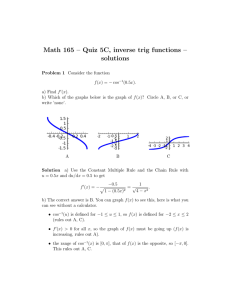
Problem 1
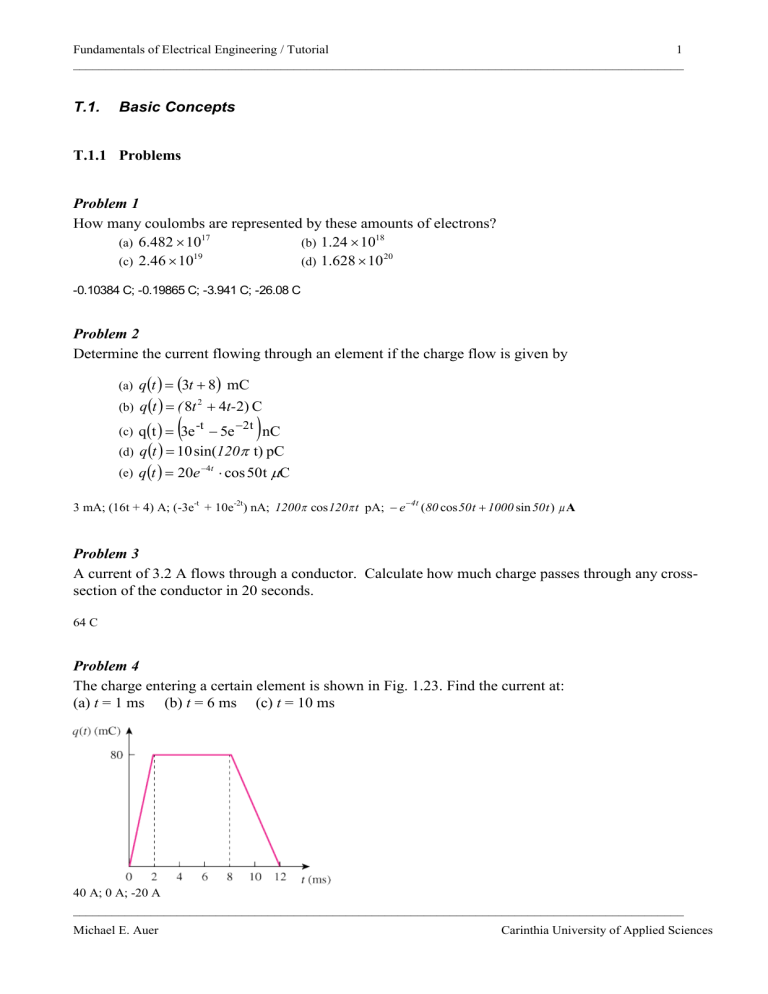
Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering / Tutorial 1
______________________________________________________________________________________________
T.1. Basic Concepts
T.1.1
Problems
Problem 1
How many coulombs are represented by these amounts of electrons?
(a)
(c)
6 .
482
×
10
17
2 .
46
×
10
19
(b) 1 .
24
×
10
18
(d) 1 .
628
×
10
20
-0.10384 C; -0.19865 C; -3.941 C; -26.08 C
Problem 2
Determine the current flowing through an element if the charge flow is given by
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e) q q
( ) (
( ) =
(
3 t
8 t
2
+
8
+
) mC
4 t2) C q q q
( )
( ) t t
( )
=
=
=
(
3 e
10
-t
−
2 sin( 120
π
20 e
−
4 t
−
⋅
5 e cos t t) pC
50
) nC t
µ
C
3 mA; (16t + 4) A; (-3e
-t
+ 10e
-2t
) nA; 1200
π cos 120
π t pA;
− e
−
4 t
( 80 cos 50 t
+
1000 sin 50 t )
µ
Problem 3
A current of 3.2 A flows through a conductor. Calculate how much charge passes through any crosssection of the conductor in 20 seconds.
64 C
Problem 4
The charge entering a certain element is shown in Fig. 1.23. Find the current at:
(a) t = 1 ms (b) t = 6 ms (c) t = 10 ms
40 A; 0 A; -20 A
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Michael E. Auer Carinthia University of Applied Sciences
Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering / Tutorial 2
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Problem 5
The current through an element is shown below. Determine the total charge that passed through the element at:
(a) t = 1 s (b) t = 3 s (c) t = 5 s
10 C; 22.5 C; 30 C
Problem 6
A rechargeable flashlight battery is capable of delivering 85 mA for about 12 h.
How much charge can it release at that rate? If its terminals voltage is 1.2 V, how much energy can the battery deliver?
3,672 C ; 4406.4 J
Problem 7
If the current flowing through an element is given by i
=
3 t A, 0
<
t
<
6s
18 A, 6
<
t
<
10s
12 A, 10
<
t
<
15s
0, t
>
15s
Plot the charge stored in the element over 0 < t < 20s.
1.5 t
2
C; (18t-54) C; (-12t+246) C; 66 C
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Michael E. Auer Carinthia University of Applied Sciences
Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering / Tutorial 3
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Problem 8
The voltage v across a device and the current I through it are v
( )
=
5
⋅ cos 2 t V, i
=
10
⋅
(
1
− e
−
0 .
5 t
)
A
Calculate:
(a) the total charge in the device at t = 1 s
(b) the power consumed by the device at t = 1 s.
2.131 C; -8.188 W
Problem 9
The figure below shows a circuit with five elements. If p
1
= −
205 W, p
2
=
60 W, p
4
=
45 W, p
5
=
30 W, calculate the power p
3 received or delivered by element 3.
70 W
Problem 10
Calculate the power absorbed or supplied by each element in the two circuits.
-36 W; 24 W; 12 W / -72 W; 27 W; 30 W; 15 W
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Michael E. Auer Carinthia University of Applied Sciences
Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering / Tutorial 4
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Problem 11
Find I in the network below.
3 A
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Michael E. Auer Carinthia University of Applied Sciences