25.3 Frequency and Period
advertisement

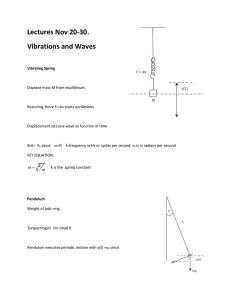
C-25 Warm-Up Question: What do pendulums, springs and waves have in common? They all exhibit periodic or simple harmonic motion! 4&8 A swinging pendulum or bouncing spring creates a wave or sine curve. Pendulum Motion The back and forth motion (vibrations or oscillations) of a swinging pendulum is called simple harmonic motion. The restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium. 2 Pendulum Motion The period (number of seconds for one complete swing) of a pendulum depends only on the length of the pendulum and the acceleration of gravity. Examples of Waves and Vibrations: Swings of a pendulum, trees in the wind Waves in a lake Electrons vibrating in an antenna Sounds from voices, music, nature Light, x-rays and other energy (EM waves) (The material that a wave travels through does not travel along with the wave, like a rope.) Frequency is the number of cycles per second. 9 Parts of a Wave 1 1-crest 2-trough 3-wavelength(lambda-λ) 4-amplitude ---equilibrium Node Antinode 4 3 2 Frequency is measured in Hertz (Hz) Frequency of 1 cycle per second is 1 Hz Frequency of 2 cycles per second is 2 Hz 1 thousand cycles per second 1 kilohertz kHz 1 million cycles per second 1 megahertz MHz 1 billion cycles per second 1 gigahertz GHz 1 trillion cycles per second 1 terahertz THz Common Frequencies How often a vibration or wave occurs Measured in hertz (cycles per second) AM 1,230,000 Hz or 1,230 kHz FM 104,700,000 Hz 104.7 MHz Microwave 2,000,000,000 Hz 2 GHz IR 10,000,000,000,000 Hz 10 THz or Terahertz 13 Frequency vs Period Vibrations per second Seconds for 1 (Hz) vibration (sec) 5 swings per second (5 Hz) 5 inverse key 1 swing every 1/5 of a second Frequency f = 1/T and Period 12 T=1/f The Sears Tower in Chicago is 110 stories tall. When the wind blows, the period of time it takes to sway back and forth once is 10 seconds. What is it’s frequency in hertz? 10, X-1, ENTER = 0.1 Hz 12 period of 10(sec) = a frequency of 0.1(Hz) So, when the Sears Tower sways back and forth in 10 seconds, it will move 1/10 of a cycle in 1 second. Transverse- motion of the medium is at right angles to the direction in which a wave travels. Types: liquids, EM, ropes Longitudinal- particles move along the direction of the wave. Types: sound waves 10 Parts of a Wave: Top: Transverse Compression Rarefraction Bottom: Longitudinal Complete lecture notes 1-13 Lab Prep Calculations Section #1. Formula for frequency (with units) #2. Formula for time period (with units) Summary Section #1. Definition longitudinal and transverse (waves) #2. Definition frequency and period #6. Definition amplitude Scoring 5/5 pts Due Today: Lab 25.1 Pendulum 3/5 1/5 Due Tomorrow: Lab 25.3