Chapter 12 Using Energy
advertisement

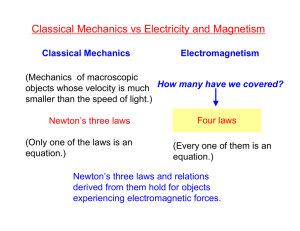
Lesson 1 Heat Lesson 2 Sound Lesson 3 Light Lesson 4 Electricity What are the different forms of energy? Lesson 5 Magnetism heat temperature conduction convection radiation thermal conductivity What is heat? Heat is thermal energy that flows between objects due to a difference in temperature. How does heat travel? conduction convection radiation What is thermal conductivity? Thermal conductivity is the ability of a material to transfer heat. When is heat waste? Cars will stop working if they cannot release their extra heat. Main Idea A candle is placed on a steel block and begins to melt. How do you know whether the candle or the steel block is hotter? Heat must flow into a candle in order for it to melt. If heat is flowing into the candle, it must be cooler than the steel block. Vocabulary __________________ Thermal conductivity is the ability of a material to transfer heat. __________________ is thermal energy that Heat flows between objects due to a difference in temperature. __________________ is the passing of heat Conduction through a material while material itself stays in place. conduction thermal conductivity heat Vocabulary ____________ is the transfer of energy through Radiation electromagnetic rays. ____________ Convection is the flow of thermal energy through a liquid or gas, which is caused by hot parts rising and cool parts sinking. ____________ Temperature is a measurement of the average kinetic energy of particles in an object. convection temperature radiation Draw Conclusions An infrared image of a house shows that the roof is brighter than the rest of the house. What does this mean? The roof is radiating more heat energy. Convection currents inside keep bringing hot air to the roof; the roof may be heated by radiation from the Sun. End of Lesson sound wave medium vacuum absorption frequency pitch amplitude echolocation How is sound produced? How does sound travel? Sound can not travel in a vacuum such as space. Sounds can travel though solids, liquids, and gases. What is pitch? Pitch is how high or low a sound is. 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 600 Hz 200 Hz What is volume? Volume is the loudness of a sound. What is echolocation? Finding objects by using sound waves is known as echolocation. Main Idea How could a stereo playing loudly rattle dishes? The vibrations from the speakers could travel as sound waves through the air and hit the dishes. The sound energy from the wave could then vibrate the dishes. Vocabulary __________ Absorption is the transfer of energy when a wave disappears into a surface. A __________is the substance through which a wave travels. A __________ is a region that contains few or no particles __________ Frequency is the number of times an object vibrates per second. vacuum medium frequency absorption Vocabulary _____________ is how high or low a sound is, Pitch and is related to frequency. _____________ Sound waves are a series of rarefactions and compressions traveling through a substance. Some animals use _____________ to find where their prey is located. _____________ is how dense the air is in the Amplitude compression or rarefactions compared to normal air. sound waves pitch amplitude echolocation Fact or Opinion Should you wear earplugs while using a vacuum cleaner? Support your opinion with facts. The sound of a vacuum cleaner is not loud enough to damage your ears. Earplugs are not necessary when using a vacuum cleaner. End of Lesson wavelength photon translucent image refraction prism spectrum electromagnetism What is light? Light is a wave made from electric and magnetic energy. electric wave magnetic wave How does light make shadows? How does light bounce and bend? flat lens flat mirror concave lens concave mirror convex lens convex mirror Why do we see colors? The band of color in a rainbow, or from light passing through a prism, is called a spectrum. Is all light visible? larger wavelength AM FM radio waves TV radar infrared visible light ultraviolet X-rays gamma rays higher frequency Main Idea What makes light able to move through empty space? Light is an electromagnetic wave; it does not need a medium to travel through. Vocabulary A __________ is a tiny bundle of energy by which light travels. A __________ is the distance between one peak and the next in a wave. The band of color in a rainbow, or from light passing through a prism is called a __________. An __________ is a “picture” of the light source that light makes bouncing off a shiny surface. wavelength photon image spectrum Vocabulary A _____________ is a cut piece of clear glass in the form of a triangle or other geometric shape. ________________ Electromagnetism is the way in which electric and magnetic forces interact. Objects that blur light as it passes through it are _____________. The bending of waves as they pass from one substance into another is called ____________. translucent refraction electromagnetism prism How does light act like a wave? Summarize has a frequency has a wavelength Light acts like a wave. has amplitude End of Lesson translucent (trans·lü΄sәnt) Blurring light as it passes through. (p. 654) electricity static electricity grounding electric current circuit resistor What is static electricity? How can electricity flow? A circuit is formed when an electric current passes through an unbroken path of conductors. What kinds of circuits are there? series circuit parallel circuit How can you use electricity safely? Main Idea Why will a comb rubbed with wool pick up bits of paper? Electrons from the wool build up on the comb (static electricity). The comb picks up paper by attracting the protons in the paper. Vocabulary A _______________ is formed when an electric current passes through an unbroken path of conductors. _______________ is the movement of electrons. Electricity _______________ Static electricity is the buildup of charged particles. static electricity electricity circuit Vocabulary _______________ Electric current is a flow of electricity through a conductor. An object in an electrical circuit that resists the flow of electrons is called a _______________. _______________ occurs when a conductor Grounding shares its excess charge with a much larger conductor. electric current grounding resistor Sequence What happens as objects rub together and form sparks? An object rubs against another object or surface. Electrons are exchanged. The buildup of electrical charge attracts the electrons to protons in the other object. The electrons discharge through the air, creating a spark End of Lesson circuit (sûr΄kit) A loop formed when electric current passes through an unbroken path of conductors. (p. 668) magnetism magnetic field electromagnet generator alternating current magnetic levitation What is magnetism? Magnetism is the ability of an object to pull on another object that has the magnetic property. What are electromagnets? N S N S How can magnets produce electricity? As the coils spins next to magnets, high-voltage electricity is generated. axle turbine water in water out What is magnetic levitation? train magnets track magnets Main Idea What happens when a bar magnet is cut in half? Two bar magnets are formed, each with a north and south pole. Vocabulary _________________ Magnetic levitation is the lifting of an object by means of magnetic forces. The directional lines of the magnetic forces around a magnet are called the _________________. _________________ Alternating current is electric current that rapidly changes directions. alternating current magnetic levitation magnetic field Vocabulary An electric circuit that produces a magnetic field is called an _______________. _______________ is the ability of an object to Magnetism push or pull on another object that has the magnetic property. A _______________ is a device that creates electric current by spinning an electric coil between the poles of a magnet. electromagnet magnetism generator Compare and Contrast How are electric doorbells and speakers similar and different? doorbells ring use electromagnets speakers carry sound End of Lesson magnetic field (mag·net΄ik fēld) A region of magnetic force around a magnet, represented by lines. (p. 679) magnetic levitation (mag·net΄ik lev΄i·tā΄shәn) The lifting of an object by means of magnetic forces. (p. 684)