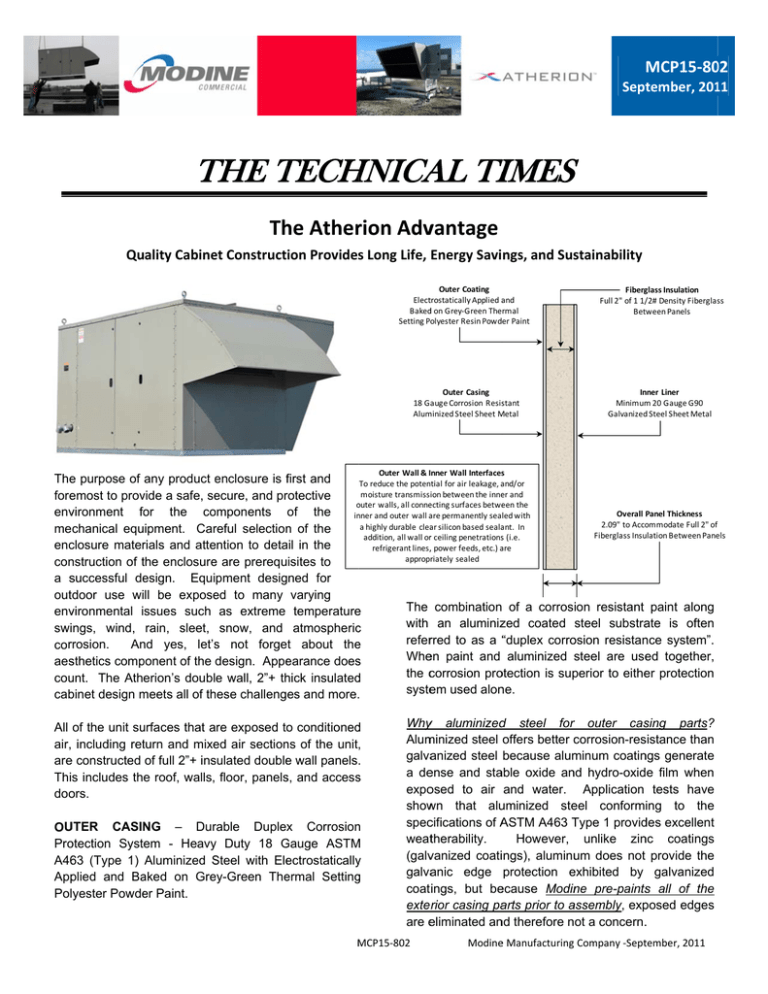
MCP15‐80 02 Septtember, 201 11 THE T TECH T HNICA AL TI TIMESS Th he Atherrion Advvantage Qu uality Cabine et Construction Providess Long Life, Energy Savings, and Susstainability Outer Coating Electtrostatically Applied aand Baked d on Grey‐Green Thermal Setting Polyester Resin Powder Paint Fibergglass Insulation Full 2" of 1 1//2# Density Fiberglasss Between Panels Outer Casing 18 G auge Corrosion Resisstant Alum minized Steel Sheet M Metal In nner Liner Minimum m 20 Gauge G90 Galvanized d Steel Sheet Metal Outer Wall & Inner Wall Interfacess e purpose of any product enclosure e is first f and The To reduce the potential for air leakage, aand/or moisture transmission between the inneer and fore emost to prov vide a safe, se ecure, and prrotective o outer walls, all conneecting surfaces betweeen the envvironment fo or the co omponents of the Overall Panel Thickness in nner and outer wall aare permanently sealed with 2.09" to Acco ommodate Full 2" off a highly durable clea ar silicon based seala ant. In mechanical equipment. Carreful selection n of the Fiberglass Insu ulation Between Paneels addition, all wall orr ceiling penetrationss (i.e. ention to deta ail in the encclosure materrials and atte refrigerant lines,, power feeds, etc.) aare appropriately sealed con nstruction of the t enclosure e are prerequisites to a ssuccessful de esign. Equipment designed for outtdoor use will be expose ed to many varying The combination of a corrosion resistant paint along e envvironmental issues such as extreme temperature ate is often with an aluminizzed coated steel substra swings, wind, rain, sleet, snow, and atmospheric c rred to as a “ osion resistan nce system”. “duplex corro refer An nd yes, let’s s not forget about the e corrrosion. Whe en paint and aluminized steel are use ed together, aessthetics comp ponent of the design. Appe earance does s the ccorrosion pro otection is sup perior to eithe er protection cou unt. The Atherion’s double wall, 2”+ th hick insulated d syste em used alon ne. cab binet design meets m all of th hese challenges and more.. All of the unit su urfaces that are a exposed to o conditioned d ed air section ns of the unit, air, including retturn and mixe e constructed of full 2”+ ins sulated double e wall panels. are This includes the roof, walls, floor, panels s, and access s ors. doo UTER CASIN NG – Durrable Duplex x Corrosion n OU Pro otection System - Heavy y Duty 18 Gauge G ASTM M A46 63 (Type 1) Aluminized Steel S with Ele ectrostatically y App plied and Ba aked on Gre ey-Green The ermal Setting g Polyester Powde er Paint. d steel forr outer cassing parts? Whyy aluminized Alum minized steel offers better ccorrosion-ressistance than galva anized steel because alum minum coatin ngs generate a de ense and sta able oxide an nd hydro-oxide film when expo osed to air and water. Application tests have show wn that alu uminized ste eel conforming to the speccifications of A ASTM A463 T Type 1 provid des excellent weattherability. However, unlike zin nc coatings (galvvanized coatings), aluminu um does not provide the galva anic edge protection e exhibited by galvanized coat ings, but be ecause Modin ne pre-paintss all of the arts prior to a assembly, exp posed edges exterrior casing pa are e eliminated an nd therefore not a concern.. MCP15‐802 M Modinee Manufacturing Company ‐Septtember, 2011 Experience has shown that aluminized steel is easier to clean and pre-treat in preparation for painting than galvanized steel and it is a better substrate for achieving an even and high quality paint adhesion system during the painting process. In addition, aluminized steel does not contain the heavy metal “zinc” which can be an environmental concern. Zinc is listed by the Environmental Protection Agency as one of 129 priority pollutants. The application of paint onto a hot dip galvanized surface requires careful surface preparation and a good understanding of both the preparation of the galvanized steel surface and the compatibility of the paint being applied. The margin for error is very small when dealing with newly galvanized steel surface preparation. When galvanized steel is pre-treated (which is a prerequisite for good paint adhesion) some of the zinc coating is removed during the pre-cleaning and abrading process and this contaminant can enter into water and waste-water systems. Elevated concentrations of zinc in water are particularly toxic to many species of algae and crustaceans. Elevated concentrations of zinc in water have especially strong impacts on macroinvertebrates such as mollusks and crustaceans. The use of aluminized steel for painted parts eliminates these concerns. Why Polyester Powder Paint (and Subsequent Paint System Analysis Under ASTM D1654, ASTM B117 and ASTM 3359, Method B, ASTM D3363 ASTM D552, ASTM, ASTM D4587, G151 and G154)? Powder coating is a type of coating that is applied as a free-flowing, dry powder. The coating is typically applied electrostatically and is then cured under heat to allow it to flow and form a "skin". Powder paint creates a hard finish that is tougher than conventional paint and is used mainly for coating metals. Modine powder paint also includes UV inhibitors to reduce coating breakdown over time. Powder coatings emit zero or near zero volatile organic compounds. This is good for the environment. In addition, overspray can be captured and recycled, and powder coating production lines produce less hazardous waste than conventional liquid coating lines. Polyester powder paint is also less permeable to moisture and is ideal for outdoor applications. It is critical that the corrosion resistance and adhesion quality of the painting process be included in any analysis of the duplex corrosion resistance system. This is why Modine has developed a painting system specification that not only tests the durability of the P a g e | 2 paint itself, but also tests the durability of the entire duplex corrosion protection system, including the metal cleaning, preparation, and application processes involved. Painted test panels are prepared per ASTM D1654 Standard Test Method for Evaluation of Painted or Coated Specimens. Test panels are scribed diagonally prior to testing. These specimens are then tested in a salt spray/fog environment per ASTM B-117 which covers the apparatus, procedure, and conditions required to create and maintain the salt spray (fog) test environment. Breakdown of the paint film in excess of 10% constitutes a test failure. Film breakdown includes corrosion spots and/or blisters and is judged by using a 6.4mm (1/4-in) transparent overlay and calculating the percentage of squares that contain corrosion spots and/or blisters. Film breakdown within 6.4 mm (1/4 in) of the diagonal scribe is ignored. Average creepage from the diagonal scribe in excess of 3.2 mm (1/8 in) constitutes a failure. ASTM B-117 does not prescribe the type of test specimen or exposure periods to be used for a specific product, nor the interpretation to be given to the results. Simply stating a painted panel has survived under ASTM B117 salt spray/fog test environment tells nothing about how the specimen was prepared (i.e. did it include diagonal scribes, and/or cross hatching for evaluation of the entire painting system and processes?) If a coating is to fulfill its function of protecting or decorating a substrate, it must adhere to the substrate for the expected service life of the equipment. Because the substrate and its surface preparation (or lack of it) have a drastic effect on the adhesion of coatings, a method to evaluate adhesion of a coating to different substrates is very important. Recognizing this Modine subjects painted test panels to ASTM 3359, Method B and requires the panel to have a rating of “5B” in the 1.6-mm (1/16-in) crosshatch tape adhesion test along with the following physical characteristic tests. Hardness - A painted test panel shall show a film hardness of “2H” minimum in the gouge hardness test (Ref ASTM D3363). Flexibility - A painted test panel shall show no film cracking during a 180°-flexibility test around a 3.2-mm (1/8-in) mandrel (Ref ASTM D 522, Method B). UV Resistance - A painted test panel shall withstand 1000 ± 5 hours exposure in a QUV Weatherability Chamber utilizing UVA-340 lamps. Cabinet operation MCP15‐802 Modine Manufacturing Company ‐September, 2011 to consist of continuous cycles with four hours UV exposure at 60 °C (140 °F) followed by four hours condensation at 50 °C (122 °F). The paint film shall not blister, show more than 30% loss of gloss, or exhibit total color difference. (Ref: ASTM D 4587, G 151, G 154). Because of the wide range of available R value designs, it is important to know which R-value designs are being compared when energy savings claims are being made. The savings between an R-2 enclosure and an R-13 enclosure is going to be much different than between an R-8 and R-13 enclosure. Discoloration - A painted test panel shall withstand a minimum of 80 hours at 191 °C (375 °F) without discoloration. Figures 3.1 and 3.2 graphically represent the added cooling load and estimated added cooling costs associated with heat gains and losses through a typical cabinet of a 15-30 ton packaged rooftop cooling unit located in Atlanta, Georgia. It is assumed that the unit is configured for 100% return air. The graphs show the average cooling temperatures and hours of duration at each temperature for a typical Atlanta cooling season. Figure 3.1 shows the added cooing load in BTU’s, and Figure 3.2 shows the estimated added cooling cost at each temperature and hours of operation data point (assuming an energy cost of $0.08/kW). It is clearly evident that the much lower R2 value unit construction has relatively high thermal losses when compared to cabinets with R8 through R13 construction. However the differences between R8 and R13 construction are almost negligible. Conclusion - The use of a highly corrosion-resistant and environmentally friendly aluminized steel substrate along with a technically advanced baked-on thermal setting polyester resin power paint system provides an attractive and long lasting, durable, duplex corrosion resistant outer casing system for the Modine Atherion unit. INSULATION – 2” R8 Fiberglass insulation between outer and inner casing wall, floor and roof panels provides energy savings over lower R-value insulating systems. Just as adding insulation to a home or building can offer substantial energy savings compared to a lesser insulated building, the same is true for mechanical HVAC equipment. The Atherion ventilation system conditions outside air in both the heating and cooling modes, and once conditioned it is important not to lose the energy in the conditioned air back to the environment via thermal losses through the unit’s cabinet. The Atherion’s 2” double-wall fiberglass insulated cabinet design offers a thermal resistance value of approximately R-8. This is a very good R-value for outdoor mechanical equipment. Some older unit cabinet construction methods provided R-values as low as R-2, which left a lot of room for improvement. Current day, higher quality HVAC equipment is usually designed with Rvalues in the range of R4 to R13. To economically achieve an insulation value of R13 in a 2” thickness configuration it almost always requires the use of petroleum based polyurethane foam insulations. Fiberglass insulation can offer values of around R8 or slightly higher. P a g e | 3 Be alert to savings claims that only provide information relative to older lower R-2 construction methods but do not provide comparative information relative to current day improved double-wall cabinet construction methods. The cooling savings for R-8 through R13 rated cabinets are substantial when compared to R-2 cabinet systems, but the savings between R8 through R13 are relatively small. Figure 3.1 MCP15‐802 Added Cooling Load (BTU's) from Cabinet Thermal Gains/Losses Based on 15‐30 Ton Unit Casing ‐ Atlanta, GA R2 R8 R9 R13 1,200,000 1,000,000 BTU's Modine’s baked-on polyester powder paint test panels have to pass all of the aforementioned test criteria before the paint material and application methods are acceptable. 800,000 600,000 400,000 200,000 0 ‐200,000 Outdoor Fo 97 92 87 82 77 72 67 Hrs per Yr 9 32 220 758 768 1037 1162 Modine Manufacturing Company ‐September, 2011 made from recyclable plastic materials. Polystyrene foams require the use of hydrochloro-fluorocarbons, which are less dangerous to the Earth's ozone layer than the old chlorofluorocarbons but still cause some damage. Figure 3.2 Added Cooling Cost from Cabinet Thermal Gains/Losses Based on 15‐30 Ton Unit Casing ‐ Atlanta, GA R2 R8 R9 R13 $26.00 $21.00 A review of a typical “Material Safety Data Sheet” for polyurethane under “Regulatory Information” states: Dollars $16.00 $11.00 $6.00 $1.00 ‐$4.00 92 87 82 77 72 67 Outdoor Fo 97 Hrs per Yr 9 32 220 758 768 1037 1162 Why Fiberglass Insulation? As seen earlier, fiberglass can provide relatively high R-values for HVAC cabinetry. Polyurethane, if properly protected against thermal drift has a higher R-value per inch of thickness than fiberglass, but polyurethane does have some downsides. Fiberglass is an environmentally friendly and sustainable insulating material. The basic raw materials for fiberglass products are a variety of natural minerals and some manufactured chemicals. The major ingredients are silica sand, limestone, and soda ash. Silica sand is used as the glass former, and soda ash and limestone help primarily to lower the melting temperature. Other ingredients are used to improve certain properties, such as borax for chemical resistance. Waste glass, called cullet, is also used as a raw material. Fiberglass is not petroleum based, therefore it offers greater sustainability and is environmentally friendlier than expanded foam options. A review of the “Material Safety Data Sheet” for fiberglass, under “Regulatory Information” states; Regulatory Information - US Federal Regulations: A: General Product Information - SARA 311/31 This product is not classified as hazardous under SARA 311/312. And further under OSHA; OSHA/HCS Status Fiberglass is treated as a nuisance dust and is regulated by OSHA as a particulate not otherwise regulated (total dust) shown in CFR 1910.1000 In contrast to fiberglass, the production of rigid foam insulation requires the use of petroleum based products, which if not properly handled can produce significant environmental issues. Most foam insulation products are also difficult to recycle, though some are P a g e | 4 Regulatory Information - US Federal Regulations: A: General Product Information - SARA 311/31 SARA 311/312 MSDS distribution - chemical inventory hazard identification: Butane, 2- methyl-: fire hazard flammable, combustible liquid, pyrophoric Cyclopentane: fire hazard - flammable, combustible liquid, pyrophoric Pentane: acu, fire hazard - flammable, combustible liquid, pyrophoric Aluminum: fire hazard - flammable, combustible liquid, pyrophoric, rea. SARA 311/312 Product Classification: Immediate (acute) health hazard. Delayed (chronic) health hazard. And further under OSHA OSHA/HCS Status This material is considered hazardous by the OSHA Hazard Communication Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200). Conclusion – The use of fiberglass insulation provides high R-value cabinetry construction without the necessity of using petroleum based insulating material. Fiberglass manufacturing involves far less chemicals than the manufacture of polyurethane foam and therefore is overall more environmentally friendly. Fiberglass is not regulated as a hazardous waste, it is recyclable, and it is made from sustainable materials. INNER LINERS – Minimum 20 Gauge G90 Galvanized Sheet Steel (Base steel per ASTM Standard Specification A924 and A653, Galvanized coating thickness when tested per ASTM Standard Test Method A 90 shall be a minimum of Z275(G90). Why galvanized steel for inner liners? As discussed earlier, galvanized coated steel provides better galvanic corrosion edge protection. During the fabrication process the steel is sheared, punched, and formed and can be scratched. Galvanized steel tends to be self-healing and the coating tends to wipe over the processed edges during fabrication. Because the inner liners are not painted, this characteristic is important for maintaining the overall corrosion resistance of the inner liners, and because these parts are not painted the better paint adhesion qualities of aluminized steel is not needed. MCP15‐802 Modine Manufacturing Company ‐September, 2011 Conclusion – The use of galvanized steel for the inner liners is the best choice when the material is not intended to be painted, but must still provide good corrosion protection and cleanability. OUTER WALL AND INNER WALL INTERFACES - To reduce the potential for air leakage, and or moisture transmission between the inner and outer walls, all connecting surfaces between the inner and outer wall are permanently sealed with a highly durable clear silicon based sealant. In addition, all wall or ceiling penetrations (i.e. refrigerant lines, power runs, etc.) are appropriately sealed. Inner Liners – All conditioned air wall, ceiling, and floor surfaces are lined with robust minimum 20 gauge G90 galvanized steel. All interfaces between the inner liner and outer casing parts, and all joints between casing parts are sealed with durable, long lasting silicon based sealant to minimize moisture and/or air infiltration and/or exfiltration. Power and Control Wiring Interfaces – All main power and control wiring runs are made between the roof and inner roof liners to keep the interior of the unit free from electrical runs thus providing unobstructed access to the unit’s interior during maintenance and cleaning. POWER AND CONTROL WIRING INTERFACES – All main power and control wiring runs are made within the area between the roof outer casing and the roof inner liners to keep the interior of the unit free from electrical runs thus providing unobstructed access to the unit’s interior during maintenance and cleaning. Individual component power and control runs are fed down from the inner roof with drop downs at the point of usage of each of the components. SUMMARY – Modine’s Atherion products are provided with a highly durable, aesthetically pleasing, and thermally efficient cabinet that maximizes the thermal efficiency of the units, uses sustainable and environmentally friendly materials wherever possible, provides maximum protection for the unit components, has excellent weatherability, and is designed to be service and maintenance friendly. Paint – Electrostatically applied and baked on greygreen thermal setting polyester resin powder paint. Outer Casing – All casing parts are painted prior to assembly. This assures full paint coverage on both the interior and exterior surfaces of the sheet metal parts and all edges and all fastener holes. The casing is made from heavy duty 18 Gauge Aluminized Steel and which is cleaned of all surface oil and debris prior to painting. After parts are powder coated, they are baked cured for a long lasting durable finish. Insulation – All conditioned air wall, ceiling, and floor surfaces are insulated with a full 2 inches of 1 ½# density fiberglass insulation providing an insulation value of at least R-8 for the double wall and insulated cabinet. P a g e | 5 MCP15‐802 Modine Manufacturing Company ‐September, 2011





