TDS 1012 Digital Oscilloscope An oscilloscope is a device that
advertisement

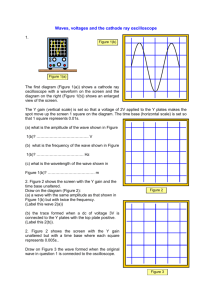
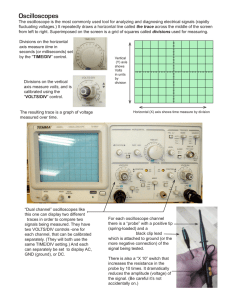
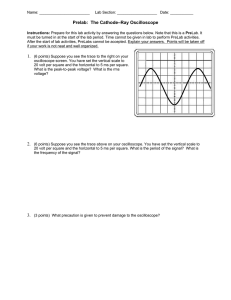
TDS 1012 Digital Oscilloscope An oscilloscope is a device that measures voltage as it changes over time. This guide will cover basic controls common on all oscilloscope designs that are used to examine and measure a signal. A Wavetek Function Generator will be used to provide signal. An oscilloscope must be set up in parallel to measure voltage, similar to a digital multi-meter. A two point probe or a BNC connector must be connected to an input. 1. Connect the Main Out of the Wavetek Function Generator to the CH 1 input on the oscilloscope (located beneath the VOLTS/DIV knob). Connect the Aux Out of the Wavetek to the CH 2 input. Set the Wavetek to frequency = 1.0kHz, Vpp (Voltage, peak to peak amplitude) = 4.0 volts, and function = sine wave. Set the Wavetek amplitude modulation = OFF and DC OFFSET = 0. The DC OFFSET adds a constant voltage to the AC signal from the Wavetek. Move the dial to see the effect before returning it to 0 since we are only concerned with the signal. 2. Turn on the oscilloscope and press the auto set button at the top right of the controls. The oscilloscope has a variety of ways to display signals. The auto set button measures incoming signals and finds a range of measurement that optimally displays the signal. Remember that when using the auto set button your oscilloscope settings will change. The oscilloscope should display two signals; a sine wave on CH 1 and a square wave on CH 2. These signals are displayed on a grid pattern. The vertical divisions (the y-axis) of the grid indicate voltages. The horizontal divisions (the x-axis) indicate an amount of time. The oscilloscope allows you to “zoom in and out” on the signal in each axis. The VOLTS/DIV and SEC/DIV knobs increase/decrease the respective scale. 3. Rotate each knob and notice how it changes the display. Also note that this changes only the display, NOT the signal. The exact settings used will vary depending on the signal being viewed and personal preferences. The Position knobs move the origin of the signal on its respective axis. 4. Pressing the CH 1 MENU button displays parameters for channel 1. Notice the box that says Coupling. Generally you use AC coupling for AC signals and DC coupling for DC signals. AC coupling removes the DC component of a signal. Ground coupling measures the ground, and is generally useful for repositioning your waveform in the center of the display. With the DC offset set to 0 on the waveform generator, toggle through coupling modes and investigate the displayed signal. The Trigger Menu also allows selection of either AC or DC coupling for the trigger signal. 5. The Trigger Level knob controls the voltage threshold a signal must reach before it will be displayed on the screen. The oscilloscope usually automatically triggers on whatever looks like an interesting waveform, such as a sinusoidal wave. If the threshold is set too high, the signal may not be displayed. Create a sine wave with the generator and play with the Trigger Level to see how it alters the display 6. The Trigger Menu button brings up adjustable parameters. For example, changing the slope can set the trigger to capture on a rising or falling edge in the signal. Changing the mode to auto is good for repetitive signals, where single will capture a single waveform. Experiment with different trigger levels and control modes (rising, falling, etc.) 7. Press the Cursor button and notice the two cursors displayed. By setting the type to voltage and source to CH1, the CH1 and CH2 knobs can be used to measure the voltage or time difference between both cursors. Cycle through and experiment with different measurement types. Measure also performs similar measurements automatically. 8. To take a screenshot of the display, select Waveforms > Source:CH1 > REF:A, and press the Save/Recall button. Pressing the lowest of the 5 display buttons will toggle the screenshot. Two screenshots (A and B) can be saved at a time. Determining Uncertainties The TDS 1012 Digital Oscilloscope has the following electrical characteristics: DC Vertical Accuracy: Time Base Accuracy: ±3% 50ppm, or ±0.005% Additionally check with your instructor for the electrical characteristics of the waveform generator you are using. Be sure to factor in these uncertainties to measurements made in the follow exercise. Exercise: Analyzing Signals with an Oscilloscope For the following waveforms, create a sketch with appropriate units similar to the diagram below in your lab notebook. Use the Cursor to measure the amplitude of the voltage, period, and frequency of the waveform. Include the DC vertical accuracy and time base accuracy error amounts in your calculations. The Sine Wave Use the Teachscope device to find sine wave. a. In your lab notebook, draw an example of your signal to scale including measurements: Amplitude _______ (in unit squares) VOLTS/DIV _______V / mv (circle) Amplitude _______ V / mv Period ________ (in unit squares) SEC/DIV ________ ms /µs / ns(circle) Period ________ ms / µs / ns Frequency __________ Hz b. What happens to the signal when you turn the VOLTS/DIV one click to the right: ________V/mV then two times to the left: ______V/mV. Turned to the right Amplitude (in squares)________ Amplitude (in volts)________ Turned to the left Amplitude (in squares)______ Amplitude (in volts)____ Return VOLTS/DIV knob to original setting. c. What happens to the signal when you turn the SEC/DIV one click to the right: _____ms/us/ns then two times to the left: ________ms/us/ns Turned to the right Turned to the left Period (square units)_______ Period (square units) _______ Period (time units) _______ Period (time units) _______ Return to original settings. Redo the above exercises for a square wave and sawtooth wave. Questions: 1. Would it be more accurate to measure the period of one wavelength, or increase the SEC/DIV knob and average the period of multiple wavelengths? Why or why not? 2. How did the amplitude, frequency, and period of the signal change during the above exercises? 3. Does the Trigger function correlate to the horizontal or vertical axis? How so?