Problem Set 2 - EECS at UC Berkeley
advertisement

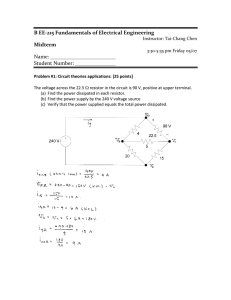
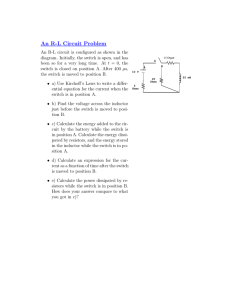
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences B. E. BOSER Problem Set 2 Due Wednesday, February 6, 2008 EE 42 / 100 Spring 2008 1. (a) Find expressions for the power P1 dissipated by source V1 and the power P2 dissipated by source I2 as a function of V1 and I2 . (b) Calculate P1 and P2 for V1 = 10 V and I2 = 1 A and verify that the total power dissipated by the circuit is zero. (c) Repeat (1b) for V1 = −10 V and I2 = 1 A. (d) Repeat (1b) for V1 = −10 V and I2 = −1 A. (e) Repeat (1b) for V1 = 10 V and I2 = −1 A. 2. (a) For the circuit shown below find expressions for the current i1 and the power P1 dissipated in resistor R1 as a function of V1 and the resistance R1 . (b) Calculate the values of i1 and P1 for V1 = 5 V and R1 = 1 kΩ. (c) Repeat (2b) for V1 = −5 V and R1 = 1 kΩ. 3. The circuit shown below is used to measure the voltage/current relationship for a practical battery. The following values are obtained for different values of R L : 12.6 V-0 A; 11.9 V-1 A; and 11.2 V-2 A. Construct an equivalent model for Vbatt consisting of an ideal voltage source V1 and a resistor R1 . Calculate the values of V1 and R1 . 1 4. (a) Find an algebraic expressions for i x and v x as a function of component values. (b) Calculate i x and v x for I1 = 1A, I2 = 0.5A, R1 = 5 kΩ, and R2 = 2 kΩ. 5. (a) Find an algebraic expressions for i x and v x as a function of I1 and resistor values. (b) Calculate i x and v x for I1 = 1A, R1 = 5 kΩ, R2 = 2 kΩ, and R3 = 1 kΩ. 6. Replace the circuit below with a single voltage source V3 that when connected between terminals A–B has the same voltage/current characteristics. Specify the value of V3 in terms of V1 and V2 . 7. Replace the circuit below with a single current source I3 that when connected between terminals A–B has the same voltage/current characteristics. Specify the value of I3 in terms of I1 and I2 . 2 8. Explain why the circuit shown below has no practical realization. 9. (a) Replace the circuit below with a single resistor R x that when connected between terminals A–B has the same voltage/current characteristics. Specify the value of R x in terms of the values of the components in the original circuit. (b) Verify that your result has the correct units (Ω). (c) Calculate the value of R x for R1 = 5 kΩ, R2 = 3 kΩ, R3 = 2 kΩ, and R4 = 1 kΩ. 10. The circuit shown below is used to power a microprocessor chip X1 drawing current i x at voltage v x from a 16 V laptop battery. (a) Calculate the value of R1 such that i x and v x have the values specified in the schematic diagram. (b) Calculate the power PS delivered by the battery. (c) Calculate the power PL dissipated by X1 . (d) Calculate the efficiency PPSL in percent. Needless to say that is is not the circuit used in actual laptops. Later in the course we will develop alternatives with much higher efficiency. 11. Design a circuit consisting of a single 1 A source and resistors only that produces a 1 V potential drop. Specify the value of all resistors used. Note: this problem has more than one correct solution. 3