Conductors Electric cell Electric circuit Electromagnet Generator
advertisement
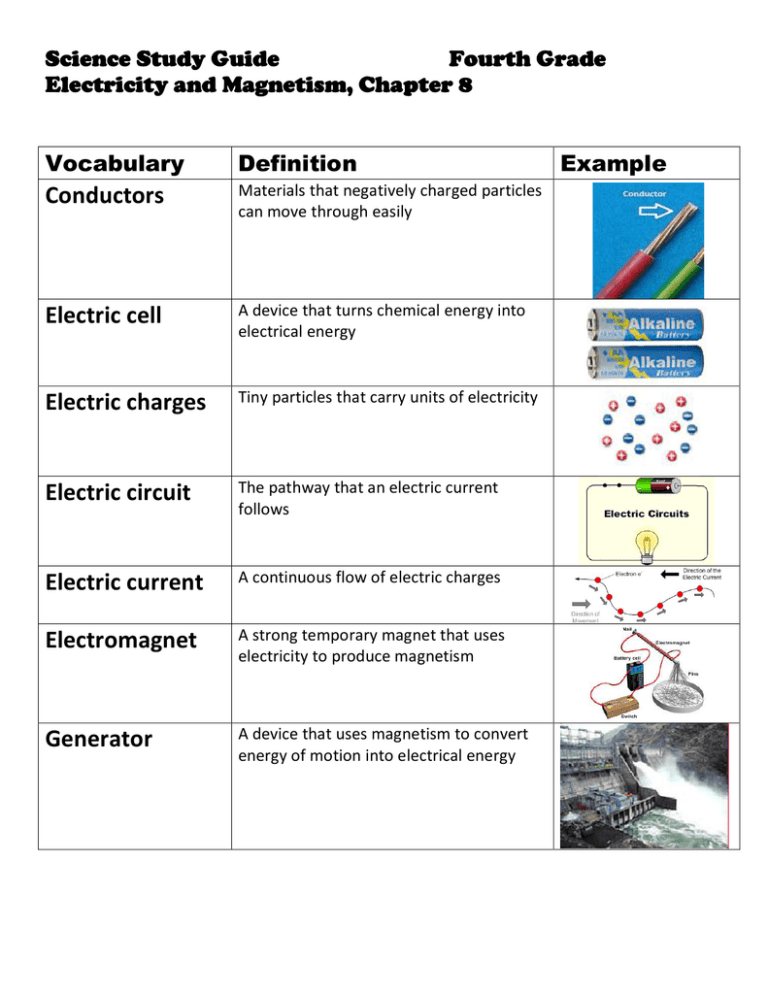
Science Study Guide Fourth Grade Electricity and Magnetism, Chapter 8 Vocabulary Definition Conductors Materials that negatively charged particles can move through easily Electric cell A device that turns chemical energy into electrical energy Electric charges Tiny particles that carry units of electricity Electric circuit The pathway that an electric current follows Electric current A continuous flow of electric charges Electromagnet A strong temporary magnet that uses electricity to produce magnetism Generator A device that uses magnetism to convert energy of motion into electrical energy Example Vocabulary Definition Insulators Materials that electric charges do not flow through easily Magnet An object that attracts certain metals, mainly iron Magnetic poles The two areas on a magnet with the greatest magnetic force Motor A device that changes electrical energy into energy of motion Parallel circuit A circuit in which the parts are connected so that the electric current passes along more than one pathway Series circuit A circuit in which the parts are connected so that the electric current passes through each part along a single pathway Static electricity An electric charge that builds up on a material Example Lesson One What Is Static Electricity? Electric Charges: Tiny particles, atoms, that carry units of electricity. Atoms: Tiny particles, many of which carry electrical charges. Electrically Neutral Matter that has the same number of positive and negative charges. Negatively Charged Matter that has more negative than positive charges. Positively Charged Matter that has more positive than negative charges. How Charges Behave: Unlike Charges Attract Like Charges Repel When brought close together, objects with unlike charges attract, or pull toward, each other. When brought close together, objects with like charges will repel, or push away, from each other. Static Electricity: When a charge builds up on a material. Static electricity can discharge when a negatively charged object comes near another object. That is called a shock. When your hair stands on end and move toward the balloon, that is static electricity. Lesson Two What Is Electric Current? Electric Current: A continuous flow of electric charges. Conductor Insulator Materials that Materials that electric charges do not flow through easily negatively charged particles can move Electric current does not flow easily through plastic, rubber, glass, air, through easily. and wood. Electric current easily moves through copper, aluminum, gold, and silver. Electric charges also flow through water, living plants and animals too. Conductors and insulators are used to conrol and direct the flow of electric charges. Circuits and Switches Electric Circuit: The pathway that electric current follows Closed Circuit: A circuit is closed, or complete, path that does not have any gaps or openings. Electric charges can flow through. Open Circuit: A circuit is open path that has a gap or opening. Electric charges cannot flow through. Types of Circuits Series Circuit A circuit in which the parts are connected so that the electric current passes through each part, one after another, along a single pathway. Parallel Circuit A circuit in which the parts are connected so that the electric current passes along more than one pathway. Party lights are usually connected in a parallel circuit. if one bulb burns outs, the others stay lit. Electric wiring in a house is connected in parallel circuits. Switch: A device that opens and closes the circuit. Lesson Three What is a Magnet? Magnet: An object that attracts certain metals, mainly iron. Magnetism: The property of attracting iron and certain other metals Magnetic Field: The space in which the force of a magnet can act. The iron filings trace the lines of force around the magnet. Magnetic Poles: The greatest area of force on a magnet. Unlike Magnetic Poles Unlike poles attract Like Magnetic Poles Like poles repel When brought close together, the When brought close together, the unlike poles on the ends of these like poles on the end of these bar bar magnets pull together until they magnets push apart. touch. Earth As a Magnet The earth’s center in made up of molten iron. As the earth spins, electric currents in the liquid iron core produce Earth’s magnetic field. Earth is surrounded by a magnetic field with lines of force. The needle of a compass will point to earths’s magnetic north pole. Lesson Four How Do Electromagnets Work? Electromagnet: A strong temporary magnet that uses electricity to produce magnetism. Magnetism and electricity work together in electromagnets. When you play a video game or turn on an electric dryer, you are using an electric magnet. When electric current passes through a wire or other conductor, the current produces a weak magnetic field around a piece of iron, the iron becomes magnetized. The magnetic field also becomes stronger. Electromagnet Facts · Attract materials made of iron · The magnetic force can be controlled · The strength of an electromagnet can be increased by increasing the number or wire coils in increasing the amount of current moving through the coils · Can be turned on and off. When the current is turned off, the electromagnet loses its magnetism Motor: A device that changes electrical energy into energy of motion How a Motor Works In a motor, electricity passes through an electromagnet. The direction of current keeps reversing. As the current changes As the shaft turns, electrical direction, the poles of the energy changes to energy electromagnet keep reversing. motion. The permanent magnet repels and attracts the electromagnet, turning the shaft of the motor. Generator: a device that uses magnetism to convert energy of motion into electrical energy. Generator Facts · Generators produce electricity to light up cities and run machinery · Generators have powerful magnets · Generators have huge coils of wire Ways to increase the amount of electrify a generator produces · Use stronger magnets · Increase the number of coils of wire Where does the energy to move the coils of a generator come from · Nuclear fuels · Burning coal or oil to heat water that will produce steam · Falling water · Blowing wind Cost of Using Electricity · Depends on the amount time electricity is used · Depends on the amount of electricity needed to run a device Ways to Save Electricity · Use a surge protector to plug in TV’s DVD players, and other appliance · Turn your computer off instead of keeping it on standby · Turn off lights, TV’s and stereos when you are not in the room