Fall wk 3 – Mon.11.Oct.04
advertisement

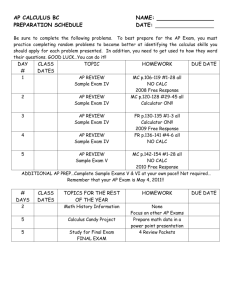
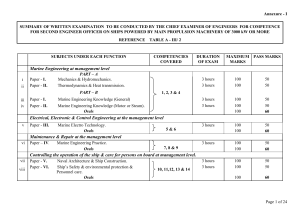
Fall wk 3 – Mon.11.Oct.04 • • • • • Welcome, roll, questions Thermal physics and Energy Ch.3 break continue Calculus Ch.1 Looking ahead Energy Systems, EJZ Discuss Ch.3, Conventional conversion of energy • Key points? • Insights from team discussion? • Questions? - questions of fact: Can we find answer in the text? What page? - Outstanding questions of fact - Outstanding significant questions Energy conversion - outline • • • • • Scientific principles – App.A Review of Thermal Physics New: Power and Efficiency Steam plant: closed cycle Engine cycles: open Laws of Thermodynamics 0. Thermal equilibrium 1. Energy can be neither created nor destroyed. Ex: Heat in = Work done + internal energy 2. Entropy increases: useful energy is lost to heat Heat = energy = work Energy = force * distance Joule = Newton * meter J = kg m2/s2, cal = 4.1868 J = 4 x 10-3 BTU Horsepower = 1 hp = 550 ft * lb/s = 746 Watt POWER = rate of doing work = Energy/time Watts = Joules/sec Efficiency = Energyin / Energyout = Powerin / Powerout Q: What is a kilowatt-hour? A measure of: A. Energy B. Power C. Efficiency Thermal energy heat engine Steam power plant • closed cycle, external combustion • burn fossil fuel heat water steam move turbines electricity Gas and diesel engines • open cycle, internal combustion • compress heat ignite expand motion Steam plant burn fuel heat water steam move turbines electricity Increase efficiency by decreasing losses Generator: motion electricity Electric Power = Voltage * Current: P = VI Ohm’s law: Voltage = Current * Resistance: V = IR Higher voltage transmission: lower ohmic losses Engine cycles compress heat ignite expand motion Gas engines are usually less efficient than diesel engines Work done by a gas (CT 3, 64, green) Work done = pressure * volume = area under curve (clockwise) Heat added = work done + change in internal energy of gas How to improve engine performance? • thermal efficiency is limited, since waste heat is exhausted • compression ratio – diminishing returns, and higher temps preignition • * lower weight better performance: a = F/m • aerodynamics – small effect • power train designs – gradual improvements • * driving habits, mass transit Calculus - outline • • Modified Calc HW Practice with logarithmic functions (Pre)Calculus question for seminar: If global energy use increases by 2.5% per year, how long will it take for global demand to double? a. First, guess. b. What is the percent increase if it doubles? c. Hint: D = D0 at Calc 1 HW 2 Homework due this Thus: Calc 1 HW 2 without Ch.1.5 1.4 # 1, 2, 9, 11, 14, 18, 26, 35 1.6 # 2, 4, 14, 28 Next Thus: Calc 1 HW 3 1.5 # 1, 10, 14, 16, 20, 29, 31, 34, 36 1.6 # 8, 18, 23 Phys 18 HW 1 Thermal (and basic) physics problems due this Thus: Ch.1 #5, 7, 16, 18, 24, 26, 29 Ch.18 #4, 5, (24), 26, 28, 35, (73, 85) Problems in (parentheses) are not available on eGrade. Hand them in separately? I will post solutions after class Thus. Phys 18 HW 2 due next Thus: Ch.18 # (27), 29, 32, 33, (94) Looking ahead • Seminar in Sem II C2109 tonight • Please put your team’s best Q on the board before 5:00 so we can start on time • Tomorrow: – Debate: Coal vs Fission – visitors will discuss sustainability and solar panels on Tuesday and Wednesday • Later: - TA available here Wed 1-3, QRC Fri 10-12 - Next Mon. CE Fair – we’ll set up telescope Heat of transformation ConcepTests 80 Work done by gas ConcepTests Steam plant cycle Diesel engine cycle Hydroplant