http://www.almaden.ibm.com/vis/stm/images/ibm.tif
advertisement

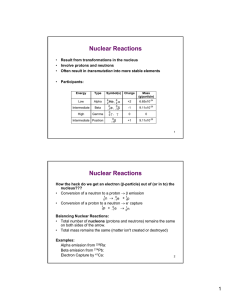
http://www.almaden.ibm.com/vis/stm/images/ibm.tif http://www.almaden.ibm.com/vis/stm/images/cover7.tif 209 83 Bi N/Z = 1.52 N/Z too high: β− decay: ie emit e− from the nucleus and turn a neutron into a proton n emission: ie lose a neutron Mass too high: α decay: lose a 4He nucleus β− decay: lose an e‐ from the nucleus turning a neutron into a proton γ emission (high energy radiation) often accompanies nuclear decay processes N/Z too low: β+ decay: lose an e+ from the nucleus turning a proton into a neutron e- capture: turn a proton into a neutron Stable Nuclides 131I is used for internal treatment of thyroid cancer (only the thyroid uses iodine). It is also a major contaminant from the damaged Japanese nuclear reactors 131 0 0 131 Xe + e + I t1/2 = 8 days 54 ‐1 0γ 53 t1/2 = “half‐life”, the time taken for half the initial sample to decay e.g. γ‐camera image of 131I (from NaI solution) uptake in a normal and diseased thyroid gland, showing localisation of iodine. 18F is incorporated into molecules like glucose and is used in positron emission tomography (PET scanning) for metabolic function and cancer detection: 18 9 F 18 0 + O + +1 e 8 t1/2 = 109.7 min Seeing Hearing Speaking Thinking Reading 99mTc is the most commonly used radioactive isotope (>85%) used for medicine scans together with a gamma camera: 99 42 Mo 99m 43Tc 99m 0 ‐ Tc + e 43 ‐1 99 0 Tc + 4 3 0γ t1/2 = 6 hours Technetium pyrophosphate is used to target bones and identify bone cancer, as in this gamma camera image. nuclear 14C is used in radiocarbon dating: 14 0 B + 7 ‐1 e t1/2 = 5568 years The ambient 14C level increased due to atmospheric nuclear testing, peaking in 1962 ‐ known as the “Bomb Pulse.” This has been accurately tracked over time as the deviation from the pre‐bomb isotope ratio, δ14C, and can be used to accurately determine the (recent) age of carbon‐containing materials. E.g. wine dating & detecting false labels or blends. dating drug crops. Zoppi, et al., Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 223–224 (2004) 770–775 http://ndep.nv.gov/lts/upshot.jpg 14 6 C Ionic Crystals: NaCl en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sodium_chloride Na+ Cl- stress Covalent Bonding electron nucleus repulsion http://courses.cm.utexas.edu/biverson/ch310n oxygen silicon Covalent Networks Diamond Silica Carbon Dioxide (Dry Ice) δ− δ+ δ− http://www.llnl.gov/str/Yoo.html Sugar (Sucrose) http://csi.chemie.tu-darmstadt.de/ak/immel/graphics/gallery/sucroses.html Water High mp/bp High liquid density (ice is less dense) High surface tension... δ+ δ− δ+ δ− δ+ δ+ δ− Metals Copper from the LIFE Science Library book Matter Silver Gold http://www.museum.mtu.edu/Gallery/Jpegs/cop1642.jpg www.topfoto.co.uk/gallery/tutankhamun Metallic Bonding Delocalised electrons Metallic Bonding Small stress Layers begin rolling over each other Layers fall back to original place Stress released Large stress Layers deform Alloys Large stress Large stress Dislocations