Physics 6C Ch26Worksheet solutions
advertisement
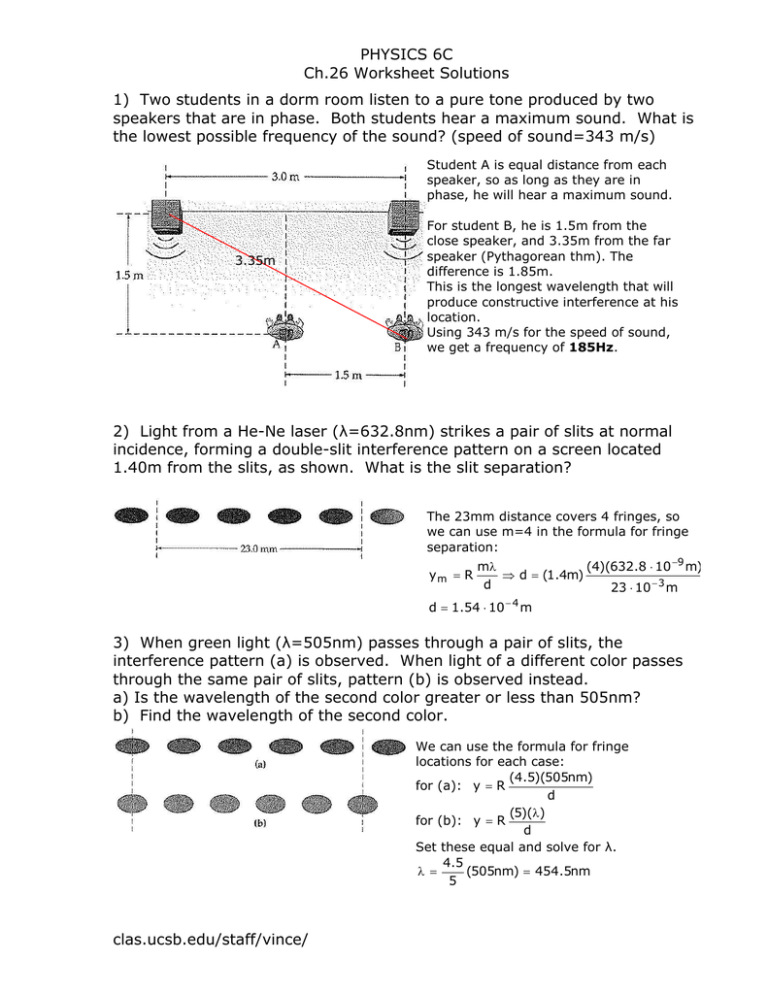
PHYSICS 6C Ch.26 Worksheet Solutions 1) Two students in a dorm room listen to a pure tone produced by two speakers that are in phase. Both students hear a maximum sound. What is the lowest possible frequency of the sound? (speed of sound=343 m/s) Student A is equal distance from each speaker, so as long as they are in phase, he will hear a maximum sound. 3.35m For student B, he is 1.5m from the close speaker, and 3.35m from the far speaker (Pythagorean thm). The difference is 1.85m. This is the longest wavelength that will produce constructive interference at his location. Using 343 m/s for the speed of sound, we get a frequency of 185Hz. 2) Light from a He-Ne laser (λ=632.8nm) strikes a pair of slits at normal incidence, forming a double-slit interference pattern on a screen located 1.40m from the slits, as shown. What is the slit separation? The 23mm distance covers 4 fringes, so we can use m=4 in the formula for fringe separation: ym = R (4)(632.8 ⋅ 10 −9 m) mλ ⇒ d = (1.4m) d 23 ⋅ 10 − 3 m d = 1.54 ⋅ 10 − 4 m 3) When green light (λ=505nm) passes through a pair of slits, the interference pattern (a) is observed. When light of a different color passes through the same pair of slits, pattern (b) is observed instead. a) Is the wavelength of the second color greater or less than 505nm? b) Find the wavelength of the second color. We can use the formula for fringe locations for each case: (4.5)(505nm) for (a): y = R d (5)(λ) for (b): y = R d Set these equal and solve for λ. 4.5 (505nm) = 454.5nm λ = 5 clas.ucsb.edu/staff/vince/ PHYSICS 6C Ch.26 Worksheet Solutions 4) An air wedge is formed by placing a human hair between two glass plates on one end, and allowing them to touch on the other end. When this wedge is illuminated with red light (λ=771nm), it is observed to have 179 dark fringes. How thick is the hair? This ray is shifted This ray is not shifted because it reflects from a lower index (glass to air) because it reflects from a higher index (air to glass) The 2 rays that are interfering have a relative phase shift, so they are already out of phase. Thus for dark fringes we use the formula 2t=mλ. Set m=179 and solve for t: t= (179)(771 ⋅ 10 −9 m) = 6.9 ⋅ 10 −5 m 2 5) The diffraction pattern shown in the figure is produced by passing He-Ne laser light (λ=632.8nm) through a single slit and viewing the pattern on a screen 1.5m behind the slit. a) What is the width of the slit? b) If monochromatic yellow light of wavelength 591nm is used with this slit instead, will the distance in the figure be greater or less than 15.2cm? The distance from the center to the 2nd dark fringe is 7.6cm (half of the distance shown). mλ with m=2. Use the formula y m = R a part (b) Longer wavelength = wider fringes. a = (1.5m) (2)(591 ⋅ 10 −9 m) = 2.4 ⋅ 10 − 5 m 0.076m 6) White light strikes a diffraction grating with 7400 lines/cm at normal incidence. How many complete visible spectra will be formed on either side of the central maximum? (visible light has λ between 400nm and 700nm) 1 cm . Lnger wavelengths 7400 correspond to larger angles, so we use λ = 700nm , complete spectra will appear on the screen only if the angle given by the formula is smaller than 90°. We can use the formula d sin(θ) = mλ with slit spacing d = sin(θ) = mλ m(700 ⋅ 10 −9 m) = = m(0.518) 1 d 7400 cm If m=2 our formula doesn’t work, so we get 1 full spectrum on either side of the center. 7) The asteroid Ida is orbited by its own small “moon” called Dactyl. If the separation between these two asteroids is 2.5km, what is the maximum distance at which the Hubble Space Telescope (aperture diameter 2.4m) can still resolve them with 550nm light? Use Rayleigh’s criterion to find the θmin. λ 550 ⋅ 10 −9 m = 1.22 = 2.8 ⋅ 10 − 7 rad 2.4m D From the triangle in the picture we get y 2500m tan(θ) = ⇒L = = 8.9 ⋅ 10 9 m L tan(2.8 ⋅ 10 − 7 rad) θ min = 1.22 clas.ucsb.edu/staff/vince/