Lecture 1.01 “Modern Board Design” Course: Organization and
advertisement

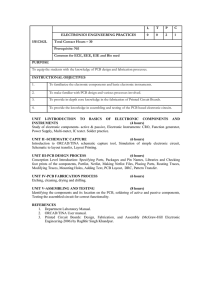
Lecture 1.01 “Modern Board Design” Course: Organization and Introduction to Board Design Lecture 1.01 1 Lecture Plan Program Information: • Program material • Recommended literature • Program rules: • Work in class and in laboratory • Grade policy Introduction to Hardware Board Design • What is an electronic board • Board Design industry and Applications Lecture 1.01 2 Course Introduction Lecture 1.01 3 Time, Location etc 1. Lecture’s days and time: Every Thursday From 18.00 to 22.00 (be at time) 2. Course duration - ~6 months [bruto], about 250 ac. Hours (frontal and for the project design). 3. Address: Ramat Gan, 7 Aba Hilel str., floor 15 1. Parking for free options: Yazira and Ahaliav str. (100-200m from CDC) Lecture 1.01 4 Program’s Grades Structure Final grade structure: Project – 40% from the semester grade Each project includes the Design Specs and the Design Environment Exam – 60% from the semester grade Each exam is in American Style (multiple choice) and closed books The minimum required exam’s and project’s grade is: 65. The required course average is: 70. Lecture 1.01 5 Study and Help with Job Search Plan The Course milestones are the Project milestones: MRD, Kickoff, PDR, CDR, FDR and final exam CV Design - Very effective and professional help Coaching for successful career building Time and project management Career planning and Job search plan design. Project FDR with Senior Designers from High Tech companies Diploma, Recommendations and Individual meetings for successful job search etc: CV/Linkedin Profile Design Job search plan design Technical Interview Simulation Lecture 1.01 6 Course rules • Work with slides – questions, comments • Study environment at home • Weekly Back up • Course Forum • Documents and code style • Design reviews and final submission. • Homework assignments, which will be done individually or in groups. ** The main target of the course is making the students mature enough in Board Design for the industry. Help yourself using internet forums and online documentation. ** Students get certificate if stand successfully in course requirements. - Every one will get the tools for working from home, plus 1 evaluation board for design group. Lecture 1.01 7 Course Material Course Material includes: Slide Sets – 4 books: (2 for Board Design, 2 for High Speed Board Design) 1. Introduction to Board Design: 1. Board Design Technologies and Design Flow 2. SoB Modern Architectures 3. Device selection 2. Board Design schematics capture. PCB design and manufacturing. Standards compliancy. Full design flow: Your “First” Board Design Project. 3. High Speed Board Design theory. Ref Project with Signal Integrity review. 4. Introduction to FPGA Design, Advanced High Speed Board Design Subjects. Reference Board Design and High Speed Board Design Projects Design Environment - Soft Copy. Lecture 1.01 8 Recommended Literature 1. Hardware Design – The Art of Electronics - Paul Horowitz, Winfield Hill (ISBN 0-521-37095-7) – Switching Powe r Supplies – A to Z – Sanjaya Manitkala (ISBN 13: 978-0-7506-7970-1) 2. Digital Design – 3. Digital Design, Morris Mano (3rd edition or late r - ISBN-13: 9780131989245) Computer Systems – – 4. Computer System Architecture, Moris Mano (ISBN-13: 9780131755635) The Indispensable PC Hardware Book – Hans Peter Messmer (ISBN: 0-20159616-4) OrCAD – Schematics capture and layout – – Inside OrCAD Capture for Windows – Chris Schroeder (ISBN-13: 978-0-75067063-0) Complete PCB Design Usign OrCAD Capture and Layout – Kraig Mitzne r (ISBN-13: 978-0-7506-8214-5) Lecture 1.01 9 Recommended Literature 5. High Speed Board Design – 6. High-Speed Digital Design – A Handbook of Black Magic – Howard Johnson FPGA Design – VHDL – – – 7. VHDL Programming by Example – Douglas L. Perry (ISBN: 0-07140070-2) RTL Hardware Design Using VHDL – Pong P. Chu (ISBN-13: 978-0471-72092-8) ModelSim User Guide Communications Fundamentals – Computer Networks - Andrew Tanenbaum (ISBN 0-13-384248-1) …and periodically, you must read quality magazines like EDN (http://www.edn.com) and Electronic Design (http://electronicdesign.com) Lecture 1.01 10 Semester A – Board Design • • • Introduction to Board Design Board Design Technologies and Design Flow SoB (System on Board) Architecture – – – – – – • • • • Modern RISC and CISC Processors DSPs Buses/Memories Peripheral Dev ices, Interfaces and Connectors Analog and Mixed Signal Blocks Power Supply Schematic Capture Theory and work with OrCAD “Ref” Board Design Project Review “First” Board Design Project - by Course’s Students Choosing Devices for Board Design – Analog and Digital chips and devices – Chip Packages Types and use. – RoHS, temperature, EMI/RFI, CE and other requirements and standards • • • • PCB Design and manufacturing theory PCB Layout and work with Allegro Coaching Part 1 – Career/life targets, Time management etc Semester A final exam Lecture 1.01 11 11 Copyr ight © 2005 AVM Brothers Ltd. Semester B – High Speed Board Design • Introduction to High Speed Board Design • • • • • • Design rules for Signal Integrity • • • • • • • • • • • • Signal Integrity for HI-SPEED Fundamentals. POWER INTEGRITY for Power Distribution System (PDS) Common High Speed standards – – 1. Parallel – DDRI to DDRIII (frequencies and applications). – 2. Serial – SATA, PCIe, XAUI, USB3.0 etc. Analog and digital issues in High Speed PCB Design. Test and characterization flow Reflections and Transmission Lines Crosstalk and EMI Issues Crosstalk Simulations Differential Traces and Impedance Clock Trees and other controlled impedance signals Eye Diagram Bypass Caps and Decoupling Systems Constraints Management and Pre and post layout Simulation “Ref” High Speed Board Design - Project Overview “Advanced” High Speed Board Design Project - by Course Students FPGA for Board Designers with VHDL Semester B – Final Board Designer Evaluation exam Lecture 1.01 12 12 Copyr ight © 2005 AVM Brothers Ltd. What is an electronic board? Lecture 1.01 13 Evolution of electronic boards - Integration • Old boards contained big discrete components, simple ICs with DIP packages and only ten to twenty pins each • Old digital chips only instantiated simple functions: Single digital gate, flip flop, operational amplifier. • New chips include thousands and even millions of functions (complete SoC). BGA packages of 1K pins are common on almost any PCB design. Lecture 1.01 14 Evolution of electronic boards – The Digital Revolution • Old analog processing was done using discrete components: Amplifiers, mixers, filters, etc. • Today, many functions are done using Digital Signal Processing. • Digital Signal Processing advantages: – Solutions done in software: Ease of testing and portability – Can be easily modified, including ISP. – DSP operations are more stable, precise and repeatable. They are independent of process and temperature – Lower cost and footprint of solution – Better precision achievable • Digital Signal Processing disadvantages: – “Strange” artifacts: Quantization noise, aliasing of signals – Speed: Need margin for running software on processor Lecture 1.01 15 Board Structure • Basic Board Components: – PCB: • Physical anchoring for chips and components, interconnection – Components • Functionality of design Lecture 1.01 16 Board Architecture The following picture shows an example of functional division on an electronic board. Analog Connectors Power Connectors Power Supply Digital Block Analog and/or RF blocks PCB Digital Connectors 17 17 Lecture 1.01 Board Design Industry and Applications Lecture 1.01 18 Electronic Design Main Applications (1) Portable electronic systems – Laptops, PDA, Mobile phones, digital cameras Powerful computer systems – Servers and personal computer, high speed communication (computer communication - Internet) Telecommunications – Voice, video and data - Access and Switching equipment with high reliability and redundancy Complex control systems – Process control systems, robots, automotive market, communication, signal and picture processing, hardware implementation of complex algorithms (encryption, compression). Systems with High Reliability Requirements – electronic medical equipment, army applications Low cost products – computer equipment, electronic games, credit cards etc… Lecture 1.01 19 Electronic Design Main Applications (2) Main players on the market of products based on electronic boards – – – – – – – – – – – – Telecommunications - Voice: Alcatel, Siemens, Motorola, Nortel, etc. Telecommunications - Video: Polycom, Tandberg, etc. Telecommunications - Data: Cisco, Lucent, etc Telecommunications – Infrastructure (CPCI, ATCA boards): Intel, MCG, Kontron, Schroff, Radysis, Artesyn, etc Telecommunications – Infrastructure (CPCI, ATCA chassis): Elma, Kapparel, Carlo Gavazzi, Rital, etc Military, aeronautic, space: IAI, GE, Lockheed, etc. Storage devices, MP3 – Sony, Samsung, SanDisk, M-Systems Mobile Phones: Nokia, Samsung, Ericsson, Motorola, Philips, LG, Sharp Personal Computers: IBM, Dell, Samsung, LG, Apple PDAs: Palm, HP, Sony, Apple, etc Cameras: Sony, Panasonic, Samsung, Sharp Medical equipment – Siemens, GE, Philips, etc. Lecture 1.01 20 Modern Digital Board Design Challenges (1) Cost and complexity – BOM cost – Component maturity – PCB complexity, cost, production site – Component lead time – Production quantity Performance and Features – Processor – Architecture, processing capability, bandwidth, scalability – Storage Type: Flash, DRAM, disk Size, bandwidth, latency Communications – Internal buses topology, bandwidth, latency, scalability – Clocks generation and distribution – External interfaces – Requirements as internal buses + standards compliancy Lecture 1.01 21 Modern Digital Board Design Challenges (2) Power – Multiple voltage and current requirements – Power distribution topology, hot swap requirements, redundancy, noise filtering – Sequencing, protection, standards compliancy Mechanical Design – Form factor – Functions separation – Thermal design – Heatsinks selection, placement (air flow) System Design – System integration with system power and communications – OA&M capabilities – R&D debug and test capabilities Design for Production – ATE capabilities – BIST, diagnostics Lecture 1.01 22 Case study – ATCA board (1) Lecture 1.01 23 Case study – ATCA board (2) Cost – Complexity, size – Production quantity Performance and Features – Processor – Storage Communications – Internal buses – Clocks generation and distribution – External interfaces Power Physical Design – Form factor – Functions separation – Thermal design System Design – System integration – OA&M capabilities – R&D debug and test capabilities Lecture 1.01 24 Case study – ATCA board (3) Lecture 1.01 25 Case study – Personal computer Cost – Complexity, size – Production quantity Performance and Features – Processor – Storage Communications – Internal buses – Clocks generation and distribution – External interfaces Power Physical Design – Form factor – Functions separation – Thermal design System Design – System integration – OA&M capabilities – R&D debug and test capabilities Lecture 1.01 26 Case study – Data acquisition board Lecture 1.01 27 Case study – Mobile phone (1) Lecture 1.01 28 Case study – Mobile phone (2) Lecture 1.01 29 And many, many more… Entertainment Medical electronics Lecture 1.01 30 And many, many more… Evaluation boards Consumer products Lecture 1.01 31 And many, many more… Military equipment Industrial control Lecture 1.01 32