Diodes - vcephysics.com
advertisement

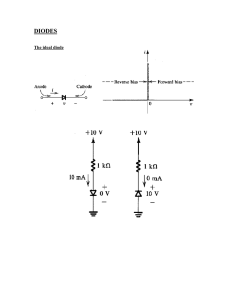
Diodes • • • • • • • • Semiconductors & doping PN junctions Reverse bias - no current Forward bias Diode IV curves Uses of diodes Calculations with diodes in series Calculations with diodes in parallel Diodes - 1 VCE Physics.com Semiconductors & doping • Semiconductors have a some conductivity, but not nearly as good as most metals. • Silicon is primarily used as a semiconductor. • Silicon has four valence electrons. Each silicon atom is covalently bonded to four others. • Doped silicon has a small (~1 part in a million) inclusion of other elements with one more or less electron. • P type material is made with a group III element one less electron. • N type material is made with a group V element one more electron. Diodes - 2 VCE Physics.com PN junctions Electrons move from the N side to fill in holes in the P side A depletion region is formed as there is now an overall charge separation & electric field. P type N type Boron atoms form bonds with electron “holes” in the Si structure. Diodes - 3 + + + + + + - - - - - - Phosphorous atoms form bonds with free electrons in the Si structure. VCE Physics.com Reverse bias - no current • In reverse bias, no current can get through the barrier of the depletion region (unless breakdown occurs at high voltages). + P type N type - + + + + + + Depletion region is strengthened & the electric field acts as a barrier to current flow. Diodes - 4 VCE Physics.com Forward bias • Once the switch on voltage is achieved, the diode conducts current. • There is a voltage drop as electrons lose energy across the depletion region. + Current flow P type N type - Diodes - 5 + + + + + + Depletion region is reduced & the diode allows current through. VCE Physics.com Diode IV curves • Diodes are non-ohmic & have a characteristic voltage current relationship. • Once the switch on voltage is reached in forward bias, the potential difference remains fairly constant, even with increasing current. • In reverse bias, no current flows until the breakdown voltage is reached. Current (mA) Breakdown voltage: may be kV. Potential difference (V) Switch on voltage ~0.7V for Si diode. hp://www.flashscience.com/electricity/diodes.htm Diodes - 6 VCE Physics.com Uses of diodes • Diodes can be used to rectify AC into DC, by blocking the flow of reverse currents. • Zener diodes are used as voltage regulators, to keep a constant potential output. • LEDs are light emitting diodes - photons of visible light are created as the electrons lose energy passing across the PN junction. LEDs are much more energy efficient than traditional incandescent globes. hp://www.flashscience.com/electricity/smoothing.htm Diodes - 7 VCE Physics.com Calculations with diodes in series • Assume that the diode is at the switch on voltage eg 0.7V. • The remaining potential difference is across the resistor(s). 9.0 V + 8.3 V 0.7 V 1000Ω 500Ω 8.3V 8.3V II == ==0.0166A 0.0083A 1000Ω 500Ω Diodes - 8 16.6mA 8.3 mA 16.6mA 8.3 mA VCE Physics.com Calculations with diodes in parallel • A diode in parallel with another component will act as a voltage regulator, limiting the potential difference across the pair. 8.3 V 9.0V 8.3V I= = 0.0166A 0.015A 500Ω 600Ω 500Ω 16.6 15 mAmA 0.7 I= = 0.007A 100Ω 9.0 V + 0.7 V 100Ω 0.7 V Diodes - 9 7.0 mA 9.6 mA VCE Physics.com