Lab 1
advertisement

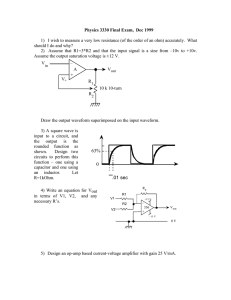
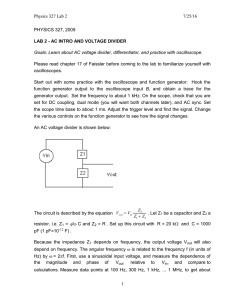
ECE221 Electrical Devices and Circuits Laboratory 1: Introduction OBJECTIVES Review and develop skills in the use of the laboratory equipment. PRELAB None. PREPARATION Bring a notebook with you to the labs to do your prelab, to record data and to answer lab questions. Breadboards will be provided if you do not have one. EXPERIMENT 1. Set the function generator to produce a 4V peak-to-peak (Vpp) 1KHz sine wave. Display this signal on the CH1 of the oscilloscope. (a) By using the oscilloscope, how do you determine whether a DC offset is present or not? Before doing so decide where the vertical coupling switch should be. (b) What is the difference between AC and DC coupling on the vertical display? 2. Construct the circuit in fig.1. Carefully determine the anode lead of the diode (1N4001). Set the function generator to produce a 0.8Vpp zero mean (no DC offset) triangular wave at 1KHz. (a) Connect the function generator to VIN. Set vertical scale to 0.2V/div and carefully sketch i. ii. iii. VIN vs. time VOUT vs. time VOUT vs. VIN (b) Repeat (a) with VIN = 4.0 Vpp and use vertical scale of 1.0V/div (c) Repeat (a) with VIN = 20.0 Vpp and use vertical scale of 10.0V/div Vin (CH1) Vout (CH2) Figure 1 3. Figure 2 shows the switching response of a typical diode, where ts is the storage time and tr is the recovery time. Set the function generator to produce 4.0Vpp square wave. (a) Describe how you would set the oscilloscope to obtain a signal proportional to the diode current. (b) By experimenting with frequency and observing the waveform, determine the frequency where the storage mechanisms of the diode become significant. That is, find the frequency where the diode switching current is observable. (c) Measure the storage and recovery times of your diode. (d) Why does the negative peak of the voltage across the 2KΩ resistor exceed -2.0V? ID (t) IF t 0.1IR IR Figure 2