Motor IEC vs. NEMA
advertisement
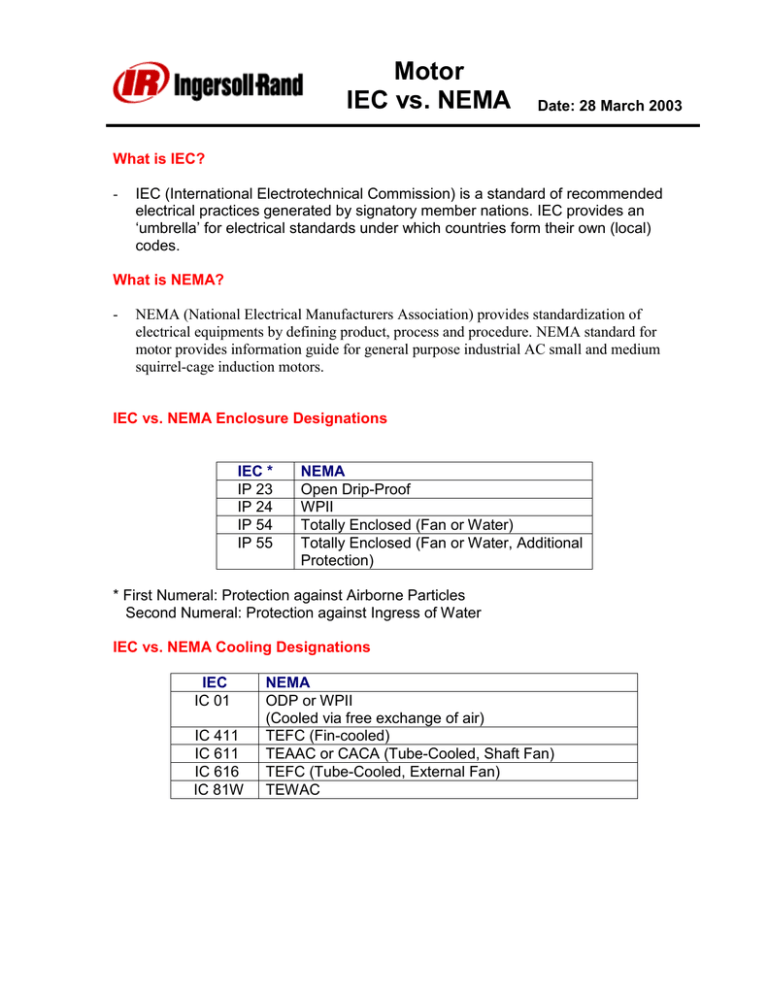
Motor IEC vs. NEMA Date: 28 March 2003 What is IEC? - IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) is a standard of recommended electrical practices generated by signatory member nations. IEC provides an ‘umbrella’ for electrical standards under which countries form their own (local) codes. What is NEMA? - NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) provides standardization of electrical equipments by defining product, process and procedure. NEMA standard for motor provides information guide for general purpose industrial AC small and medium squirrel-cage induction motors. IEC vs. NEMA Enclosure Designations IEC * IP 23 IP 24 IP 54 IP 55 NEMA Open Drip-Proof WPII Totally Enclosed (Fan or Water) Totally Enclosed (Fan or Water, Additional Protection) * First Numeral: Protection against Airborne Particles Second Numeral: Protection against Ingress of Water IEC vs. NEMA Cooling Designations IEC IC 01 IC 411 IC 611 IC 616 IC 81W NEMA ODP or WPII (Cooled via free exchange of air) TEFC (Fin-cooled) TEAAC or CACA (Tube-Cooled, Shaft Fan) TEFC (Tube-Cooled, External Fan) TEWAC Motor IEC vs. NEMA Date: 28 March 2003 IEC Tolerances Tolerance Summation of Losses ≤ 50 KW > 50 KW Total Losses (>50 KW) Power Factor Slip Locked-Rotor Current Locked-Rotor Torque Maximum Torque -15% of (1-ε ) -10% of (1-ε ) +10% of Total Losses -1/6 of (1-Cos θ) ± 20% + 20% -15%, +25% -10% IEC vs. NEMA Performance Considerations Characteristics Power Supply Max. Voltage Variation Max. Frequency Variation Max. Wave Shape Deviation Max. Negative Sequence Voltage Max. Zero Sequence Voltage Standard Service Conditions Cooling Air Cooling Water Altitude Stray-Load Loss IEC NEMA ±5% ± 10 % ±2% 5% 2% 2% ±5% 5% 1% -- ≤ 400 C ≤ 250 C 1000 Meters 0.5 % of Input ≤ 400 C ≤ 300 C 1000 Meters 1.2% of Output < 2500 HP 0.9% of Output ≥ 2500 HP IEC vs. NEMA Hazardous Areas IEC ZONE 0 ZONE 1 ZONE 2 ( * ) No direct comparison NEMA (*) DIV. 1 DIV. 2 Motor IEC vs. NEMA Date: 28 March 2003 Classification of Gases and Vapors According to Temperature Code and Transmission of Ignition: Ignition Class IIA T-1 T-2 Temperature Class T-3 Amylactrate-nbutane N-butyl-alcohol Cyclohexanon 1,2 dichlorethane Acetic anhydride Napthas Petrol Fuels for engines Jet Engine fuels Fuel oils N-hexane IIB Acetone Ethane Ethylchloride Ammonia Benzene Acetic Acid Carbon Monoide Methane Methanol Town Gas Ethanol ethylene Hydrogen sulfide IIC Hydrogen Acetylene T-4 Maximum Surface Temperature, 0C 450 300 200 135 100 85 Hazardous Areas to IEC 79-10 Zone 2, Area unlikely in normal operation, may happen for short time only. Designation E xnAII Zone 0, or Zone 1, Area likely in normal operation. Zone 1, designation E xde IIC IEC Types of Protection EE x (n) II T3: ‘NON-SPARKING’ - ZONE 2 EE x (en) II T3: ‘INCREASED SAFETY’ – ZONE 1 OR 2 EE x (de) IIC T3 or T4: ‘FLAMEPROOF’ – ZONE 1 EE x (pe) II T3: ‘ PRESSURIZED’ – ZONE 1 T-6 Acetaldehyde Diethylether IEC Temperature Classes Temperature Class T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T-5 Carbon Sulfide