Cell Processes Purpose of the Process? Why Where in the cell What
advertisement

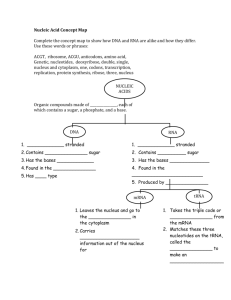
Cell Processes Cell Transport Integrated 1 *288-292 *294 *Triple T-Bar Mitosis Integrated 1 297-301 *Cells Divided *WEBQUEST Purpose of the Process? Why is it important? Outcomes? Where in the cell does this process occur? What organelles are involved? How does this process work? (quick summary or steps) Other Critical Details -Move substances in and out of the cell (waste or nutrients). Diffusion: O2 and CO2 Osmosis: H20 Facilitated diffusion: Glucose Active transport: Potassium -Produce more cells for growth, or replacement of old/damaged cells. Cell membrane “phospholipid bilayer” “membrane proteins” “protein channel” -Starts in nucleus of eukaryotes, Cytoplasm of prokaryotes. Cell membrane -Movement of molecules from high to low down the concentration gradientno energy required. -Active is up gradient, required energy. Facilitated-needs helpers. Nucleus, CytoplasmExpands to include many and duplication of all. I-interphase: Cell growth and DNA duplication (chromosome replication in S phase.) P-prophase: Chromosomes thicken M-metaphase: Chromosomes line up and nucleus dissolves A-Anaphase: Chromosomes are pulled apart T-chromosomes at the poles and nucleus reforms. Cytokinesis-cytoplasm separates and two separate cells have from. IPMAT, once and PMAT again -Diploid, two pair chromosomes replicated. -Homologous pairs line up and crossing over occurs. -Chromosomes line up, move apart and divide (doubled chromosomes, one of each pair). -Divide again with NO duplication. - End with 4 cells half the chromosomes. 1. Sections of DNA unzip 2. Proteins make a copy of DNA 3. New strand of DNA forms -Cell membrane has polar and nonpolar parts. -Active requires energy, passive does not. Differentiation: Cells in the body (somatic) that specialize due to protein expression (example, same human has heart and lung cells that are different) -Produces two diploid cells with same # chromosomes -Asexual Meiosis Integrated 2 *Pg. 355-359 *WEBQUEST -Produce sex cells “gametes”. -Produces 4 haploid cells with half of the original number of chromosomes. -Sexual-fertilization required. -Produce offspring and determines gender. Replication Integrated 2 *413-415 *WEBQUEST -The process of duplicating or producing an exact copy of a DNA so new cells can have a complete set. -New cells need these instructions to function. **Nucleus of eukaryotes dissolves and reform in the cytoplasm. Eventually takes up the whole cell. Starts in nucleus of eukaryotes, Cytoplasm of prokaryotes. **Nucleus of eukaryotes dissolves and reform in the cytoplasm. Eventually takes up the whole cell. Nucleus Nucleus, CytoplasmExpands to include many and duplication of all. Nucleus (chromosomes, enzymes involved) -Duplicate once, spilt twice. -Crossing over=genetic variation. -4 haploids have HALF of the original cell chromosomes Pairing: A-T G-C -Occurs in S phase Transcription Integrated 2 *Pg. 425-426 *WEBQUEST To make a copy of the gene so a protein can be formed. Proteins are machines that make cells work. Nucleus Nucleus (DNA to mRNA, Enzymes) 1. Small section upzips 2.Protein copy DNA to RNA 3.RNA is modified to make mRNA -DNA becomes RNA Pairing: A-U T-A G-C Occurs all the time in the cell cycle Translation Integrated 2 * 428-433 *WEBQUEST To convert mRNA into a chain of amino acids. To make the actual protein. Protein/gene expression. Cytoplasm and Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosomes (mRNA to tRNA to Amino Acids) 1. mRNA travels out of nucleus and combines with a ribosome 2.tRNA combines enters with 1 amino acid and matches with a codon 3. More tRNA comes until mRNA is completely read and chain is formed. 1st part of protein synthesis RNA makes chains of amino acids (proteins) . Pairing: A-U G-C Occurs all the time in the cell 2nd part of protein synthesis