Bipolar Transistors and Amplifiers Introduction The bipolar junction
Bipolar Transistors and Amplifiers
Introduction
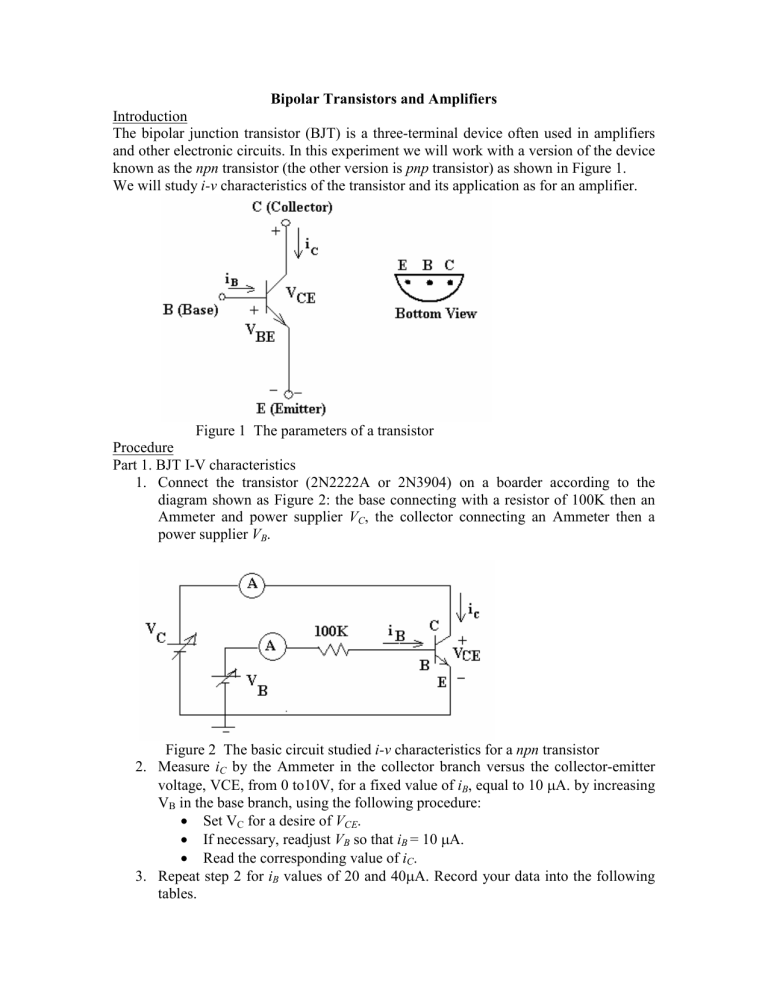
The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a three-terminal device often used in amplifiers and other electronic circuits. In this experiment we will work with a version of the device known as the npn transistor (the other version is pnp transistor) as shown in Figure 1.
We will study i-v characteristics of the transistor and its application as for an amplifier.
Figure 1 The parameters of a transistor
Procedure
Part 1. BJT I-V characteristics
1.
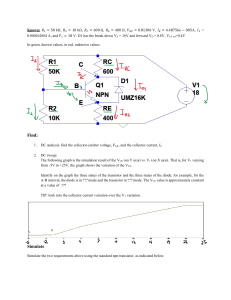
Connect the transistor (2N2222A or 2N3904) on a boarder according to the diagram shown as Figure 2: the base connecting with a resistor of 100K then an
Ammeter and power supplier V
C
, the collector connecting an Ammeter then a power supplier V
B
.
Figure 2 The basic circuit studied i-v characteristics for a npn transistor
2.
Measure i
C
by the Ammeter in the collector branch versus the collector-emitter voltage, VCE, from 0 to10V, for a fixed value of i
B
, equal to 10 µ A. by increasing
V
B
in the base branch, using the following procedure:
• Set V
C
for a desire of V
CE
.
• If necessary, readjust V
B
so that i
B
= 10 µ A.
• Read the corresponding value of i
C
.
3.
Repeat step 2 for i
B
values of 20 and 40 µ A. Record your data into the following tables.
i i
B
=10 µ A
C
V
CE i i
B
=20 µ A
C
V
CE i i
B
=40 µ A
C
V
CE
4.
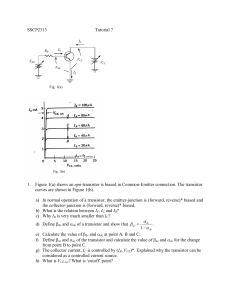
Using the data you have collected in the previous two steps, plot a family of curves for the collector current, i
C
, versus the collector-emitter voltage, V
CE
, from
0 to 10 V, with i
B
as a parameter. Your plot should be similar to the Figure 3.
5.
What is the approximate value of the current gain, β =i
C
/i
B
calculated on your measurement when i
B
=10 and 40 µ A.
Figure 3 A typical diagram of i
C
~V
CE
Part 2. AC amplifier with BJT
Figure 4 A typical circuit of amplification by use of a npn transistor
1.
Try the circuit as an amplifier by connecting the function generator with 1Kz signals at the input and a speaker at the output indicated as Figure 4.
2.
Vary the frequency of input signal and its amplitude slowly, and observe VCE with the scope or hear the sound at the output. Compare the volume of sound from the speaker, is there any amplifying? At what output amplitude is the output waveform obviously distorted?