Name:_____________________ Date: ________Period:_____
advertisement

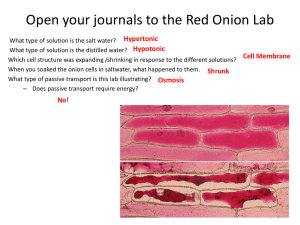
Name:_____________________ Date: ________Period:_____ Agenda Week of 28 Sept – 2 Oct 2009 Class website: www.marric.us/teaching 1a. Students know cells are enclosed within semi permeable membranes that regulate their interaction with their surroundings Monday 9/28/09 Collect Ch 6 Sci Notebook Worksheets Enzyme Activity and Macro concept map - Osmosis experimental design HW: Study for Quiz #1 - Unit 2 Quiz #2 Oct 7, 2009 1. A student could tell the difference between onion skin cells and cheek cells because the onion skin cells have a _______________________ 2. Which of the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that eukaryotes have Tuesday 9/29/09 Unit 2 Quiz 1 (15 min). Cells Are Us reading comprehension HW: Ch 7 Sci Notebook due 10/8 - __________________ and prokaryotes do not. 3. An example of an organism that is a prokaryotes is a _______________________ Wednesday 9/30/09 –Late Start Chapter 7 Powerpoint – Cell organelle introduction - Cell Basics Prokaryotes vs Eukayrotes HW: Ch.7 Science Notebook due 10/8 - 4. The function of a cell membrane is to __________ ______________________________________ 5. Osmosis is defined as the movement of _________ ___________________________________ Thursday 10/1/09 – Selectively Permeable Membranes Lab demonstration - Cell Membrane-bound Proteins - Ch 7 ppt HW: Ch.7 Science Notebook due 10/8 - Friday 10/2/09 – Osmosis Lab design critique The Cell Overview – Begin summary table of cellular organelles HW: Ch.7 Science Notebook due 10/8 - Parents/Guardian – I have reviewed my child’s activities and homework for the week of 9/28-10/2. I understand that is important for me to make sure that my child is studying to be prepared for the quiz and has completed all assignments this week. Unit 1 EXAM Score __________ Parent/Guardian Printed Name 6. Most cell membranes are mainly composed of ___________________________________ 7. Which parts do prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells, and viruses all share? __________________________ 8. Explain the differences between: Active transport Passive transport Facilitated transport 9. The cell structures that make proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus are _________________ Vocabulary Chlorophyll Eukaryote Osmosis Hypotonic Signature Passive transport Ionic Concentration Active transport Facilitated transport Diffusion Isotonic Hypertonic Denaturation Date Bell Ringers: Week of 28 Sep – 2 Oct 2009 Monday –Which substance would be extensively studied during a college organic chemistry course? A. B. C. D. glucose oxygen sodium water Explain Tuesday - A chemical reaction is a process by which atoms or groups of atoms in substances are A. dissolved in other substances. B. ionized by the loss of protons. C. mixed together with atoms in other substances. D. reorganized into different substances . Explain Wednesday - Each enzyme function best at a particular temperature, called its optimum temperature. The graph shows the optimum temperature for three enzymes, X, Y, and Z. At temperatures above an enzyme's optimum temperature, the enzyme's structure begins to break down, a process called "denaturation." At 35 degrees C, which enzyme has undergone denaturation? a) all of the enzymes b) X c) Y d) Z Explain Thursday -Which equation is balanced properly? A. B. C. D. 3O2 + 2Al 2AlO3 3O2 + Al 3AlO3 4O2 + 3Al 4AlO3 4O2 + Al AlO3 Explain Friday – Placing wilted lettuce in cold water will make it crisp again. Which statement best describes what happens to restore the lettuce to its original condition? A Water left the lettuce cells by diffusion. B Water entered the cells of the lettuce by osmosis. C Osmosis caused salts to enter the lettuce cells. D Salts in the leaf caused water to leave the cells. Explain Name:________________________________ Date:________________ Period:_______ Unit 2 Quiz 2 1. 2. An example of an organism that is a prokaryotes is a _______________________ Which of the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that eukaryotes have __________________ and prokaryotes do not. 3. Most cell membranes are mainly composed of ___________________________________ 4. The function of a cell membrane is to __________ ______________________________________ 5. Which parts do prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells, and viruses all share? __________________________ 6. A student could tell the difference between onion skin cells and cheek cells because the onion skin cells have a _______________________ 7. Osmosis is defined as the movement of _________ ___________________________________ 8. Explain the differences between: Active transport Passive transport Facilitated transport 9. The cell structures that make proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus are _________________ Chlorophyll Osmosis DNA Passive transport Denaturation Ionic Concentration Active transport Facilitated transport Diffusion Hypertonic Eukaryote Hypotonic Isotonic Prokaryote _______________________ A. a nucleic acid which is the hereditary material of most organisms _______________________ B. simple cell without specialized membrane-bound structures _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ C. net movement of particles from an area where there are many particles of the substance to an area where there are fewer D. converts fuel particles (sugars) into useable energy E. same concentration of a solute inside as outside of a cell membrane _______________________ F. A monosaccharide that is a product of photosynthesis and a reactant of cellular respiration _______________________ G. A highly folded membrane that is the site of ribosome attachment. Important structure for the synthesis of proteins excreted from the cell. _______________________ H. modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for transport outside the cell _______________________ I. Molecule that absorbs solar energy which is the first step of photosynthesis _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ J. a higher concentration of a solute outside of a cell membrane than insided K. cell with specialized structures, which include the nucleus and other organelles L. diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane _______________________ _______________________ Lipids and carbohydrates are important in animal cells because both — a. store energy _ b. contain nitrogen c. form cell walls d. provide insulation Cell walls are made of cellulose, a complex carbohydrate. Which of the following compounds is the basic unit of the cell wall? a. amino acids c. nucleotides b. sugars d. lipds Because the cell membrane is highly selective with respect to the materials that can cross its boundary, it is described as being selectively… a. permeable c. mosaic b. porous d. fluid 1. A student could tell the difference between onion skin cells and cheek cells because the onion skin cells have a rigid cell wall. 2. Which of the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles and prokaryotes do not. 10. An example of an organism that is a prokaryotes is a bacterium. 11. The function of a cell membrane is to control what enters and leaves the cell. 12. Osmosis is defined as the movement of water molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane 13. Most cell membranes are mainly composed of proteins and lipids. 14. Which parts do prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells, and viruses all share? nucleic acids and proteins 15. The three functions of the nucleus are to 1) stores DNA 2) controls most of the cell’s processes and 3) contains the information needed to make proteins 16. The structures that make proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus are ribosomes. Name:________________________________ Date:________________ Period:_______ Unit 2 Quiz 2 (retake) 1. Osmosis is defined as the movement of ____________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. The three functions of the nucleus are a. _____________________________________________________________ b. _____________________________________________________________ c. _____________________________________________________________ 3. An example of an organism that is a prokaryotes is a _________________________ 4. The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that eukaryotes have ____________________________ __________________ and prokaryotes do not. 5. Which parts do prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells, and viruses all share? __________________________________________________________________ 6. A student could tell the difference between onion skin cells and cheek cells because the onion skin cells have a __________ ____________ 7. The structures that make proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus are _________________ 8. Most cell membranes are mainly composed of ________________________________ 9. The function of a cell membrane is to ___________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ EXTRA CREDIT NOT GRANTED ON RETAKES