Name:___________________________ Date: ____________Period:_____
advertisement

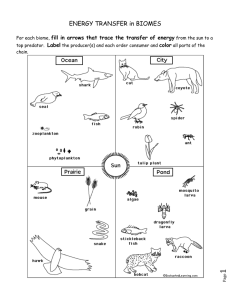
Name:___________________________ Date: ____________Period:_____ Agenda Week of 23 Aug – 27 Aug 2010 Class website: www.marric.us/teaching Monday 8/23/10 Unit 1 Quiz #3 September 4, 2007 - Ecological interactions – niche Energy Pyramids Textbook Notes (15 mins) HW: Study for Quiz #2 Chapter 2 Assessment Questions: 1,2,3,5,6,7,14,15,18,20,21,30,31 due 8/27 - Tuesday 8/24/10 Quiz #2 – 15 minutes Food Chains/Food Webs Textbook Notes (15 mins) HW: Ch2 Assessment Questions (www.marric.us/Flashcards) - 1. Scientists are concerned that global warming is the result of ______________________________________. 2. A living plant, animal or microbe is a(an) ______________. 3. A community of organisms interacting with abiotic environmental factors is called a(an)__________________. 4. A group of similar-looking organisms that breed with each other and produce fertile offspring make up a(an)________________ and a(an)_________________ if they live in the same area. 5. What is the variety of species in a given area called? _____________________ 6.According to the food web, which organism(s) is a carnivore? Wednesday 8/25/10 – Late Start - Community Interactions: competitions, predation and symbiotic relationships 7. What relationship describes the one between a snake and a chipmunk? HW: Ch 3 Study Guide due 8/31 Thursday 8/26/10 Primary and Secondary Succession - Sand dunes/Glacial retreat HW: Ch 3 review biomes - Friday 8/27/10 GUHS Formative Forest Food Web HW: Study for Quiz #3 8. Which combination of five organisms shows a single food chain in this web. - Parents/Guardian – I have reviewed my child’s activities and homework for the week of 8/23/10 – 8/27/10. I understand that is important for me to make sure that my child is studying to be prepared for the quiz and has completed all assignments this week. Open House will be scheduled on _____________. Parent/Guardian Printed Name 9. Sea otters eat sea urchins. Sea urchins eat kelp, a type of brown algae. a.Is this a food chain or a food web? b.What might be the short-term effect on the ecosystem if great numbers of sea otters were removed from this environment? 10. List in order of complexity the following: biosphere, population, organism, biological community, ecosystem, and biome Vocabulary Words Ecosystem Energy pyramid Habitat Population Signature Emigration Food chain Niche Community Estuary Herbivore Immigration Biome Date Bell Ringers: Week of 23 Aug – 27 Aug 2010 Monday As we move up an energy or biomass pyramid, the top levels get smaller like an Egyptian pyramid. Label an energy pyramid identifying organism types in each trophic level with the energy distributions and explain why the top levels get smaller. Explain. Tuesday Your friends sister is learning about symbiotic relationships and she understands that there are three main kinds of symbiotic relationships 1) commensalism, 2) mutualism, and 3) parasitism; but she can’t remember how to distinguish these relationships. Write a short explanation that is easy to remember. Wednesday A new species of mouse is introduced to an environment. As the mice reproduce and the population grows, food resources decrease and predation by hawks increases. Eventually, the number of mice levels off so that the rate of birth equals the rate of death. This nearly constant number of organisms, represented by the dotted line in the diagram below, is called. A. carrying capacity. B. exponential growth. C. linear growth. D. competition. Thursday As soon as rock forms, as it does almost continually on the island of Hawaii, biological changes begin. Describe some examples of plant life at each level of succession starting from new rock. Friday If a population grows larger than the carrying capacity of the environment what will most likely happen and why? Name:________________________________ Date:________________ Period:_______ Unit 1 Quiz 3 1. List in order of complexity the following: biosphere, population, organism, biological community, ecosystem, and biome 2. A living plant, animal or microbe is a(an) ______________________. 3. A community of organisms interacting with abiotic environmental factors is called a(an) ____________________________________. 4. A group of similar-looking organisms that breed with each other and produce fertile offspring make up a(an)________________ and a(an)_________________ if they live in the same area. 5. What is the ultimate source of energy for the majority of life on Earth?_____________________ 6. Scientists are concerned that global warming is the result of ______________________________ _______________________________________. 7. According to the food web, which organism(s) is a carnivore? 8. According to the food web which organisms(s) are producers? 9. What relationship describes the one between a snake and a chipmunk? 10. Identify a combination of five organisms that show a single food chain in this web. 11. Sea otters eat sea urchins. Sea urchins eat kelp, a type of brown algae. Draw out below: a. Is this a food chain or a food web? b.What might be the short-term effect on the ecosystem if great numbers of sea otters were removed from this environment? 12. What is the variety of species in a given area called? _____________________ Extra Credit 6. a. A student is building a terrestrial biome model that represents the greatest biodiversity on Earth. The model will be of a ___________________________________ A. taiga. B. temperate forest. C. tropical rain forest. D. tundra. Vocabulary Matching Ecosystem Emigration Biome Herbivore Population Community Estuary Habitat Energy pyramid Niche Food chain Immigration __________________ A. the physical area where an organism lives, e.g., cave, soil, dead log in a forest, fish aquarium, stream, river, ocean, etc. __________________ B. the movement of individuals away from a population. __________________ C. an organism that only eats plants. __________________ D. a place where freshwater river(s) and stream(s) flow into the ocean, mixing with the seawater. Characterized by diverse organisms. __________________ E. A model showing a single path for energy to flow through an ecosystem. __________________ F. biological communities and all nonliving (abiotic) factors in the environment __________________ G. A group of organisms of the same species that lives in the same area at the same time __________________ H. the movement of an individual into a population. __________________ I. Diagram showing energy conversions which are not very efficient (lost energy as heat) giving the diagram a characteristic shape. __________________ J. is the role that an organism plays in a place (profession of the organism). __________________ K. different populations in an area. These populations interact with each other in an area. __________________ L. climatically and geographically defined areas of ecologically similar climatic conditions such as communities of plants, animals, and soil organisms, and are often identified with particular patterns of ecological succession and climax vegetation Extra Credit 6. c A new species of mouse is introduced to an environment. As the mice reproduce and the population grows, food resources decrease and predation by hawks increases. Eventually, the number of mice levels off so that the rate of birth equals the rate of death. This nearly constant number of organisms, represented by the dotted line in the diagram below, is called. A. carrying capacity. B. exponential growth. C. linear growth. D. competition. Identify on the graph the lag time.