Content Benchmark P.8.A.1 substance. E/S
advertisement

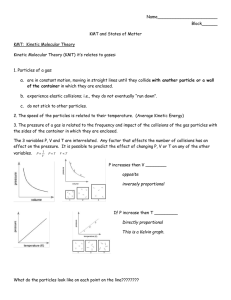
Content Benchmark P.8.A.1 Students know particles are arranged differently in solids, liquids, and gases of the same substance. E/S Sample Test Questions 1st Item Specification: Identify substances as solids, liquids, and gases. Depth Of Knowledge Level 1 1. Which of the following is a liquid at room temperature? A. Milk B. Jell-o C. Helium D. Popcorn 2. Which of the following is a gas at room temperature? A. Jell-o B. Milk C. Helium D. Popcorn Depth Of Knowledge Level 2 3. A student has five unknown substances they must classify into states of matter. Which properties would they use? A. Mass and volume. B. Shape and volume. C. Weight and shape. D. Volume and weight. 4. An object was found inside of a clear, round container. It sat at the bottom of the container and remained there when the lid was removed. When it was transferred to a square container, it reformed to fit the bottom of the new container. What state of matter is the object and why? A. It is a solid because it remained inside the container when the lid was removed and took the shape of the square container. B. It is a gas because it remained inside the container when the lid was removed and took the shape of the square container. C. It is a liquid because it remained inside the container when the lid was removed and took the shape of the square container. D. It was originally a liquid because it remained inside the container when the lid was removed and then became a gas because the square container was colder. 2nd Item Specification: Describe the different states of matter using the terms shape and volume. Depth Of Knowledge Level 1 5. Which of the following describes milk? A. It has a specific volume and shape. B. It has a specific volume, but not a specific shape. C. It has a specific mass and shape. D. It has a specific shape, but not a specific mass. 6. Which of the following best describes paper? A. It has a specific volume and shape. B. It has a specific volume, but not a specific shape. C. It has a specific mass and shape. D. It has a specific shape, but not a specific mass. Depth Of Knowledge Level 2 7. Students were using a ruler to determine the volume of an object. What state of matter was the object and how do you know? A. The object is a solid because it has a fixed shape that can be measured. B. The object is a liquid because it has a fixed shape that can be measured. C. The object is a solid because it does not have a fixed shape. D. The object is a liquid because it does not have a fixed shape. 8. Students were given a container of helium and asked to calculate its density. Which of the following is important when calculating the density of a gas (Density = mass/volume)? A. Knowing the volume of the container and the mass and temperature of the gas. B. Measuring the shape of the gas and knowing its temperature and mass. C. Calculating the mass of the gas and knowing its temperature. D. Knowing the nature of the gas, its shape and its temperature. 3rd Item Specification: Given a diagram, recognize the arrangement of particles in solids, liquids, and gases. Depth Of Knowledge Level 1 9. Use diagrams #1-4 to answer the question below. Which of the following illustrates the particle arrangement of a solid? A. Diagram 1 B. Diagram 2 C. Diagram 3 D. Diagram 4 10. Use diagrams #1-4 to answer the question below. Which of the following illustrates the particle arrangement of helium? A. Diagram 1 B. Diagram 2 C. Diagram 3 D. Diagram 4 Depth Of Knowledge Level 2 11. What happens to the particles of a substance when it condenses? A. Particles speed up and spread out. B. Particles slow down and clump together. C. Particles stick together and stop moving. D. Particles vibrate as they lose energy. 12. Predict the change in molecular kinetic energy and particle arrangement of molten steel after becoming completely solid. A. Decrease in average molecular kinetic energy and decrease in average distance between particles. B. Decrease in average molecular kinetic energy and increase in average distance between particles. C. Increase in average molecular kinetic energy and decrease in average distance between particles. D. Increase in average molecular kinetic energy and increase in average distance between particles. 4th Item Specification: Describe the different states of matter as having more or less molecular kinetic energy. Depth Of Knowledge Level 1 13. Which of the following has the GREATEST average molecular kinetic energy at room temperature? A. Water B. Gold C. Oxygen D. Mercury 14. Which of the following has the LEAST average molecular kinetic energy per at room temperature? A. Water B. Gold C. Oxygen D. Mercury Depth Of Knowledge Level 2 15. This graph shows the changes of state that occur as thermal energy is added to water. Heating and Cooling Curve of Water 140 Temperature (degrees Celsius) 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 -20 -40 -60 Time (s) Which of the following BEST describes what is occurring in the graph over time? A. The average molecular kinetic energy of the water is increasing. B. The average molecular kinetic energy of the water is decreasing. C. The average molecular kinetic energy of the water is unchanged. D. The average temperature of the water is unchanged. 16. This graph shows the changes of state that occur as thermal energy is added to water. Heating and Cooling Curve of Water 140 Temperature (degrees Celsius) 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 -20 -40 -60 Time (s) In this experiment, the water is contained in a closed container and thermal energy is added at a constant rate, but the temperature does not always increase as seen in the flattened parts of the graph. Why? A. Energy is escaping from the system during certain times. B. Energy is increasing the size of the water molecules. C. Energy is absorbed by the water molecules during phase changes. D. Energy is decreasing the mass of the water molecules. Constructed Response P.8.A.1 1. The graph below shows changes in temperature as thermal energy is added a closed container of water. E ___________________________ C __________________________ A __________________________ A. Label lines A, C, and E with the state of matter the water is in for Legs A, C, and E, respectively. B. Compare the average molecular kinetic energy of the water Legs A, C, and E and explain what is happening to the average molecular kinetic energy of the water as thermal energy is added. C. Explain what is happening at Legs B and D in relation to energy and temperature. Content Benchmark P.8.A.1 Students know particles are arranged differently in solids, liquids, and gases of the same substance. E/S Answers to Sample Test Questions 1. A, DOK level 1 2. C, DOK level 1 3. B, DOK level 2 4. C, DOK level 2 5. B, DOK level 1 6. A, DOK level 1 7. A, DOK level 2 8. A, DOK level 2 9. C, DOK level 1 10. B, DOK level 1 11. B, DOK level 2 12. A, DOK level 2 13. C, DOK level 1 14. B, DOK level 1 15. A, DOK level 2 16. C, DOK level 2 Constructed Response 3-point Answer and Score Rubric: E- Gas C -Liquid A -Solid 3 points Response addresses all parts of the question clearly and correctly. The graph is labeled to match the key. The average molecular energy in the water is greatest in Leg E, less in Leg C, and least in Leg D. As thermal energy is added to the water, the average molecular kinetic energy increases overall. In Legs B and D, energy is being added to the water, but temperature is not increasing because the added thermal energy is changing the phase of the water. 2 points Response addresses all parts of the question and includes only minor errors. 1 point Response does not address all parts of the question. 0 points Response is totally incorrect or no response provided.